Spine Cervical or Thoracic or Lumbar Laminectomy
India
-
Our Price USD 4680
-
Hospital Price USD 5200
-
You Save : USD 520
Booking Amount: USD 468. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Spine Cervical or Thoracic or Lumbar Laminectomy
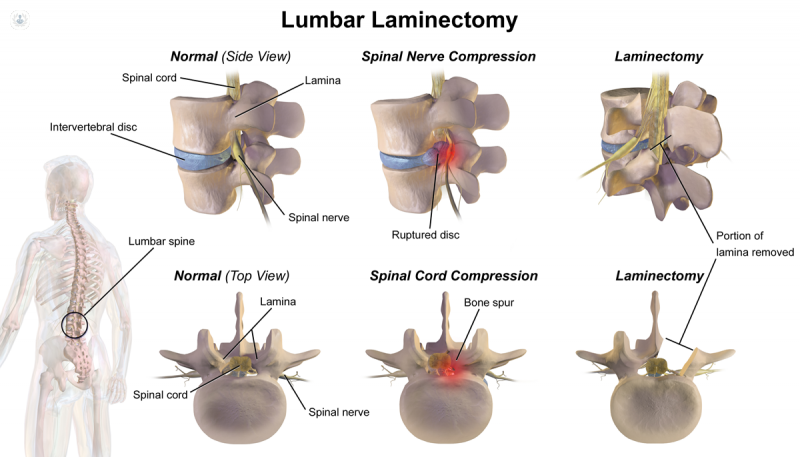
Cervical laminectomy is an orthopaedic operation for treating neck spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal). Cervical laminectomy is a procedure that includes making a tiny incision at the back of the neck to provide access to the vertebrae. The lamina (bony arch on backside of vertebrae) and bone spurs (tiny outgrowths of bone produced by inflammation) are carefully removed, allowing the spinal cord and nerve roots to breathe easier.
The orthopaedic surgery thoracic and lumbar laminectomy, commonly known as decompression, is performed to cure thoracic (midback) and lumbar (lower back) spinal stenosis. Depending on what the spine surgeon thinks is ideal, a laminectomy can be done as open surgery or with minimally invasive procedures.
Disease Overview
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the gaps in your spine, putting pressure on the nerves that run through it. The lower back and neck are the most common sites for spinal stenosis.
Some persons with spinal stenosis don't show any signs or symptoms. Pain, tingling, numbness, and muscular weakness may be experienced by others. Symptoms might become more severe over time.
Wear-and-tear alterations in the spine produced by osteoarthritis are the most prevalent cause of spinal stenosis. Doctors may propose surgery to make more room for the spinal cord or nerves in severe cases of spinal stenosis.
The many kinds of spinal stenosis are categorized based on where the problem develops in the spine. It is possible to have many types. There are two forms of spinal stenosis:
Cervical stenosis is a condition in which the neck is narrowed. The narrowing happens in the region of the spine in your neck with this ailment.
Lumbar stenosis is a condition that affects the lower back. The narrowing occurs in the lower back region of the spine in this disorder. The most prevalent type of spinal stenosis is this.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Many persons with spinal stenosis have signs of it on an MRI or CT scan but no symptoms. When they do happen, they usually start slowly and get worse over time. The symptoms vary depending on where the stenosis is located and which nerves are impacted.
- In the cranium (cervical spine)
- Hand, arm, foot, or leg numbness or tingling
- Hand, arm, foot, or leg weakness
- Problems with balance and walking
- Neck ache
- Bowel or bladder dysfunction can be severe in some circumstances (urinary urgency and incontinence)
- Lower back pain (lumbar spine)
- tingling or numbness in the foot or leg
- A foot or leg that is weak
- When you stand for long periods of time or walk, you may have pain or cramping in one or both legs, which normally subsides when you bend forward or sit.
