Congenital Heart disease treatment cost in India
The cost of Congenital Heart Disease Treatment in India ranges from USD 4500 to USD 9000
Congenital Heart Disease Treatment
Treatment is not always necessary for individuals with congenital heart defects (CHD). Certain individuals might merely require a visit to a cardiologist and observation. In some situations, a cardiac catheterization or surgery may be required to fix the heart abnormality or lessen its symptoms. Even if a deformity is corrected while it is a child, it may still improve with time and require further medical care.
To ensure that the heart functions at its peak, numerous medical interventions are available. A child may occasionally have several ailments, each of which may need to be treated with medication. Many common illnesses, such as the following, may require medical treatment for children and people with congenital heart defects:
1- Heart failure with congestion
2- heart rhythm issues
3- Heart hypertension
4- Cardiac catheterizations used for intervention
Options for congenital cardiac problems' care and therapy include:
1- Procedures involving surgery
2- Catheterizations of the heart
3- heart replacement surgery
4- Getting kids ready for surgery
5- Advice on feeding your infant if they have CHD
6- Children with CHD have unique needs.
7- Exercise for people with congenital cardiac defects
8- Advice on heart health for those with congestive heart failure
The American Heart Association is here to support parents raising a child with a congenital heart condition. Check out our peer-to-peer Support Network and our caregiver resources.
Procedure Description:
Treatment is not always necessary for individuals with congenital heart defects (CHD). Certain individuals might merely require a visit to a cardiologist and observation. In some situations, a cardiac catheterization or surgery may be required to fix the heart abnormality or lessen its symptoms. Even if a deformity is corrected while it is a child, it may still improve with time and require further medical care.
To ensure that the heart functions at its peak, numerous medical interventions are available. A child may occasionally have several ailments, each of which may need to be treated with medication. Many common illnesses, such as the following, may require medical treatment for children and people with congenital heart defects:
1- Heart failure with congestion
2- heart rhythm issues
3- Heart hypertension
4- Cardiac catheterizations used for intervention
Options for congenital cardiac problems' care and therapy include:
1- Procedures involving surgery
2- Catheterizations of the heart
3- heart replacement surgery
4- Getting kids ready for surgery
5- Advice on feeding your infant if they have CHD
6- Children with CHD have unique needs.
7- Exercise for people with congenital cardiac defects
8- Advice on heart health for those with congestive heart failure
The American Heart Association is here to support parents raising a child with a congenital heart condition. Check out our peer-to-peer Support Network and our caregiver resources.
Disease Description:
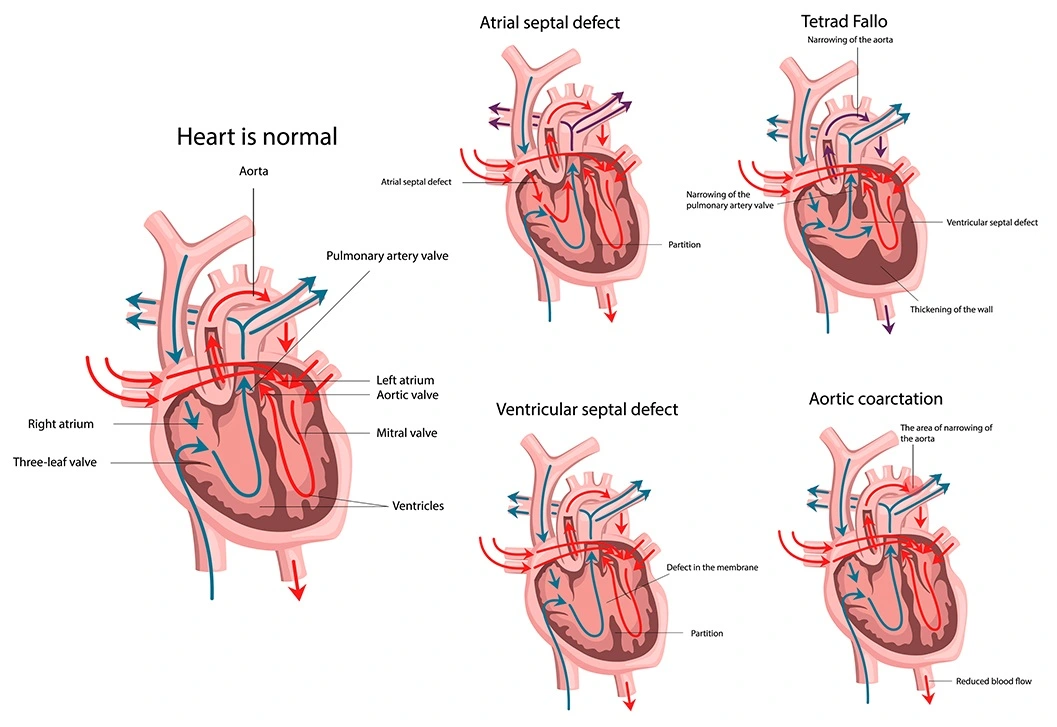
A congenital heart defect (CHD) is an anatomic abnormality of the heart or major vessels that develops during foetal development, regardless of age at presentation. CHDs include ventricular septal defect and aortic coarctation, to name a few.
Congenital heart disease is a condition in which one or more structural flaws in the heart have existed since birth. The term "congenital" refers to a deformity that is present from birth. Congenital heart disease, also known as congenital heart defect, affects how blood flows through your heart from birth. Some congenital cardiac abnormalities may not be life-threatening. Complex malformations, on the other hand, might have life-threatening consequences.
Congenital heart disease newborns can now live well into adulthood because to advances in detection and therapy. Congenital heart disease might have indications and symptoms that aren't visible until you're an adult.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
Congenital heart disease can cause a variety of symptoms, especially in newborns and children, such as a fast heartbeat and shallow breathing.
