The cost of Prostate Cancer - Surgical in India
ranges from USD 6200 to USD 12000
Prostate Cancer - Surgical
In cases where prostate cancer is assumed to have not migrated outside the prostate gland, surgery is a typical treatment option.
A radical prostatectomy is the most common surgical procedure for prostate cancer. The urologist performing the surgery removes the prostate gland in its entirety along with some surrounding tissue, including the seminal vesicles. Occasionally, adjacent lymph nodes are also resected.
A surgeon can perform a radical prostatectomy in two major ways:
1. During an open prostatectomy, the prostate and surrounding tissues are removed by the surgeon through a single, lengthy skin incision (cut).
2. The prostate and surrounding tissues are removed during a laparoscopic prostatectomy by the surgeon using a series of tiny incisions and the use of long, thin surgical instruments.
Procedure Description:
Prostate Cancer - Surgical
In cases where prostate cancer is assumed to have not migrated outside the prostate gland, surgery is a typical treatment option.
A radical prostatectomy is the most common surgical procedure for prostate cancer. The urologist performing the surgery removes the prostate gland in its entirety along with some surrounding tissue, including the seminal vesicles. Occasionally, adjacent lymph nodes are also resected.
A surgeon can perform a radical prostatectomy in two major ways:
1. During an open prostatectomy, the prostate and surrounding tissues are removed by the surgeon through a single, lengthy skin incision (cut).
2. The prostate and surrounding tissues are removed during a laparoscopic prostatectomy by the surgeon using a series of tiny incisions and the use of long, thin surgical instruments.
Disease Overview:
Prostate cancer:
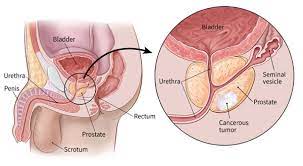
Cancer that develops in the prostate is known as prostate cancer. The seminal fluid, which feeds and carries sperm, is produced by the prostate, a little gland in men that resembles a walnut. One of the most prevalent forms of cancer is prostate cancer. A large number of prostate tumors are slow-growing and localized to the prostate gland, where they might not do much damage. On the other hand, aggressive forms of prostate cancer can spread swiftly, whilst slow-growing varieties may require little or no treatment at all.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
Many patients with colon cancer initially show no symptoms. Symptoms may probably vary depending on the location and extent of the cancer in the large intestine.
Colon cancer symptoms can include:
1. A shift in digestive patterns, such as increased frequency of diarrhea or constipation.
2. Bleeding in the rectum or blood in the stool.
3. Persistent abdominal pain, gas, or cramping.
4. The impression that a bowel movement doesn't completely empty the colon.
5. Exhaustion or weakness.
6. Losing weight effortlessly.
Disease Causes:
Prostate cancer's cause is unknown. Physicians are aware that DNA alterations in prostate cells are the first sign of prostate cancer. The instructions that inform a cell what to do are encoded in its DNA. The alterations instruct the cells to proliferate and divide more quickly than typical cells. When other cells would die, the aberrant cells would not perish. The aberrant cells build up into a tumor that can spread and infect surrounding tissue. Certain aberrant cells have the ability to split out and travel (metastasize) to different areas of the body over time.
The following are some factors that may raise your risk of prostate cancer:
1. Getting older: Prostate cancer risk rises with age. After age 50, it becomes more prevalent.
2. Race: Black people are more likely than people of other races to develop prostate cancer, although the exact cause of this higher risk is unknown. Prostate cancer is also more likely to be aggressive or progressed in Black individuals.
3- Family history: Your risk may be elevated if a parent, sibling, child, or other blood relative has been diagnosed with prostate cancer.
4- Obesity
Disease Diagnosis:
Tests for prostate cancer may include:
1- Digital rectal exam (DRE): In a DRE, your doctor examines your prostate, which is located next to the rectum, by putting a gloved, lubricated finger inside it. You could require more testing if your doctor discovers any anomalies in the gland's size, shape, or texture.
2- PSA test, or prostate-specific antigen test. Your arm vein is used to extract a blood sample, which is then tested for PSA, a hormone that your prostate gland naturally produces. It's typical for your blood to contain trace amounts of PSA. On the other hand, if a greater than normal level is discovered, it might be a sign of cancer, inflammation, enlargement, or prostate infection.
In the event that a prostate cancer screening identifies an anomaly, your physician might suggest additional testing to ascertain the presence of prostate cancer, including:
1. Ultrasound: A tiny probe the size and shape of a cigar is put into your rectum during a transrectal ultrasound. The probe takes an image of your prostate gland using sound waves.
2. Prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): an MRI scan to produce a more comprehensive image. Your doctor may use MRI pictures to plan the removal of prostate tissue samples.
3. Gathering a sample of prostate tissue: A tiny needle is commonly placed into the prostate during a prostate biopsy procedure in order to gather tissue. In a laboratory, the tissue sample is examined to ascertain whether cancer cells are present.
Disease Treatment:
Your options for treating prostate cancer will vary depending on a number of circumstances, including how quickly the cancer is progressing, if it has spread, how well you are overall, and any possible advantages or disadvantages of the treatment.
Treatment for low-grade prostate cancer might not be necessary immediately away. Some people may never require medical attention.
Regular follow-up blood tests, rectal exams, and prostate biopsies may be carried out as part of active surveillance to track the advancement of your cancer. You may choose to get radiation therapy or surgery for prostate cancer if testing reveal that the disease is spreading.
Prostate excision surgery:
In cases where prostate cancer is assumed to have not migrated outside the prostate gland, surgery is a typical treatment option.
A radical prostatectomy is the most common surgical procedure for prostate cancer. The urologist performing the surgery removes the prostate gland in its entirety along with some surrounding tissue, including the seminal vesicles. Occasionally, adjacent lymph nodes are also resected.
A surgeon can perform a radical prostatectomy in two major ways:
1. During an open prostatectomy, the prostate and surrounding tissues are removed by the surgeon through a single, lengthy skin incision (cut).
2. The prostate and surrounding tissues are removed during a laparoscopic prostatectomy by the surgeon using a series of tiny incisions and the use of long, thin surgical instruments.
Country wise cost comparison for Prostate Cancer Treatment:
| Country |
Cost |
| India |
$6480 |
| Thailand |
$15656 |
| United Arab Emirates |
$14570 |
| Iran |
$2842 |
| Singapore |
$28345 |
| Canada |
$22056 |