ICD Procedure
Iran
-
Our Price USD 5434
-
Hospital Price USD 5720
-
You Save : USD 286
Booking Amount: USD 543. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
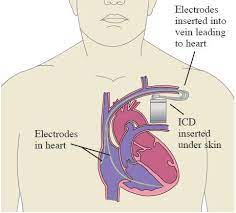
ICD Procedure
A small battery-powered device called an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is implanted in the chest to detect and stop abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias). An ICD continually monitors the heartbeat and, if necessary, administers electric shocks to reestablish a normal cardiac rhythm. If you have a dangerously fast heartbeat that prevents your heart from pumping enough blood to the rest of your body (ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation), or if you are at high risk of developing such a heart rhythm problem (arrhythmia), usually due to a weak heart muscle, you may need an ICD.
A pacemaker, which is an implanted device that can prevent dangerously slow heartbeats, is not the same as an ICD.
Disease Overview:
Cardiac arrest
The sudden cessation of heart function, respiration, and awareness is known as cardiac arrest. A issue with your heart's electrical system causes the disorder, which affects your heart's pumping motion and prevents blood flow to your body.
A heart attack, in which blood flow to a portion of the heart is interrupted, is not the same as sudden cardiac arrest. A heart attack, on the other hand, can occasionally cause an electrical disruption that results in rapid cardiac arrest.
Sudden cardiac arrest can be fatal if not addressed quickly. With prompt and adequate medical attention, survival is feasible. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), the use of a defibrillator, or even simple chest compressions can increase the odds of survival until help arrives.
Signs and Symptoms:
The following are immediate and severe signs of sudden cardiac arrest:
- Sudden collapse
- No pulse.
- No breathing.
- Consciousness loss
Other indications and symptoms may appear prior to sudden cardiac arrest. These might include the following:
- Uncomfortable chest
- Breathing problems
- Weakness
- Heart fluttering, or thumping (palpitations)
Sudden cardiac arrest, on the other hand, frequently happens without warning.
Disease Causes:
An abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia), which occurs when your heart's electrical circuitry fails, is the most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest.
The electrical system of your heart regulates the rate and rhythm of your heartbeat. Your heart may beat too rapidly, too slowly, or irregularly if something goes wrong (arrhythmia). Although most arrhythmias are short and harmless, some might result in cardiac arrest.
An arrhythmia in a lower chamber of your heart is the most prevalent heart rhythm at the moment of cardiac arrest (ventricle). Your ventricles quiver ineffectively instead of pumping blood due to rapid, irregular electrical impulses (ventricle fibrillation).
Diagnosis:
If you survive sudden cardiac arrest, your doctor will try to figure out what caused it so that you can avoid it in the future. The following tests may be recommended by your doctor:
Blood test: Blood tests are used to screen for indicators of heart disease.
Echocardiogram: An echocardiography is a type of ultrasonography of the heart. Sound waves are employed to produce moving images of the heart. An echocardiography allows doctors to examine the aortic valve and aorta in greater detail. It can assist in determining the source of aortic valve disease as well as the severity of the condition.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): The electrical activity of the heart is recorded in this noninvasive examination.
Chest X-ray: It can provide information about the heart and lungs' health.
Cardiac MRI: It creates precise pictures of the heart using magnetic fields and radio waves.
Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan: In this, Series of X-rays are used to obtain detailed pictures of the heart and heart valves. This imaging approach may be used by doctors to determine the size of the aorta and examine the aortic valve in greater detail.
Coronary Angiogram: This test involves inserting a thin, flexible tube (catheter) into a blood artery, commonly in the groyne, and guiding it to the heart arteries. A dye (contrast) is administered into the catheter to assist the doctor locate blockages by making the arteries appear more clearly on an X-ray
Myocardial biopsy: A doctor inserts a thin, flexible cable into a vein in the neck or groyne and takes extremely small sections of the heart muscle for inspection during this procedure. This test may be used to diagnose heart failure caused by certain types of heart muscle diseases..
Disease Treatment:
For survival, cardiac arrest necessitates rapid intervention.
CPR: It is critical in the treatment of sudden cardiac arrest. CPR can offer a key connection until more sophisticated emergency treatment is available by sustaining a flow of oxygen-rich blood to the body's important organs.
Defibrillation: The administration of an electrical shock through the chest wall to the heart is usually part of advanced treatment for ventricular fibrillation, a type of arrhythmia that can cause sudden cardiac arrest. Defibrillation is a process that temporarily pauses the heart and its erratic beat. This frequently causes the heart to return to its regular beat.
After you recover, your doctor will discuss with you or your family what other tests might help determine the cause of the cardiac arrest. Your doctor will also discuss preventive treatment options with you to reduce your risk of another cardiac arrest.
Treatments might include:
Drugs: For immediate or long-term therapy of arrhythmias or probable arrhythmia consequences, doctors employ a variety of anti-arrhythmic medications. Beta blockers are a type of drug that is routinely prescribed to persons who are at risk of abrupt cardiac arrest.
Implantable Cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD): Your doctor is likely to propose an ICD, a battery-powered device implanted near your left collarbone, after your condition has stabilized. The ICD sends one or more electrode-tipped cables via your veins to your heart.
Angioplasty of the coronary arteries: This surgery clears clogged coronary arteries, allowing more blood to circulate freely to your heart and perhaps lowering your risk of significant arrhythmia. A long, thin tube is inserted into an artery in your leg and then into a clogged artery in your heart. This catheter has an unique balloon tip that inflates temporarily to unblock a blocked artery.
Coronary bypass surgery: It is a procedure that involves bypassing the coronary arteries Bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass grafting, restores blood flow to your heart by stitching veins or arteries in place beyond a blocked or constricted coronary artery. This can help to increase your heart's blood flow and minimise the frequency of racing heartbeats.
Radiofrequency catheter ablation.
Corrective heart surgery.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
1 Days
Days in Hotel
*
5 Days
Room Type
Private