Swelling in the legs, stomach, or eyelids.
severe exhaustion and weariness
skin or lips with a blue tint (cyanosis)
When a baby is nursing, it might cause exhaustion and fast respiration.
Disease Causes:
The majority of congenital heart abnormalities are caused by issues that arise during the development of the baby's heart before birth. Most congenital cardiac abnormalities have an unknown origin. Certain environmental and genetic risk factors, on the other hand, may have a role. They are as follows:
Rubella is a contagious disease that affect (German measles). Rubella can affect your baby's heart development if you get it while pregnant. Before you are pregnant, your doctor can check for immunity to this viral illness and vaccine you if you aren't.
Diabetes. By carefully regulating blood sugar levels before and during pregnancy, a woman who had diabetes before becoming pregnant can lower her risk of congenital heart abnormalities. Diabetes that develops during pregnancy (gestational diabetes) does not raise the chance of a heart abnormality in the newborn.
Medications. Certain drugs can cause birth problems, including congenital heart disorders, if used during pregnancy. Before attempting to conceive, give your doctor a thorough list of your drugs.
Thalidomide (Thalomid), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, statins, the acne treatment isotretinoin (Absorica, Amnesteem, others), several epileptic medications, and some anxiety drugs are all known to raise the risk of congenital cardiac abnormalities.
Consumption of alcoholic beverages when pregnant. Consumption of alcoholic beverages during pregnancy raises the chance of congenital cardiac abnormalities.
Smoking. Quit smoking if you're a smoker. Smoking during pregnancy raises the likelihood of the baby developing a congenital heart condition.
Genetics and family history Congenital cardiac problems can run in families (i.e., they are inherited) and be linked to a genetic condition. Heart abnormalities are common in children who have an additional 21st chromosome (Down syndrome). Heart abnormalities can potentially be caused by a missing piece of genetic material (deletion) on chromosome 22.
Diagnosis for disease:
Your doctor will perform a physical exam and use a stethoscope to listen to your heart to determine congenital heart disease. You'll be quizzed about your symptoms, as well as your medical and family history.
The following tests can be used to detect or rule out congenital cardiac disease:
An EKG is a type of electrocardiogram (ECG). The electrical signals in your heart are recorded during this painless examination. Many cardiac disorders, such as irregular heartbeats and clogged arteries, can be diagnosed using an ECG. ECGs are sometimes taken while you exercise, usually on a bike or treadmill. A stress test is the name for this approach.
X-ray of the chest. Changes in the size and form of your heart, as well as issues with your lungs, can be shown on these scans.
Pulse oximetry is the measurement of oxygen saturation in the blood. The amount of oxygen in your body may be estimated using a tiny sensor linked to your finger.
Echocardiogram. Ultrasound waves produce pictures of the beating heart. This test can be used by your doctor to see how your heart's chambers and valves flow blood through it. Echocardiograms can also be performed while you're doing out on a bike or treadmill.
Transesophageal echocardiography is a kind of echocardiogram that is performed via the esophag A transesophageal echocardiography may be recommended if more detailed pictures of your heart are required. A flexible tube housing the transducer is directed down your neck and into the tube that connects your mouth and stomach in this test (esophagus). The procedure is carried out while you are anaesthetized.
CT scan and MRI of the heart. Images of your heart and chest are created throughout these exams. X-rays are used in cardiac CT scans. Cardiac MRI creates pictures of your heart using a magnetic field and radio waves. You lie on a table that glides within a long tubelike machine for both exams.
Catheterization of the heart. This test may be used by your doctor to examine your heart's blood flow and blood pressure. You'll be given sedatives to help you sleep. The doctor will then carefully place a catheter into an artery or vein in your groyne, neck, or arm and guide it up to your heart. The catheter is guided to the proper place using X-rays. Dye is sometimes injected into the catheter. The dye aids in the visibility of blood vessels on pictures.
Disease Treatment:
Congenital cardiac disease is typically effectively treated in childhood. Some cardiac abnormalities, on the other hand, may not be substantial enough to be repaired during childhood, but they might create issues later in life.
Adults with congenital cardiac disease are treated differently depending on the severity of their condition. You could just need to be watched, or you might need medicine or surgery.
waiting with bated breath
Minor cardiac problems may just necessitate periodic examinations with your doctor to ensure that your condition does not worsen. Inquire with your doctor about how frequently you should be visited.
Medications
Medications that help the heart perform more effectively can be used to treat some moderate congenital heart abnormalities. Medications to prevent blood clots or manage an irregular heartbeat may also be required.
Surgical treatments and other medical procedures
Adults with congenital cardiac disease can undergo a variety of operations and treatments.
Devices for the heart that can be implanted. A pacemaker or an implanted cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) that helps control your heart rate or corrects life-threatening irregular heartbeats may help alleviate some of the difficulties associated with congenital heart abnormalities.
Treatments that rely on catheters. Catheterization procedures can be used to fix some congenital heart abnormalities. These procedures make it possible to heal the heart without requiring open-heart surgery. Instead, the doctor inserts a tiny tube (catheter) into a leg vein or artery and uses X-ray pictures to guide it to the heart. The doctor threads small instruments through the catheter to correct the problem once it is in place.
Open-heart surgery is a type of surgery in which the patient's heart is Your doctor may prescribe open-heart surgery if catheter methods fail to correct your heart problem.
A heart transplant is a procedure in which a person' A heart transplant may be a possibility if a major cardiac defect cannot be fixed.
Country wise cost comparison for Congenital Heart disease treatment:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $4455 |
Treatment and Cost
17
Total Days
In Country
- 2 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 15 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from