Intramedullary Tumor (Im Tumor) Surgery
India
-
Our Price USD 5040
-
Hospital Price USD 5600
-
You Save : USD 560
Booking Amount: USD 504. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
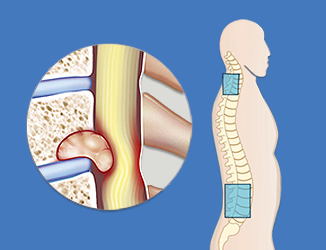
Intramedullary Tumor (Im Tumor) Surgery
Intramedullary tumours are growths that form within the spinal cord's supporting (glial) cells. A spinal tumour is a development that grows within your spinal canal or among your spine's bones.
Long-term tumour control or cure with functional preservation is the surgical goal with spinal intramedullary tumours, especially benign encapsulated tumours. Using all available techniques, a better balance between tumour control and functional preservation must be attained.
Disease Overview
Intramedullary tumors
Intramedullary tumours are growths that form within the spinal cord's supporting (glial) cells. A spinal tumour is a development that grows within your spinal canal or among your spine's bones.
Ependymomas, astrocytomas, and hemangioblastomas are the most frequent intramedullary spinal tumours. Spinal ependymomas and astrocytomas together account for 80-90 percent of intramedullary spinal tumours, with ependymomas occurring twice as often as astrocytomas.
Adults' most frequent intramedullary spinal cord tumour is ependymoma. All ependymal tumours are classified as confined gliomas rather than diffuse/infiltrative gliomas based on their pathologic appearance.
Disease Symptoms:
Stmptoms can be as following:
- Pain at the tumour site owing to tumour development may be one of the signs and symptoms.
- Back discomfort that spreads to other portions of the body.
- Pain, heat, and cold seem to affect you less.
- Deficiency in bowel and bladder function.
- Walking difficulties, which might lead to falls.
- Back ache that becomes progressively worse at night.
Disease Causes:
They might be caused by anything in the environment, such as chemical exposure. Spinal cord tumours, on the other hand, have been related to genetic diseases including neurofibromatosis 2 and von Hippel-Lindau disease in some cases.
Disease Diagnosis:
Because spinal tumours are uncommon and their symptoms are similar to those of more prevalent illnesses, they are commonly missed. As a result, it's critical that your doctor has a thorough understanding of your medical history and does both general physical and neurological evaluations.
These tests can help confirm the diagnosis and define the site of a spinal tumour if your doctor suspects one:
Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine (MRI). MRI produces precise pictures of your spine, spinal cord, and nerves by using a strong magnetic field and radio waves. When it comes to diagnosing malignancies of the spinal cord and adjacent tissues, an MRI is typically the best option. During the exam, a contrast agent may be injected into a vein in your hand or forearm to assist highlight certain tissues and structures.
Inside the MRI scanner, some people may feel claustrophobic or find the loud pounding sound unsettling. However, earplugs are frequently provided to cope with the noise, and some scanners include televisions or headphones. If you're feeling very worried, inquire about a moderate sedative to help you relax. In some cases, a general anaesthesia may be required.
Tomography using a computer (CT). This examination produces detailed pictures of your spine using a small beam of radiation. It's sometimes used in conjunction with an injected contrast dye to help detect pathological alterations in the spinal canal or spinal cord. A CT scan is only utilised in the rarest of cases to aid in the diagnosis of spinal malignancies.
Biopsy. Only a little tissue sample (biopsy) may be examined under a microscope to detect the particular type of spinal tumour. The results of the biopsy will be used to assist select treatment choices.
Disease Treatment:
The objective of spinal tumour treatment is to fully remove the tumour, although this can be difficult due to the danger of lasting damage to the spinal cord and surrounding nerves. Doctors must also consider your age and overall health. In choosing a treatment strategy, the sort of tumour and whether it comes from the structures of the spine or spinal canal or has spread to your spine from elsewhere in your body must also be addressed.
The following are some of the treatment options for most spinal tumours:
Monitoring. Some spinal tumours are detected before they create symptoms, usually while you're being checked for another problem. If tiny tumours aren't expanding or pushing on nearby tissues, diligent observation may be all that's required.
During observation, your doctor will most likely propose frequent CT or MRI scans to monitor the tumour at an acceptable interval.
Surgery.
This is frequently the therapy of choice for malignancies that can be removed without causing harm to the spinal cord or nerves.
