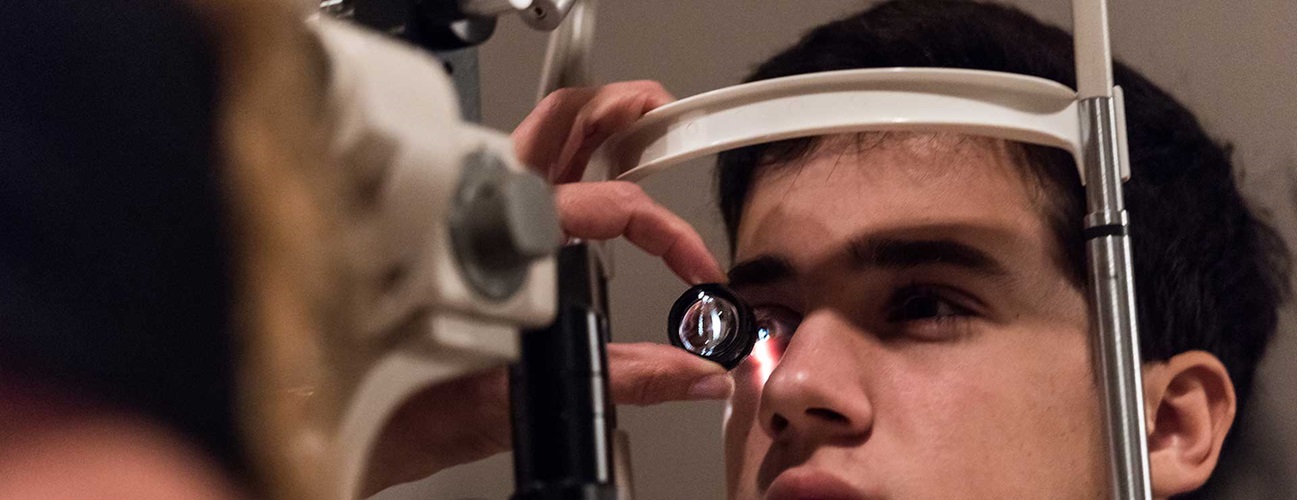
Glaucoma Treatment cost in India
The cost of Glaucoma Treatment in India ranges
from USD 400 to USD 1500
Procedure Description:
Glaucoma Treatment
Once glaucoma develops, it cannot be stopped. On the other hand, if the problem is detected early, treatment and regular exams can help reduce or avoid visual loss.
Glaucoma (intraocular pressure) is treated with decreased eye pressure. Depending on your situation, you may be able to receive laser therapy, surgery, oral medications, prescription eyedrops, or a combination of these.
Eye drops with a prescription are frequently used to treat glaucoma. By altering the way fluid exits your eye or lowering the amount of fluid your eye produces, these can help lower your intraocular pressure.
1. Oral medications: If eyedrops don't reduce your eye pressure, your doctor might recommend an oral medication like a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Possible side effects include tingling in the fingers and toes, kidney stones, depression, stomach pain, and frequent urination.
2. Surgical techniques and other therapies: Two other therapeutic options are laser therapy and various surgical techniques. The goal of the following treatments is to lower pressure by increasing the fluid outflow from the eye:
3. The application of lasers is one form of treatment that You might be a candidate for laser trabeculoplasty if you have open-angle glaucoma. It is done in the physician's office. Your doctor uses a small laser beam to clear clogged trabecular meshwork passageways. The full effect of this procedure may not be felt for a few weeks.
4- The process of filtering surgery entails the elimination of impurities. A trabeculectomy is a surgical procedure in which a portion of the trabecular meshwork is removed along with a hole made in the sclera, the white component of the eye.
Drainage tubes. Your eye surgeon will install a thin tube shunt to drain out extra fluid and lower the pressure in your eyes.
5. Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS). Your doctor might suggest a MIGS procedure to lower the pressure in your eyes. When compared to trabeculectomy or the implantation of a drainage device, these therapies are less invasive and require less immediate postoperative care. They are commonly combined with cataract surgery. Your doctor will discuss the various MIGS therapies available to you and help you make the best decision.
