Thalassemia Treatment
Turkey
-
Our Price USD 58023
-
Hospital Price USD 61077
-
You Save : USD 3054
Booking Amount: USD 5802. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Procedure Description:
Thalassemia Treatment
Treatment for mild cases of thalassemia trait is not necessary.
Treatment options for moderate to severe thalassemia could be:
1. Regular transfusions of blood. Blood transfusions are frequently necessary for more severe cases of thalassemia, sometimes as frequently as every few weeks. Iron builds up in the blood after blood transfusions, which can harm your heart, liver, and other organs.
2. Chelation treatment. This is a procedure to rid your blood of extra iron. Regular transfusions might cause an accumulation of iron. When thalassemia patients do not receive frequent transfusions, they may also acquire an excess of iron. It's critical to remove excess iron for your health.
You may need to take an oral drug, such as deferasirox (Exjade, Jadenu) or deferiprone (Ferriprox), to assist your body get rid of the excess iron. A needle is used to administer deferoxamine, also known as Desferal.
3. Stem cell exchange. In certain circumstances, a stem cell transplant—also known as a bone marrow transplant—may be an option. It can remove the need for lifelong blood transfusions and medication to manage iron overload in children with severe thalassemia.
Receiving stem cell infusions from a suitable donor—typically a sibling—is part of this process.
Disease Overview:
Thalassemia
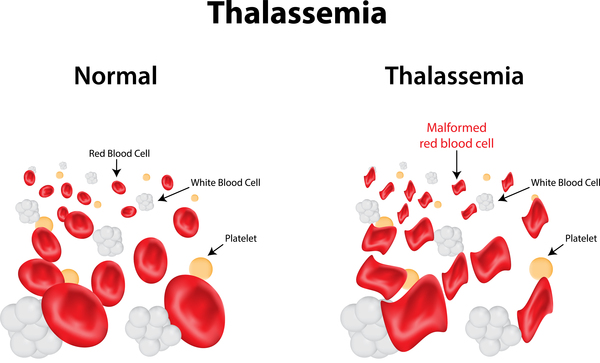
A hereditary blood condition called thalassemia results in your body having less hemoglobin than usual. Red blood cells can carry oxygen because hemoglobin is present. Anemia from thalassemia can make you feel exhausted.
In mild cases of thalassemia, therapy may not be necessary. However, more severe types may necessitate frequent blood transfusions. You can manage your weariness by exercising frequently and maintaining a nutritious diet.
Disease Sign and Symptoms
Thalassemia comes in various forms. Your condition's kind and severity will determine the symptoms and signs you experience.
Signs and symptoms of thalassemia may include:
- Exhaustion
- Weakness
- Yellowish or pale complexion
- Deformities of the facial bones
- Slow rate of expansion
- Swelling in the abdomen
- Dark urine
Some infants with thalassemia exhibit symptoms and indicators from birth, whereas others experience them in their first two years of life. Some patients without signs of thalassemia have only one mutated hemoglobin gene.
Disease Causes:
Mutations in the DNA of the cells that produce hemoglobin, the component of red blood cells that transports oxygen throughout your body, are the cause of thalassemia. Children inherit the thalassemia-related mutations from their parents.
The alpha and beta chains that make up hemoglobin molecules are subject to mutation. Alpha- or beta-thalassemia can be caused by a reduction in the production of either the alpha or beta chains in thalassemia.
The quantity of gene mutations you receive from your parents determines the severity of your alpha-thalassemia. Your thalassemia will be more severe if you have more mutated genes.
The following are some factors that raise your risk of thalassemia:
1- Family history of thalassemia. Parents can pass on thalassemia to their offspring by way of altered hemoglobin genes.
2. A certain lineage. People of Mediterranean and Southeast Asian heritage, as well as African Americans, are the most common populations to have thalassemia.
Disease Diagnosis:
Within the first two years of life, the majority of children with moderate to severe thalassemia exhibit signs and symptoms. Blood testing can confirm a diagnosis of thalassemia if your child's physician has suspicions about the condition.
Blood tests can identify anomalies in size, shape, or color as well as the quantity of red blood cells. DNA analysis can also be performed on blood samples to search for gene mutations.
Prenatal examinations: To find out if a newborn has thalassemia and how serious it might be, testing can be done before to birth. The following tests are used to identify thalassemia in fetuses:
1. Chorionic villus sampling: This test, which is often performed during the eleventh week of pregnancy, involves taking a small sample of the placenta for analysis.
2. Amniocentesis: This test, which is often performed during the sixteenth week of pregnancy, entails analyzing a sample of the fluid that envelops the fetus.
Disease Treatment:
Treatment for mild cases of thalassemia trait is not necessary.
Treatment options for moderate to severe thalassemia could be:
1. Regular transfusions of blood. Blood transfusions are frequently necessary for more severe cases of thalassemia, sometimes as frequently as every few weeks. Iron builds up in the blood after blood transfusions, which can harm your heart, liver, and other organs.
2. Chelation treatment. This is a procedure to rid your blood of extra iron. Regular transfusions might cause an accumulation of iron. When thalassemia patients do not receive frequent transfusions, they may also acquire an excess of iron. It's critical to remove excess iron for your health.
You may need to take an oral drug, such as deferasirox (Exjade, Jadenu) or deferiprone (Ferriprox), to assist your body get rid of the excess iron. A needle is used to administer deferoxamine, also known as Desferal.
3. Stem cell exchange. In certain circumstances, a stem cell transplant—also known as a bone marrow transplant—may be an option. It can remove the need for lifelong blood transfusions and medication to manage iron overload in children with severe thalassemia.
Receiving stem cell infusions from a suitable donor—typically a sibling—is part of this process.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
20 Days
Days in Hotel
*
90 Days
Room Type
Private