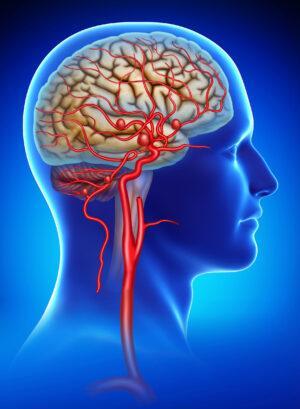
Angioplasty of the brain arteries
Iran
-
Our Price USD 3867
-
Hospital Price USD 4071
-
You Save : USD 204
Booking Amount: USD 387. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Procedure Description:
Angioplasty of the brain arteries:
In order to temporarily open the blocked artery and allow blood to flow freely to your brain, a small balloon is inserted and inflated into the artery. Carotid angioplasty frequently takes place in conjunction with stenting. Inserting a tiny metal coil, or "stent," into the obstructed artery is the process of stenting.
Disease Overview
When a portion of the brain's blood supply is cut off or obstructed, an ischemic stroke happens. This keeps oxygen and nutrients from reaching the brain tissue. Within minutes, brain cells start to die. Hemorrhagic strokes are another kind of stroke. Bleeding in the brain happens when a blood vessel leaks or bursts in the brain. The blood destroys brain cells by putting them under increased strain.
An emergency in medicine is a stroke. The urgent need for medical attention cannot be overstated. Rapid access to emergency medical care can lessen brain damage and other consequences of stroke.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
If you think that you or someone you know could be having a stroke, note when the symptoms started. Certain medications work best when administered shortly after the onset of a stroke.
A stroke's symptoms include:
1. Difficulty communicating and comprehending others. A stroke victim may exhibit confusion, slur words, or lose their ability to comprehend spoken words.
2. Paralysis, weakness, or numbness in the arm, leg, or face. Usually, this just affects one side of the body. One may attempt to lift both arms above the head. A stroke may be indicated if one arm starts to droop. When attempting to grin, one side of the mouth may also droop.
3. Issues with one or both eyes' vision. One or both of the person's eyes may suddenly become blacked out or blurry. Or they might see two things.
4- Headache. An abrupt, excruciating headache could be a sign of a stroke. Along with the headache, nausea, vertigo, and unconsciousness are possible side effects.
Difficult to navigate. A stroke victim may falter or experience balance or coordination issues.
Disease Causes:
Stroke is caused by two basic factors. A cerebral artery blockage is the cause of an ischemic stroke. A brain blood vessel leak or burst is what causes a hemorrhagic stroke. Some people might only experience transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), which are brief interruptions in blood supply to the brain. The symptoms of a TIA are transient.
1. Ischemic stroke: This kind of stroke occurs most frequently. It occurs when blood arteries in the brain constrict or become obstructed. This results in ischemia, which is a decreased blood flow. The accumulation of fatty deposits within blood arteries might result in blocked or constricted blood vessels.
2. Hemorrhagic stroke: This kind of stroke is brought on by a leaky or burst blood vessel in the brain. Brain hemorrhages, or internal bleeding in the brain, can be caused by a variety of blood vessel-related illnesses.
3. Transient ischemic attack: A transient ischemic attack, often known as a TIA, is a brief episode of stroke-like symptoms. However, a TIA doesn't result in long-term harm. A brief reduction in blood flow to a portion of the brain results in a transient ischemic attack (TIA). The decline might end after just five minutes. A ministroke is another name for a transient ischemic attack.
4. A number of things can raise one's risk of stroke. Among the stroke risk factors that may be treated are: - Lifestyle risk factors
- Being too big or overweight.
- A lack of exercise.
Abundant or heavy drinking.
- The usage of illicit substances like methamphetamine and cocaine.
Risk factors for health:
Elevated blood pressure.
- Smoking cigarettes or being around secondhand smoke.
Elevated cholesterol levels.
Diabetes.
- sleep Apnea
- Cardiovascular disease, which includes irregular heart rhythms including atrial fibrillation, heart failure, heart defects, and infections.
History of stroke, heart attack, or transient ischemic attack in oneself or one's family.
Disease Diagnosis:
Once at the hospital, things happen quite quickly after a stroke. Your medical team strives to identify the type of stroke you are experiencing. Soon after you arrive, you'll probably get a CT scan or another imaging test. A brain tumor or a medication response are two more potential reasons of your symptoms that medical specialists must rule out.
Exams:
1. CT scan of stroke-damaged brain tissue
2. Angiogram of the brain
Among the tests you might take are:
1. A medical examination. A medical practitioner takes your blood pressure and listens to your heart, among other tests. A neurological examination examines the effects of a possible stroke on your nervous system.
2- Blood testing. Tests may be necessary to determine whether your blood sugar is too high or too low and to see how quickly your blood clots. It's possible that you'll undergo testing to check for infections.
3- CT scan (computerized tomography). A CT scan builds a detailed picture of your brain by using a sequence of X-rays.
4. MRIs, or magnetic resonance imaging. Strong radio waves and a magnetic field are used in an MRI to produce a detailed image of the brain. The test can identify brain hemorrhages and brain tissue destroyed by an ischemic stroke.
5. carotid ultrasound. This examination uses sound waves to provide finely detailed images of the neck's carotid arteries. Blood flow in the carotid arteries and the accumulation of fat deposits known as plaques can both be seen on a carotid ultrasound.
6. Angiogram of the brain. Although less common, this examination offers a thorough view of the brain and neck arteries. A tiny incision is made, generally in the groin, to implant a thin, flexible tube known as a catheter.
7. Echocardiography. Sound waves are used in an echocardiogram to provide finely detailed pictures of the heart. An echocardiography can identify the origin of heart clots that may have spread to the brain and resulted in a stroke.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
7 Days
Days in Hotel
*
7 Days
Room Type
Private