Following your procedure, you will need to see your doctor for follow-up examinations. You might also require more procedures if your eye pressure keeps rising or if other anomalies in your eyes develop.
6. Treatment for acute angle-closure glaucoma: An acute angle closure in glaucoma is a medical emergency. Should this disease be identified as yours, you will need to start treatment right away to reduce your intraocular pressure. Usually, this will require the use of medication in addition to laser or other surgical methods.
7- A laser peripheral iridotomy is a procedure when a medical professional makes a tiny hole in your iris using a laser. This lessens eye strain by allowing fluid, or aqueous humour, to move through it.
Disease Overview:
Glaucoma is a collection of eye diseases that affect the optic nerve, which is essential for proper vision. An excessively high pressure in your eye is typically the source of this injury. Glaucoma is one of the most common causes of blindness in persons over 60.
It can strike anyone at any age, although it is more frequent among the elderly.
Many types of glaucoma have no symptoms. Because the effect is so slow, you may not detect a change in vision until the problem has progressed significantly.
Because glaucoma vision loss is irreversible, it's critical to get frequent eye exams that include measures of your eye pressure so that a diagnosis may be established early and treatment can begin. Vision loss can be delayed or avoided if glaucoma is detected early. You'll almost certainly require therapy for the remainder of your life if you have the disease.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Glaucoma signs and symptoms vary based on the kind and stage of the disease. Consider the following scenario:
- Glaucoma with an open angle
- Blind patches in your peripheral (side) or central vision, often in both eyes
- Advanced phases of tunnel vision
Glaucoma with acute angle closure
- Headache that is severe
- Pain in the eyes
- Vomiting and nausea
- Vision is hazy
- Lights with halo effects
- Redness in the eyes
Glaucoma will eventually cause blindness if left untreated. Even with therapy, roughly 15% of glaucoma patients lose vision in at least one eye within 20 years.
Disease.
Disease Causes:
The injury to the optic nerve causes glaucoma. Blind patches form in your vision field when this nerve deteriorates. This nerve injury is frequently linked to increased ocular pressure for reasons that doctors don't completely understand.
A accumulation of a fluid (aqueous humour) that circulates across the interior of your eye causes increased ocular pressure. At the angle where the iris and cornea meet, this internal fluid generally drains out through a tissue called the trabecular meshwork. When fluid is overproduced or the drainage system fails, the fluid cannot flow out at its normal rate, causing increased eye pressure.
Glaucoma is a disease that runs in families. Scientists have discovered genes linked to excessive eye pressure and optic nerve injury in certain people.
Glaucoma comes in a variety of forms, including:
Glaucoma with an open angle
The most prevalent kind of glaucoma is open-angle glaucoma. The trabecular meshwork is partially occluded, yet the drainage angle produced by the cornea and iris remains open. As a result, the pressure in the eye steadily rises. The optic nerve is harmed by this pressure. It happens so slowly that you can lose your vision before you even realise there's a problem.
Angle-closure glaucoma
Also known as closed-angle glaucoma, is a condition in which the iris bulges forward, narrowing or blocking the drainage angle created by the cornea and iris.
It can develop quickly (acute angle-closure glaucoma) or gradually (progressive angle-closure glaucoma) (chronic angle-closure glaucoma). Glaucoma with acute angle closure is a medical emergency.
Glaucoma with a normal intraocular pressure
Even if your eye pressure is within the usual range, your optic nerve is injured with normal-tension glaucoma. No one knows why this is the case. It's possible that you have a sensitive optic nerve or that your optic nerve isn't getting enough blood. Atherosclerosis, or the accumulation of fatty deposits (plaque) in the arteries, or other disorders that affect circulation might be to blame for the reduced blood flow.
Children with glaucoma
Glaucoma is a condition that can affect newborns and children. It might be present from birth or evolve over time. Drainage obstructions or an underlying medical issue might cause optic nerve injury.