- Back ache
Disease Causes:
From your neck to your lower back, the backbone (spine) runs. The spinal canal is formed by the bones of your spine and protects your spinal cord (nerves).
Some individuals are born with a narrow spinal canal. However, the majority of spinal stenosis develops when something narrows the free area within the spine. Spinal stenosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
Tumors. Inside the spinal cord, within the membranes that surround the spinal cord, or in the space between the spinal cord and vertebrae, abnormal growths can occur. These are infrequent and can be seen on MRI or CT scans of the spine.
Injuries to the spine. Dislocations or fractures of one or more vertebrae can occur as a result of car accidents or other trauma. The contents of the spinal canal may be damaged by displaced bone following a spinal fracture. Swelling of the surrounding tissue following back surgery can also exert strain on the spinal cord and nerves.
Factors that are at risk
The majority of persons with spinal stenosis are over 50 years old. While degenerative changes can induce spinal stenosis in younger persons, there are additional explanations to consider. Trauma, congenital spinal deformities like scoliosis, and a hereditary condition that affects bone and muscle growth throughout the body are all examples. These reasons can be distinguished via spinal imaging.
Disease Diagnosis:
Your doctor may question you about your signs and symptoms, examine your medical history, and do a physical examination to diagnose spinal stenosis. To assist establish the origin of your signs and symptoms, he or she may request numerous imaging tests.
Tests of imaging
These tests may involve the following:
X-rays. Bony changes, such as bone spurs, can be shown on an X-ray of your back, which may be limiting the space within the spinal canal. Each X-ray exposes you to a little amount of radiation.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of imaging that (MRI). An MRI creates cross-sectional pictures of your spine using a strong magnet and radio waves. Damage to your discs and ligaments, as well as the existence of malignancies, can all be detected with this test. Most importantly, it can reveal where pressure is being placed on the nerves in the spinal cord.
CT scan, often known as a CT myelogram. If an MRI isn't an option, your doctor may suggest a CT scan, which combines X-ray pictures collected from a variety of angles to provide comprehensive cross-sectional views of your body. A CT scan is performed after a contrast dye is injected in a CT myelogram. The dye can identify herniated discs, bone spurs, and malignancies by highlighting the spinal cord and nerves.
Disease Treatment:
Treatment for spinal stenosis is determined by the severity of your symptoms and the location of the stenosis.
Consult your doctor to determine the best course of action for you. If your symptoms are minor or you don't have any, your doctor may want to keep track of your progress with regular follow-up sessions. He or she may provide you with some self-care suggestions that you may use at home. He or she may prescribe drugs or physical therapy if these don't work. If other therapies have failed, surgery may be a possibility.
Physical therapy is a type of treatment that is used
People with spinal stenosis frequently become less active in order to alleviate discomfort. However, this might result in muscular weakening, which can contribute to additional discomfort. Exercises that a physical therapist may teach you include:
- Strengthen and extend your endurance.
- Maintain your spine's flexibility and stability.
- Boost your equilibrium.
Injections of steroid
In the areas where your nerve roots are squeezed, they may become irritable and inflamed. While injecting a steroid medicine (corticosteroid) into the area around the impingement will not cure the stenosis, it will assist to lessen inflammation and discomfort.
Injections of steroid hormones do not work for everyone. Because frequent steroid injections might damage adjacent bones and connective tissue, these injections should only be done a few times a year.
Procedure for decompression
To enhance spinal canal space and alleviate nerve root impingement, needle-like devices are used to remove a part of a thicker ligament in the rear of the spinal column. This form of decompression is only for people who have lumbar spinal stenosis and a thicker ligament.
Percutaneous image-guided lumbar decompression is the name of the procedure (PILD).
Because PILD does not need general anaesthesia, it may be a viable alternative for certain patients who are at high surgical risk due to other medical issues.
