Ovarian Cyst Removal
Thailand
-
Our Price USD 2083
-
Hospital Price USD 2193
-
You Save : USD 110
Booking Amount: USD 208. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Procedure Description:
Ovarian Cyst Removal
Your age, the kind, and the size of your cyst will determine how you are treated. Your symptoms will also play a role. Your medical professional may recommend:
1. Watchful waiting: You can often wait a few months to have another examination to see if the cyst disappears. Regardless of your age, this is usually an option if an ultrasound reveals you have a tiny cyst packed with fluid, but you don't have any symptoms. A series of follow-up pelvic ultrasounds may be performed to monitor any changes in the size or appearance of your cyst.
2. Medication: Hormonal contraceptives prevent ovulation, such as birth control pills. This could prevent further ovarian cyst development. Birth control pills, however, won't get rid of an existing cyst.
3. Surgery: If your cyst is huge, does not appear to be functional, is expanding, or is causing pain, your provider may recommend removing it. Cystectomy—the removal of a cyst—can be performed without removing the ovary. Sometimes the cysted ovary is removed (oophorectomy).
Many times, minimally invasive surgery, or laparoscopy is used to perform surgery. Through tiny abdominal incisions, a laparoscope and other devices are inserted. An open operation involving a larger cut can be required if the cyst is large or malignancy is a worry.
Sometimes, an ovarian cyst that appears after menopause is cancerous. You might need to see a gynecologic cancer specialist in this situation. Your ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix may need to be removed surgically. You could additionally require chemotherapy or radiation.
Disease Overview:
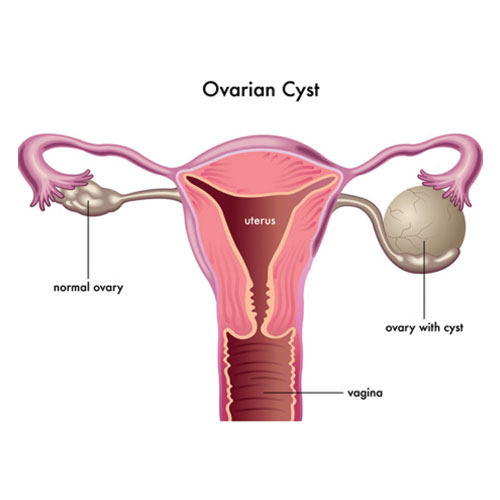
Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian cysts are sacs within or on the surface of an ovary that are often filled with fluid. The ovaries are two in females. On either side of the uterus is one ovary.
Every ovary resembles an almond in both size and shape. Eggs grow and develop inside the ovaries. Monthly cycles of egg release occur during the childbearing years. Cysts in the ovaries are prevalent. Most of the time, the cysts are innocuous, and you experience little to no discomfort. Without medical intervention, most cysts disappear in a few months. However, ovarian cysts can occasionally twist or rupture.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
The majority of ovarian cysts are asymptomatic and disappear on their own. However, a big ovarian cyst may result in:
1- Pelvic pain that may be intermittent. In the region below your bellybutton, you might have a severe or dull discomfort that is directed toward one side.
2- feeling of fullness, pressure, or weight in your abdomen.
3- bloating.
Disease Causes:
The menstrual cycle is the primary cause of most ovarian cyst formation. We refer to these as functioning cysts. Cysts of other sorts are far less common.
Every month, little cysts called follicles develop on your ovaries. When you ovulate, follicles burst open to release an egg and release the chemicals progesterone and estrogen.
Other kinds of cysts, such as dermoid cysts, are unrelated to menstrual cycles. This cyst, also known as a teratoma, develops from ovarian germ cells, which are reproductive cells that produce eggs. Tissue from the skin, hair, or teeth may be present in the cyst. Seldom is this kind of cyst cancerous.
Cystadenoma. The cells that form this kind of cyst are found on the ovary's surface. There's a chance that the cyst is packed with mucus or water. Large cystadenoma growth is possible.
Endometrioma. A disorder known as endometriosis causes cells that line the inside of the uterus to proliferate outside of it. A cyst may develop from tissue that has attached itself to the ovary. We refer to this as an endometrioma.
Disease Diagnosis:
An imaging test, like a pelvic ultrasound, or a pelvic exam can detect an ovarian cyst. Your healthcare professional will probably suggest tests to identify the type of cyst and evaluate whether you require treatment, depending on the size of the cyst and whether it is filled with fluid or solid.
Potential examinations consist of:
1- Pregnancy test. An early pregnancy could be suggested by a positive test. During pregnancy, corpus luteum cysts are a common sight.
2. Ultrasound of the pelvis. Ultrasound uses a wand-like instrument called a transducer to send and receive high-frequency sound waves in order to create an image of your ovaries and uterus on a video screen.
3. The laparoscope. A tiny incision is made in your belly to accommodate the insertion of a thin, illuminated device called a laparoscope. Your doctor can view your ovaries and any cysts with a laparoscope. Treatment is typically administered during the same surgery if a cyst is discovered. Since this is a surgical treatment, anesthetic is needed.
4. Tests for tumor markers. In ovarian cancer, blood levels of a protein known as a cancer antigen are frequently high. In the event that your cyst seems solid and you have a high risk of developing ovarian cancer, your doctor may prescribe additional blood tests or the cancer antigen 125 (CA125) test. In non-cancerous disorders such endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease, CA 125 levels can also be raised.
Disease Treatment:
Your age, the kind, and the size of your cyst will determine how you are treated. Your symptoms will also play a role. Your medical professional may recommend:
1. Watchful waiting: You can often wait a few months to have another examination to see if the cyst disappears. Regardless of your age, this is usually an option if an ultrasound reveals you have a tiny cyst packed with fluid but you don't have any symptoms. A series of follow-up pelvic ultrasounds may be performed to monitor any changes in the size or appearance of your cyst.
2. Medication: Hormonal contraceptives prevent ovulation, such as birth control pills. This could prevent further ovarian cyst development. Birth control pills, however, won't get rid of an existing cyst.
3. Surgery: If your cyst is huge, does not appear to be functional, is expanding, or is causing pain, your provider may recommend removing it. Cystectomy—the removal of a cyst—can be performed without removing the ovary. Sometimes the cysted ovary is removed (oophorectomy).
Many times, minimally invasive surgery, or laparoscopy, is used to perform surgery. Through tiny abdominal incisions, a laparoscope and other devices are inserted. An open operation involving a larger cut can be required if the cyst is large or malignancy is a worry.
Sometimes, an ovarian cyst that appears after menopause is cancerous. You might need to see a gynecologic cancer specialist in this situation. Your ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and cervix may need to be removed surgically. You could additionally require chemotherapy or radiation.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
2 Days
Days in Hotel
*
5 Days
Room Type
Private