ZapX Brain Surgery cost in India
The cost of ZapX Brain Surgery for Brain Tumor (Level 1) in
India ranges from USD 7950 to USD 12000
ZapX brain surgery:
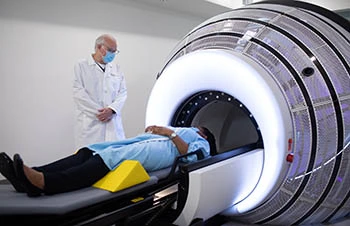
ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery: ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery or ZapX brain surgery is a state-of-the-art technique designed to accurately identify and manage brain tumors. ZAP-X employs a novel self-shielded, gyroscopic linear accelerator architecture in contrast to more traditional techniques. As a result, it may target tumors from every direction surrounding the head, increasing its effectiveness and precision.
ZAP-X has a high success rate and little long-term negative effects, making it a viable treatment for a variety of illnesses. Because of ZAP-X's accuracy, specific treatments for a range of brain-related disorders are available. ZAP-X aids in:
1. Benign Brain Tumors: Assists in the treatment of non-cancerous tumors such as meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, and vestibular schwannoma.
2. Metastatic Brain Tumors: Manages cancers that have metastasized from other body areas to the brain.
3. Blood Vessel Malformations: Corrects blood flow problems brought on by knotted vessels.
4- Relief from Severe Facial Pain (Trigeminal Neuralgia): This condition relieves severe facial pain brought on by nerve disorders.
5. Targeted Therapy for Aggressive Brain Tumors: Personalized care for certain recurrent aggressive brain tumor subtypes
Benefits of ZAP-X over Conventional Brain Surgery:
1. Enhanced Precision: Unlike more conventional techniques like craniotomy, which involve exposing the entire region, ZAP-X specifically targets the afflicted area.
2. Non-invasive Treatment: Unlike conventional surgical methods, which require opening the skull, ZAP-X applies highly targeted radiation straight to the lesion.
3. Reduce Treatment Time: ZAP-X treats patients in a single session that lasts no longer than 30 minutes, whereas typical brain procedures take three to four hours.
4. Daycare Convenience: Unlike typical operations that need 4–7 days or more of hospitalization and anesthesia, ZAP-X allows for a daycare procedure, letting patients to return home post-treatment.
Procedure Description:
ZapX brain surgery:
ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery: ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery or ZapX brain surgery is a state-of-the-art technique designed to accurately identify and manage brain tumors. ZAP-X employs a novel self-shielded, gyroscopic linear accelerator architecture in contrast to more traditional techniques. As a result, it may target tumors from every direction surrounding the head, increasing its effectiveness and precision.
ZAP-X has a high success rate and little long-term negative effects, making it a viable treatment for a variety of illnesses. Because of ZAP-X's accuracy, specific treatments for a range of brain-related disorders are available. ZAP-X aids in:
1. Benign Brain Tumors: Assists in the treatment of non-cancerous tumors such as meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, and vestibular schwannoma.
2. Metastatic Brain Tumors: Manages cancers that have metastasized from other body areas to the brain.
3. Blood Vessel Malformations: Corrects blood flow problems brought on by knotted vessels.
4- Relief from Severe Facial Pain (Trigeminal Neuralgia): This condition relieves severe facial pain brought on by nerve disorders.
5. Targeted Therapy for Aggressive Brain Tumors: Personalized care for certain recurrent aggressive brain tumor subtypes
Benefits of ZAP-X over Conventional Brain Surgery:
1. Enhanced Precision: Unlike more conventional techniques like craniotomy, which involve exposing the entire region, ZAP-X specifically targets the afflicted area.
2. Non-invasive Treatment: Unlike conventional surgical methods, which require opening the skull, ZAP-X applies highly targeted radiation straight to the lesion.
3. Reduce Treatment Time: ZAP-X treats patients in a single session that lasts no longer than 30 minutes, whereas typical brain procedures take three to four hours.
4. Daycare Convenience: Unlike typical operations that need 4–7 days or more of hospitalization and anesthesia, ZAP-X allows for a daycare procedure, letting patients to return home post-treatment.