Neurosurgeons may now reach tumours that were previously thought to be unreachable because to newer procedures and devices. Microsurgery's high-powered microscopes make it simpler to identify malignancy from healthy tissue.
During surgery, doctors may also monitor the function of the spinal cord and other critical nerves, reducing the risk of injury. During surgery, very high-frequency sound waves may be utilised to break up tumours and remove the fragments in some cases.
However, even with the most advanced surgical technology, not all tumours can be completely eliminated. Surgery may be followed by radiation treatment, chemotherapy, or both if the tumour cannot be entirely removed.
Depending on the method, spinal surgery recovery might take weeks or even months. You may have a temporary loss of feeling as well as other consequences such as bleeding or nerve tissue injury.
Radiation therapy is a type of treatment that involves the use of This might be used to remove tumour remains that remain after surgery, to treat inoperable tumours, or to treat tumours that are too dangerous to operate on.
Some of the negative effects of radiation, such as nausea and vomiting, may be alleviated with medication.
Your radiation therapy plan may need to be tweaked from time to time to assist reduce the amount of healthy tissue that is destroyed and improve the treatment's effectiveness. Modifications can range from altering the radiation dosage to adopting advanced techniques like 3-D conformal radiation treatment.
Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy is a common cancer treatment that employs drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from developing. Your doctor can assess if chemotherapy, alone or in conjunction with radiation treatment, might be useful to you.
Fatigue, nausea, vomiting, an increased risk of infection, and hair loss are all possible side effects.
Other medications are available. Doctors sometimes give corticosteroids to minimise swelling after surgery or during radiation treatments because surgery and radiation therapy, as well as tumours themselves, can trigger inflammation inside the spinal cord.
Although corticosteroids decrease inflammation, they are typically only administered for a limited amount of time to avoid major side effects such muscular weakness, osteoporosis, high blood pressure, diabetes, and an increased susceptibility to infection.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
7 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr Rahul Gupta
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Endovascular Neurosurgeon, microscopic surgery, Meningiomas, Craniopharyngioma, Brain Tumor Surgery, Cranio Vertebral anomalies, Intraventricular Tumour Surgery, Skull Base Anterior Surgery, Pituitary Adenoma including endonasal, Endoscopic Acoustic Schwanomas, CSF rhinorrhia, Cerebrovascular Neurosurgery
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
27 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Prof. (Col.) Dr. Bipin Walia
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery, Kyphoplasty, Brain suite, Laminectomy, Traumatic brain injury (tbi) treatment, Cervical Disc Replacement
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
26 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Tarun Sharma
Neuro surgeon,Spine Surgeon- Peripheral nerve, Pediatric neurosurgery, Epileptic Surgery, Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy, Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) of the brain and spinal cord, Foot Drop, Foot Drop Spinal Surgery, Petrosal Sinus Sampling
Metro Hospital (Heart Institute with Multispeciality) Faridabad, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Praveen Gupta
Neurologist- Stroke Intervention, Stroke Rehabilitation, Celebral Palsy, Advanced Second line management for multiple scleoris, Epileptic Surgery, DBS Surgery
Fortis Memorial Research Institute Gurgaon, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Ravi Bhatia
Neuro surgeon- Neuro Oncology, Craniovertebral Junction (CVJ) Anomalies, Brain and Spine Tumors, Celebrovasculkar Surgey
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
60 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Shamsher Dwivedee
Neurologist- Alzheimer Specialist, Epilepsy Disorder, Stroke Specialist, Headache Specialist, Sleep Disorder, Parkinson's Disease, Dementias, Neuromuscular Disorders
Vimhans Nayati Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
33 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Asha Kishore
Neurologist- Ankle surgery, Knee Replacement, Hip resurfacing with computer navigation, Anthroscopic Meniscus Surgery, ACL Reconstruction Procedure
Aster Medcity, Kochi Cochin, India
31 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Aditya Gupta
Neuro surgeon- Cerebrovascular Surgery, Movement disorder, Deep brain Stimulation, Brain Tumor Surgery, Nerve and brachial plexus surgery, Rradiosurgery, Epilepsy Surgery, Stereotactic Radio Surgery (SRS)
Artemis Hospitals Gurgaon, India
22 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Sumit Sinha
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Minimal Invasive Neurosurgery, Peripheral Nerve Surgery, Endoscopic Neurosurgery
Paras Hospitals Gurgaon, India
17 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. DESHPANDE RUSHIKESH RAVINDRANATH
Neurologist-
Deenanath Mangeshker Hospital and research centre, Pune Pune, India
Years of Experience