ACL Reconstruction
Iran
-
Our Price USD 3080
-
Hospital Price USD 3242
-
You Save : USD 162
Booking Amount: USD 308. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Procedure Description:
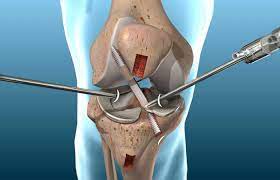
ACL Reconstruction
During ACL reconstruction surgery, a graft of replacement tissue from one of two sources is used to create a new ACL:
- an allograft (tissue from a human organ donor)
- a section of the patient's own hamstring, quadriceps, patellar tendon, or iliotibial band
Each patient's specific needs will determine the type of graft chosen; however, because young individuals have a considerably higher risk of reinjury and graft failure, allograft tissue is not recommended.
Minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures, which combine tiny incisions, tiny equipment, and fiber optics, are utilized to do ACL repair surgery. However, in order to obtain the tissue graft, a considerably larger incision is necessary. Patients undergoing ACL restoration can return home the same day of surgery because it is an outpatient (ambulatory) treatment.
Disease Overview:
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
An anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury is a rupture or sprain of one of the strong bands of tissue that connects your thigh bone (femur) to your shinbone (tibia). ACL injuries are most frequent in sports like soccer, basketball, football, and downhill skiing, which entail rapid pauses or changes in direction, jumping, and landing.
When an ACL damage occurs, many patients hear a pop or experience a "popping" feeling in their knee. It's possible that your knee will expand, become unstable, and become too painful to bear weight on.
Rest and rehabilitation exercises can help you restore strength and stability, or surgery to repair the torn ligament followed by rehabilitation, depending on the degree of your ACL damage. An effective training programme can assist to lower the chance of ACL damage.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
The following are common signs and symptoms of an ACL injury:
- The sensation of a loud pop or "popping" in the knee
- Pain that is unbearable and makes it impossible to continue doing things
- Rapid enlargement
- Range of motion loss
- With weight bearing, a sense of instability or "giving way"
Disease Causes:
Ligaments are strong tissue bands that join two bones together. The ACL links your thighbone to your shinbone and helps maintain your knee joint. It is one of two ligaments that cross in the centre of your knee.
ACL injuries commonly occur as a result of sports and fitness activities that place stress on the knee:
- abruptly slowing down and altering course (cutting)
- Pivoting while keeping your foot firmly on the ground
- A clumsy landing after a jump
- abruptly halting
- Taking a direct strike to the knee or colliding with another object, such as a football tackle
- When a ligament is torn, it typically results in a partial or full tear of the tissue. A little damage to the ligament may stretch it yet leave it intact.
- Factors that are at risk
There are several variables that enhance your chances of tearing your ACL, including:
- Because of variations in anatomy, muscle strength, and hormonal impacts, being female
- Soccer, football, basketball, gymnastics, and downhill skiing are some of the activities that people participate in.
- Inadequate air conditioning
- Using incorrect movement patterns, such as squatting with the knees inward.
- Putting on shoes that don't fit correctly
- Using sporting equipment that isn't well-maintained, such as ski bindings that aren't correctly adjusted
- Playing on a synthetic surface
Disease Diagnosis:
Your doctor will examine your knee for swelling and discomfort during the physical exam, comparing your damaged knee to your uninjured knee. He or she may also move your knee into different positions to evaluate its range of motion and general function.
Often, a physical exam is enough to make a diagnosis, but testing may be required to rule out other causes and evaluate the severity of the injury. These tests may involve the following:
X-rays. To rule out a bone fracture, X-rays may be required. Soft tissues, such as ligaments and tendons, are not visible on X-rays.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of imaging that (MRI). An MRI creates pictures of both hard and soft tissues in your body using radio waves and a strong magnetic field. An MRI can reveal the degree of an ACL injury as well as evidence of damage to other knee tissues, such as the cartilage.
Ultrasound. Ultrasound can be used to examine for injuries in the ligaments, tendons, and muscles of the knee by using sound waves to see interior structures.
Disease Treatment
Immediate first-aid treatment can help to minimise discomfort and swelling after a knee injury. At home, use the R.I.C.E. model of self-care:
Rest. Rest is essential for recovery, as is limiting weight bearing on your knee.
Ice. When you're awake, ice your knee for 20 minutes every two hours at the very least.
Compression. Wrap your knee with an elastic bandage or compression wrap.
Elevation. Place your knees on cushions and lie down.
Rehabilitation
An ACL damage requires several weeks of rehabilitative therapy before it can be treated medically. A physical therapist will give you exercises that you may do in the clinic or at home with supervision. You can also use crutches for a bit to prevent placing weight on your knee while wearing a brace to stabilise it.
The objective of rehabilitation is to alleviate pain and swelling while also restoring complete range of motion and strengthening muscles in your knee. Individuals who are generally sedentary, participate in modest exercise and recreational activities, or play sports that place less stress on the knees may benefit from this course of physical therapy.
Surgery may be recommended by your doctor if:
- You're a sportsperson who wants to keep doing what you're doing, especially if it includes jumping, cutting, or rotating.
- In your knee, more than one ligament or fibrous cartilage is affected.
- Your knee is buckling as a result of the damage during regular activities.
- During ACL restoration, the surgeon removes the injured ligament and replaces it with a tendon — tissue that links muscle to bone and functions similarly to a ligament. A graft is the term for the replacement tissue.
- A tendon from another portion of your knee or a tendon from a dead donor will be used by your surgeon.
- Following surgery, you'll begin a new round of rehabilitative treatment. Your knee may generally be stabilized and functioned again after a successful ACL replacement and vigorous rehabilitation.
- Athletes have no predetermined time limit for returning to play. According to recent study, up to one-third of athletes will get another knee injury in the same or opposite knee within two years. The risk of re-injury may be reduced with a longer healing period.
In typically, it takes a year or more for players to be able to return to play safely. At various points during your recovery, doctors and physical therapists will do tests to assess your knee's stability, strength, function, and readiness to return to athletic activities. Before returning to an activity that puts your ACL at risk, make sure your strength, stability, and movement patterns are all in good shape.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
2 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private