Glaucoma with pigmentation
Pigment granules from your iris build up in the drainage ducts of your eye in pigmentary glaucoma, delaying or stopping fluid exiting your eye. Jogging, for example, can mix up pigment granules, causing them to lodge on the trabecular meshwork and producing occasional pressure increases.
Risk Factors
Because chronic types of glaucoma can cause vision loss before any symptoms or indications appear, be aware of the following risk factors:
- Internal eye pressure that is too high (intraocular pressure)
- Being over 60 years old
- Being black, Asian, or Hispanic has its advantages and disadvantages.
- Having a glaucoma family history
- Diabetes, heart disease, high blood pressure, and sickle cell anaemia are examples of medical problems.
- Having corneas with a narrow central layer
- Being excessively nearsighted or farsighted is a condition that affects a person's vision.
- If you've had an eye injury or certain types of eye surgery, you're at a higher risk.
- Long-term use of corticosteroid medicines, particularly eyedrops
Disease Diagnosis:
Your doctor will go over your medical history with you and do a thorough eye check. He or she may conduct a variety of tests, including:
- Intraocular pressure measurement (tonometry)
- A dilated eye examination and imaging studies are used to check for optic nerve injury.
- Examining for regions of vision impairment (visual field test)
- The thickness of the cornea is measured (pachymetry)
- Taking a look at the drainage angle (gonioscopy)
Disease Treatment:
Glaucoma can't be reversed once it's started. Treatment and frequent examinations, on the other hand, can help decrease or prevent vision loss, especially if the condition is caught early.
Reduced eye pressure is used to treat glaucoma (intraocular pressure). Prescription eyedrops, oral drugs, laser therapy, surgery, or a combination of these may be available depending on your circumstances.
Prescription eyedrops are commonly used to treat glaucoma. These can help lower eye pressure by changing the way fluid drains from your eye or reducing the quantity of fluid produced by your eye.
Medications taken orally
If eyedrops alone aren't enough to lower your eye pressure, your doctor may prescribe an oral drug, such as a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Frequent urination, tingling in the fingers and toes, sadness, stomach distress, and kidney stones are all possible adverse effects.
Surgical procedures and other treatments
Laser therapy and different surgical procedures are two more therapeutic possibilities. The following treatments are designed to increase fluid outflow within the eye and thereby reduce pressure: Laser therapy is a type of treatment that involves the use of If you have open-angle glaucoma, laser trabeculoplasty may be a possibility. It's carried out at the doctor's office. A tiny laser beam is used by your doctor to unblock congested passages in the trabecular meshwork. It might take a few weeks for the full impact of this surgery to be felt.
Filtering surgery is a procedure that involves the removal of contaminants. A trabeculectomy is a surgical treatment that involves making a hole in the white of the eye (sclera) and removing part of the trabecular meshwork.
Tubes for draining. A tiny tube shunt is inserted into your eye by your eye surgeon to drain out excess fluid and relieve your eye pressure.
Glaucoma surgery that is minimally invasive (MIGS). To reduce your eye pressure, your doctor may recommend a MIGS surgery. These treatments are less risky and need less immediate postoperative care than trabeculectomy or the placement of a drainage device. They're frequently used in conjunction with cataract surgery. There are several MIGS treatments to choose from, and your doctor will explain which one is best for you.
You'll need to see your doctor for follow-up checks after your operation. Additionally, if your eye pressure continues to rise or other abnormalities in your eye occur, you may need to undergo additional operations.
Acute angle-closure glaucoma treatment
Glaucoma with acute angle closure is a medical emergency. If you've been diagnosed with this illness, you'll require immediate therapy to lower your eye pressure. This will usually necessitate the use of medicine as well as laser or other surgical techniques.
A laser peripheral iridotomy is a technique in which a doctor uses a laser to create a tiny hole in your iris. This permits fluid (aqueous humour) to pass through it, reducing strain on the eyes.
Country wise cost comparison for Glaucoma Treatment:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $540 |
| Iran | $1733 |
| Iran | $1733 |
Treatment and Cost
4
Total Days
In Country
- 1 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 3 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from