Surgery
If alternative therapies have failed or your symptoms have rendered you handicapped, surgery may be considered. By creating extra room within the spinal canal, the operation aims to relieve strain on your spinal cord or nerve roots. The most definite technique to try to alleviate symptoms of spinal stenosis is surgery to decompress the region of stenosis.
The following are some examples of surgical treatments used to treat spinal stenosis:
Laminectomy. The afflicted vertebra's rear half (lamina) is removed during this treatment. Because it relieves the strain on the nerves by creating more space around them, a laminectomy is also known as decompression surgery.
To retain the spine's strength, that vertebra may need to be joined to surrounding vertebrae using metal hardware and a bone transplant (spinal fusion).
Laminotomy. Only a section of the lamina is removed in this treatment, with a hole carved only large enough to alleviate pressure in a specific area.
Laminoplasty. Only the vertebrae in the neck are treated with this treatment (cervical spine). It creates a hinge on the lamina, which opens up the area within the spinal canal. Metal hardware spans the gap in the spine's opening part.
The term "minimally invasive surgery" refers to surgery that is performed with the least amount This kind of surgery removes bone or lamina while minimising injury to neighbouring healthy tissue. This reduces the requirement for fusions.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
6 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. P. N. Renjen
Neurologist- Stroke (Thrombolytic Therapy), Botox Therapy for Post Stroke Spasticity, Surgical Epilepsy, DBS (Deep Brain Stimulation) and Headache, Celebrovasculkar Surgey
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
36 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Rahul Gupta
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Endovascular Neurosurgeon, microscopic surgery, Meningiomas, Craniopharyngioma, Brain Tumor Surgery, Cranio Vertebral anomalies, Intraventricular Tumour Surgery, Skull Base Anterior Surgery, Pituitary Adenoma including endonasal, Endoscopic Acoustic Schwanomas, CSF rhinorrhia, Cerebrovascular Neurosurgery
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
27 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Prof. (Col.) Dr. Bipin Walia
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery, Kyphoplasty, Brain suite, Laminectomy, Traumatic brain injury (tbi) treatment, Cervical Disc Replacement
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
26 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Tarun Sharma
Neuro surgeon,Spine Surgeon- Peripheral nerve, Pediatric neurosurgery, Epileptic Surgery, Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy, Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) of the brain and spinal cord, Foot Drop, Foot Drop Spinal Surgery, Petrosal Sinus Sampling
Metro Hospital (Heart Institute with Multispeciality) Faridabad, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Praveen Gupta
Neurologist- Stroke Intervention, Stroke Rehabilitation, Celebral Palsy, Advanced Second line management for multiple scleoris, Epileptic Surgery, DBS Surgery
Fortis Memorial Research Institute Gurgaon, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Ravi Bhatia
Neuro surgeon- Neuro Oncology, Craniovertebral Junction (CVJ) Anomalies, Brain and Spine Tumors, Celebrovasculkar Surgey
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
60 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Shamsher Dwivedee
Neurologist- Alzheimer Specialist, Epilepsy Disorder, Stroke Specialist, Headache Specialist, Sleep Disorder, Parkinson's Disease, Dementias, Neuromuscular Disorders
Vimhans Nayati Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
33 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Asha Kishore
Neurologist- Ankle surgery, Knee Replacement, Hip resurfacing with computer navigation, Anthroscopic Meniscus Surgery, ACL Reconstruction Procedure
Aster Medcity, Kochi Cochin, India
31 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Aditya Gupta
Neuro surgeon- Cerebrovascular Surgery, Movement disorder, Deep brain Stimulation, Brain Tumor Surgery, Nerve and brachial plexus surgery, Rradiosurgery, Epilepsy Surgery, Stereotactic Radio Surgery (SRS)
Artemis Hospitals Gurgaon, India
22 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Sumit Sinha
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Minimal Invasive Neurosurgery, Peripheral Nerve Surgery, Endoscopic Neurosurgery
Paras Hospitals Gurgaon, India
17 Years of Experience