Spine Transoral Decompression
India
-
Our Price USD 7470
-
Hospital Price USD 8300
-
You Save : USD 830
Booking Amount: USD 747. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
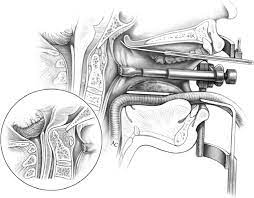
Spine Transoral Decompression
The most frequent surgical treatment for Chiari malformation is posterior fossa decompression, which is done through a back-of-the-neck incision. A Chiari malformation may, however, be accompanied by other skull base defects, causing compression of the brain stem that originates from the front side of the skull. It may be essential to access the affected area through the mouth or nasal passages in these complicated circumstances. Transoral (through the mouth) or transnasal (through the nose) decompression is the term for this type of surgery.
Disease Overview:
Cervical myelopathy
Cervical myelopathy is a disorder that causes spasticity (continuous muscular contractions), hyperreflexia, pathologic reflexes, digit/hand clumsiness, and/or gait disruption due to compression of the spinal cord at the cervical level of the spinal column.
Cervical myelopathy is a kind of myelopathy in which the spinal cord is compressed in the cervical spine (neck). Seven vertebrae (C1 to C7), six intervertebral discs, and eight nerve roots make up your cervical spine. The spinal cord travels within the vertebral column, which is made up of vertebrae in the front, cushioned by intervertebral discs, and facet joints and lamina in the rear. Eight nerve roots grow out from the cervical spine, controlling the function of your shoulders, arms, and hands.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Pain, numbness, and weakness in the neck or arms, as well as coordination issues, are common symptoms.
Also, People may have the following experiences:
- Areas of pain include the back and neck.
- Muscular: irregular walking, lack of coordination, muscle weakness, coordination issues, rhythmic muscle spasm, tight muscles, muscle loss, or hyperactive reflexes are all examples of muscular disorders.
- Sensory: decreased touch sensitivity or unpleasant tingling and burning
- Balance issues are also frequent.
Disease Causes:
Many people suffer from neck discomfort, but not all of it is caused by cervical myelopathy. Some people with this illness don't even feel neck discomfort. It's possible that your neck ache is caused by muscle rather than nerves. If you're experiencing persistent neck pain, see your doctor.
Spondylotic Myelopathy of the Cervical Spine
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy is a prevalent kind of cervical myelopathy. The term "spondylotic" refers to one of the probable causes of myelopathy, which is the slow deterioration of the spine as you become older. As a result, adults over the age of 50 are more likely to develop cervical spondylotic myelopathy.
Cervical spinal stenosis, or narrowing of the spinal canal in the neck, is a common symptom of progressive spine deterioration. Some persons are born with a small spinal canal (congenital spinal stenosis), and if the canal narrows further, they may develop myelopathy sooner than others. Other kinds of spinal degeneration that can stress on the spinal cord and induce myelopathy include bulging or ruptured discs and bone spurs in the neck.
Cervical myelopathy can be caused by ossification (hardening) of the ligaments surrounding the spinal cord, such as the posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum, in addition to progressive wear and tear of the spine.
The ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL) is the most prevalent kind of ossification. This implies that the soft tissue that links the bones of the spine loses flexibility and gradually transforms to bone (ossification). As the ligament thickens, it begins to take up more space and exert pressure on the spinal cord, resulting in myelopathy. The most prevalent site of OPLL ossification is in the neck region of the spine.
Cervical myelopathy can also be caused by:
- Rheumatoid arthritis of the neck is a kind of rheumatoid arthritis that affects the
- Trauma to the cervical spine, such as whiplash.
- Infections of the spine
- Tumors and malignancies of the spine
Disease Diagnosis:
The earlier cervical myelopathy is discovered, the better the chances of a successful therapy. Cervical myelopathy symptoms, on the other hand, are not specific to this disorder and are frequently misdiagnosed as "typical" indicators of ageing.
Your doctor may use the following methods to diagnose cervical myelopathy:
- Measure your muscular strength and reflexes through a physical examination.
- Additional diagnostics, such as an MRI scan, an X-ray, or a CT myelogram of your neck, should be performed.
- Conduct electrical tests to see how well your arms and hands' nerves communicate with your brain via the spinal cord.
Disease Treatment:
Physical therapy and a cervical collar brace are two nonsurgical treatments for treating cervical myelopathy symptoms. However, surgery is frequently required to relieve spinal cord compression and prevent the disease from deteriorating.
Cervical myelopathy can be treated with a variety of surgical techniques that your doctor may prescribe. For certain individuals, spinal canal widening (laminoplasty) might be a useful motion-saving alternative. Others may benefit from spine decompression surgery combined with spinal fusion, which is intended to stabilise the spine after herniated discs, bone spurs, or ossified ligaments have been removed completely or partially.
These procedures can be done from the rear of the neck (posteriorly) or the front of the neck (anteriorly) (anteriorly).
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
8 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. P. N. Renjen
Neurologist- Stroke (Thrombolytic Therapy), Botox Therapy for Post Stroke Spasticity, Surgical Epilepsy, DBS (Deep Brain Stimulation) and Headache, Celebrovasculkar Surgey
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
36 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Rahul Gupta
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Endovascular Neurosurgeon, microscopic surgery, Meningiomas, Craniopharyngioma, Brain Tumor Surgery, Cranio Vertebral anomalies, Intraventricular Tumour Surgery, Skull Base Anterior Surgery, Pituitary Adenoma including endonasal, Endoscopic Acoustic Schwanomas, CSF rhinorrhia, Cerebrovascular Neurosurgery
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
27 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Prof. (Col.) Dr. Bipin Walia
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery, Kyphoplasty, Brain suite, Laminectomy, Traumatic brain injury (tbi) treatment, Cervical Disc Replacement
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
26 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Tarun Sharma
Neuro surgeon,Spine Surgeon- Peripheral nerve, Pediatric neurosurgery, Epileptic Surgery, Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy, Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) of the brain and spinal cord, Foot Drop, Foot Drop Spinal Surgery, Petrosal Sinus Sampling
Metro Hospital (Heart Institute with Multispeciality) Faridabad, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Praveen Gupta
Neurologist- Stroke Intervention, Stroke Rehabilitation, Celebral Palsy, Advanced Second line management for multiple scleoris, Epileptic Surgery, DBS Surgery
Fortis Memorial Research Institute Gurgaon, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Ravi Bhatia
Neuro surgeon- Neuro Oncology, Craniovertebral Junction (CVJ) Anomalies, Brain and Spine Tumors, Celebrovasculkar Surgey
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
60 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Shamsher Dwivedee
Neurologist- Alzheimer Specialist, Epilepsy Disorder, Stroke Specialist, Headache Specialist, Sleep Disorder, Parkinson's Disease, Dementias, Neuromuscular Disorders
Vimhans Nayati Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
33 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Asha Kishore
Neurologist- Ankle surgery, Knee Replacement, Hip resurfacing with computer navigation, Anthroscopic Meniscus Surgery, ACL Reconstruction Procedure
Aster Medcity, Kochi Cochin, India
31 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Aditya Gupta
Neuro surgeon- Cerebrovascular Surgery, Movement disorder, Deep brain Stimulation, Brain Tumor Surgery, Nerve and brachial plexus surgery, Rradiosurgery, Epilepsy Surgery, Stereotactic Radio Surgery (SRS)
Artemis Hospitals Gurgaon, India
22 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Sumit Sinha
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Minimal Invasive Neurosurgery, Peripheral Nerve Surgery, Endoscopic Neurosurgery
Paras Hospitals Gurgaon, India
17 Years of Experience