Polypectomy
Thailand
-
Our Price USD 2789
-
Hospital Price USD 2936
-
You Save : USD 147
Booking Amount: USD 279. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Procedure Description:
Polypectomy
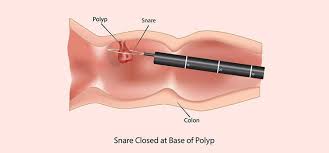
The surgical excision of a polyp is known as a polypectomy. Although they can be removed with open abdominal surgery, colon polyps are usually removed during a colonoscopy. Using forceps, the endoscopist can cut out a little polyp or use a snare that burns through the polyp's base to remove a larger one.
Disease Overview:
Uterine Polyps
Growths known as uterine polyps are affixed to the uterine wall and proliferate inside the uterus. Endometrial polyps, another name for uterine polyps, develop when cells in the endometrium—the lining of the uterus—grow too quickly. Although some of these polyps are cancerous or have the potential to become cancer (precancerous polyps), most of them are benign (noncancerous).
The size of uterine polyps varies from a few millimeters, or no bigger than a sesame seed, to several centimeters, or bigger than a golf ball. They cling to the uterine wall with a tiny stalk or a big base.
One or more uterine polyps may be present. Although they often remain inside the uterus, they have the ability to enter the vagina through the cervix, the entryway to the uterus. The majority of cases of uterine polyps occur in women who are going through or have finished menopause. However, younger people can also get them.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
Uterine polyp signs and indicators include:
1. Postmenopausal vaginal bleeding.
2. Bleeding in between the menses.
3. Recurrent, erratic intervals with varying weights and lengths.
4. Very intense times.
5. The inability to conceive.
Some people experience no symptoms at all, while others just have minor bleeding or spotting.
Disease Causes:
It seems that hormonal elements are involved. Because uterine polyps are estrogen-sensitive, their growth is triggered by the body's production of estrogen.
The following are risk factors for uterine polyps to develop:
1. Experiencing menopause or perimenopause.
2. Being overweight.
3. Using the medication tamoxifen as a breast cancer treatment.
4. Hormone therapy for symptoms related to menopause.
Disease Diagnosis:
Tests for uterine polyps include the following ones:
1. Transvaginal ultrasound: An instrument that resembles a thin wand is inserted into the vagina to produce sound waves that create an image of the uterus, including its interior. There could be a noticeable polyp or a thicker endometrial tissue area.
2. Hysteroscopy: In this procedure, a thin, flexible, illuminated telescope (called a hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterus through the cervix and vagina. The uterus' inside can be seen during hysteroscopy.
3. Endometrial biopsy: A specimen is taken for laboratory analysis using a suction catheter inserted inside the uterus. An endometrial biopsy may confirm uterine polyps, however it may also miss the polyp.
4. Transvaginal ultrasound: You recline on an examination table as a medical professional or a medical technician inserts a transducer, which resembles a wand, into your vagina. The uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes are depicted in images by the transducer's sound waves.
5. Hysterosonography: It is a medical professional injects saline (salt water) into the uterus's hollow section using a thin, flexible tube called a catheter. An ultrasonography probe obtains images of the uterus' inside to look for anomalies.
6. Hysteroscopy: During hysteroscopy, an internal view of the uterus is obtained using a thin, illuminated device called a hysteroscope.
Disease Treatment:
Uterine polyps may be treated with:
1. Be cautious when waiting: Tiny polyps that don't cause any symptoms may go away on their own. For those who do not have a risk of uterine cancer, treatment of tiny polyps is not necessary.
2. Medication: Progestins and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists are two examples of hormonal drugs that may minimize polyp symptoms. However, using these drugs is usually only a temporary fix at best because, when the drug is stopped, the symptoms frequently return.
3. Surgical removal: Polyps can be surgically removed via a hysteroscopy by means of devices that are placed through the hysteroscope, a device that allows vision into the uterus. Most likely, a lab will get the excised polyp for analysis.
Your healthcare professional will discuss with you the following steps in assessment and treatment if a uterine polyp includes cancer cells.
Uterine polyps may recur in rare cases. If so, additional care is required.
The surgical excision of a polyp is known as a polypectomy. Although they can be removed with open abdominal surgery, colon polyps are usually removed during a colonoscopy. Using forceps, the endoscopist can cut out a little polyp or use a snare that burns through the polyp's base to remove a larger one.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
1 Days
Days in Hotel
*
3 Days
Room Type
Private