Disease Overview:
Brain Tumour
A brain tumour is an abnormal cell growth in the brain's tissues. Brain tumours can be benign (no cancer cells) or malignant (fast-growing cancer cells). Some of them are primary brain tumours, meaning they begin in the brain. Others are metastatic, which means they begin elsewhere in the body and spread to the brain.
As new cells replace old or damaged ones, normal cells proliferate in a regulated manner. Tumor cells multiply uncontrolled for reasons that are unknown.
A primary brain tumour is a benign tumour that begins in the brain and seldom spreads to other regions of the body. Primary brain tumours can be either benign or cancerous.
A benign brain tumour develops slowly, has well-defined borders, and spreads only infrequently. Benign tumours can be life threatening if they are placed in a key region, despite the fact that their cells are not cancerous.
A malignant brain tumour spreads to neighbouring brain regions, develops swiftly, and has irregular borders. Malignant brain tumours, despite their common name, do not meet the criteria of cancer since they do not spread to organs outside of the brain and spine.
Metastatic (secondary) brain tumours start out as cancer in another part of the body and then spread to the brain. When cancer cells are transported through the bloodstream, they develop tumours. Lung and breast cancers are the most prevalent malignancies that spread to the brain.
A brain tumour, whether benign, malignant, or metastatic, can all be life-threatening. The brain can't expand to make place for a growing mass since it's encased in a bony skull. The tumour compresses and displaces normal brain tissue as a result.
Some brain tumours cause the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that circulates around and through the brain to become clogged. This obstruction raises intracranial pressure and can cause the ventricles to expand (hydrocephalus). Swelling is a symptom of certain brain tumours (edema). The "mass effect" is caused by the size, pressure, and swelling of the body, which causes many of the symptoms.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Tumors can cause damage to the brain by killing healthy tissue, squeezing healthy tissue, or raising intracranial pressure. The kind, size, and location of the tumour in the brain all influence the symptoms. Symptoms in general include:
- Seizures with headaches that seem to get worse in the morning
- stumbling, dizziness, and walking difficulties
- issues with speech (e.g., difficulty finding the right word)
- irregular eye movements, visual difficulties
- Increased intracranial pressure due to weakness on one side of the body produces sleepiness, headaches, nausea and vomiting, and slow reactions.
The following are examples of specific symptoms:
Behavioral and emotional problems; poor judgement, motivation, or inhibition; decreased sense of smell or visual loss; paralysis on one side of the body; lower mental ability and memory loss are all possible adverse effects of frontal lobe tumours.
Parietal lobe tumours can cause difficulty with speaking, writing, drawing, and naming, as well as lack of recognition, spatial impairments, and eye-hand coordination.
Vision loss in one or both eyes, visual field cuts, fuzzy vision, illusions, and hallucinations are all possible symptoms of occipital lobe tumours.
Temporal lobe tumours can cause issues with speaking and interpreting language, as well as short- and long-term memory.
aggressiveness on the rise
Behavioral and emotional problems, trouble speaking and eating, tiredness, hearing loss, muscular weakness on one side of the face (e.g., head tilt, crooked grin), uncoordinated walking, drooping eyelid or double vision, and vomiting are all symptoms of brainstem tumours.
Increased hormone secretion (Cushing's Disease, acromegaly), cessation of menstruation, irregular milk secretion, and diminished libido are all possible side effects of pituitary gland tumours.
Disease Causes:
hereditary illnesses, such as neurofibromatosis, extended exposure to pesticides, industrial solvents, and other toxins cancer elsewhere in the body
ZapX brain surgery
ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery: ZAP-X Gyroscopic Radiosurgery or ZapX brain surgery is a state-of-the-art technique designed to accurately identify and manage brain tumors. ZAP-X employs a novel self-shielded, gyroscopic linear accelerator architecture in contrast to more traditional techniques. As a result, it may target tumors from every direction surrounding the head, increasing its effectiveness and precision.
ZAP-X has a high success rate and little long-term negative effects, making it a viable treatment for a variety of illnesses. Because of ZAP-X's accuracy, specific treatments for a range of brain-related disorders are available.
Country wise cost comparison for ZapX Brain Surgery:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $8406 |
Treatment and Cost
4
Total Days
In Country
- 1 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 3 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from