Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Thailand
-
Our Price USD 49117
-
Hospital Price USD 51702
-
You Save : USD 2585
Booking Amount: USD 4912. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Procedure Description:
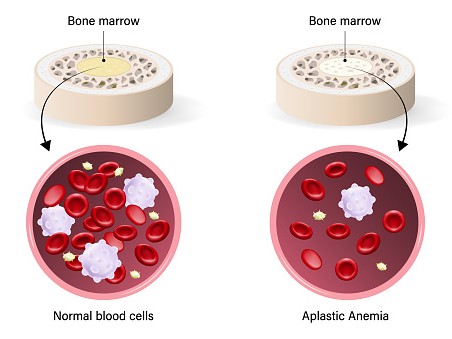
Aplastic Anemia Treatment
Aplastic anemia treatments could involve any of the following: Bone marrow and blood transplants: they may help certain patients with aplastic anemia. transfusions of blood. medications that prevent the bone marrow's stem cells from being destroyed by your immune system. drugs that aid in the production of new blood cells in your body.
Disease Overview:
Aplastic Anemia
Your body can develop aplastic anemia if it stops making enough red blood cells. You become exhausted from the disease and become more vulnerable to infections and uncontrollable bleeding.
Aplastic anemia is a rare and dangerous illness that can strike at any age. It may start off slowly and get worse over time, or it may happen quickly. It could be minor or serious.
Medication, blood transfusions, or stem cell transplantation—also referred to as a bone marrow transplant—may be used as treatments for aplastic anemia.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
Anemia aplastic may not exhibit any symptoms. Signs and symptoms that may be present include:
1. Exhaustion
2. Breathlessness
3. An erratic or fast heartbeat
4. Pale skin
5. Prolonged or recurring illnesses
6. Easily or unexplainably bruised
7. Bleeding gums and nosebleeds
8. Extended bleeding after wounds
9. Skin rash;
10. Dizziness
11. Headache
12. Fever
Aplastic anemia may develop into a chronic condition or be transient. It may be very serious or even deadly.
Disease Causes:
The most frequent cause of aplastic anemia is an immune system attack on bone marrow stem cells. Other conditions that can damage bone marrow and impact the generation of blood cells are chemotherapy and radiation therapy. These anti-cancer treatments destroy cancer cells, but they can harm good cells as well, such as bone marrow stem cells. One transient side effect of these treatments may be aplastic anemia.
exposure to harmful substances. Aplastic anemia has been connected to toxic chemicals, including some found in insecticides and pesticides, as well as benzene, an element in gasoline. If you stay away from the chemicals that caused your disease repeatedly, your kind of anemia might get well.
1. The usage of specific medications. Aplastic anemia can be brought on by certain drugs, including certain antibiotics and those used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Immune system conditions. Your bone marrow may contain stem cells if you have an autoimmune illness, which is characterized by an immune system attack on healthy cells.
3. A virus outbreak. Aplastic anemia can arise as a result of bone marrow-related viral infections. Aplastic anemia has been associated with a number of viruses, including HIV, CMV, parvovirus B19, Epstein-Barr, and hepatitis.
4. Being pregnant. During pregnancy, your immune system may target your bone marrow.
unknown elements. Physicians frequently are unable to determine the etiology of aplastic anemia (idiopathic aplastic anemia).
Disease Diagnosis:
Testing for aplastic anemia can be done in the following ways:
1. Hematologic testing. The normal ranges for red blood cell, white blood cell, and platelet counts are maintained. All three of these blood cell counts are decreased in aplastic anemia.
2. Biopsy on bone marrow. A tiny sample of bone marrow is taken by a doctor using a needle from a big bone in your body, like your hipbone. A microscope is used to look at the sample in order to rule out other blood-related disorders. Bone marrow in aplastic anemia has a lower than usual concentration of blood cells. The diagnosis of aplastic anemia must be confirmed by bone marrow biopsy.
Disease Treatment:
Depending on the severity of your condition and your age, your doctor may recommend bone marrow transplants, blood transfusions, medication, or observation as treatments for aplastic anemia. Your blood cell counts will be dangerously low if you have severe aplastic anemia, which necessitates emergency hospitalization.
1. Transfusions of blood: Blood transfusions help manage bleeding and alleviate symptoms of aplastic anemia by supplying blood cells that your bone marrow isn't able to produce. However, they are not a cure for the condition. You could possibly get:
- Red blood cells: These assists reduce fatigue and anemia by increasing red blood cell numbers.
- Platelets: These aid in halting excessive bleeding.
2. Stem cell transplant: For patients with severe aplastic anemia, a stem cell transplant that replaces the bone marrow with donor stem cells may be the only effective course of treatment. In general, younger patients who have a compatible donor, usually a sibling, are treated with a stem cell transplant, commonly known as a bone marrow transplant.
3. Immunosuppressants: Medication that modifies or suppresses the immune system may be used as a kind of treatment for individuals who are unable to have a bone marrow transplant or whose aplastic anemia is brought on by an autoimmune disease.
4. Bone marrow stimulants: A number of medications, such as colony-stimulating factors like epoetin alfa (Epogen/Procrit), eltrombopag (Promacta), filgrastim (Neupogen), and pegfilgrastim (Neulasta), assist in encouraging the bone marrow to create new blood cells.
5. Antivirals and antibiotics
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
8 Days
Days in Hotel
*
28 Days
Room Type
Private