DJ Stent Removal Unilateral Without Anesthesia
India
-
Our Price USD 675
-
Hospital Price USD 750
-
You Save : USD 75
Booking Amount: USD 68. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
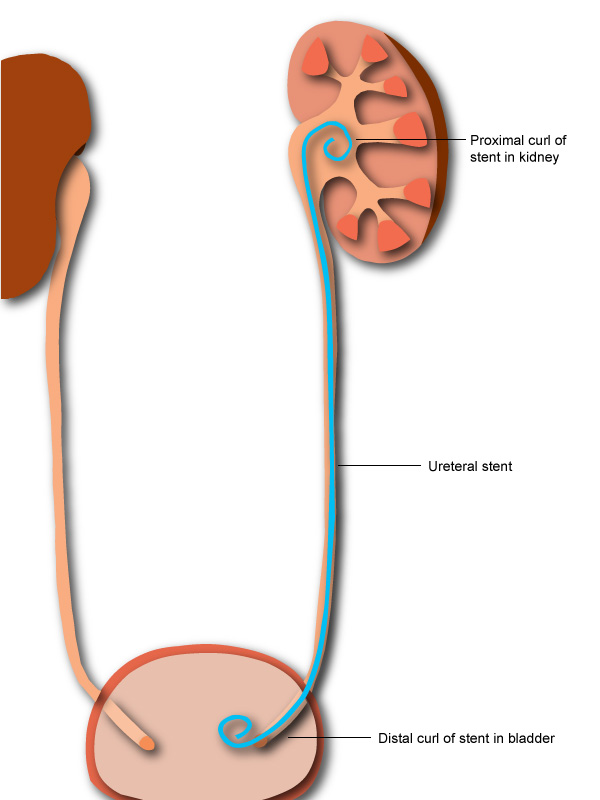
DJ Stent Removal Unilateral Without Anesthesia:
Cystoscopy and DJ stent removal is the procedure used to remove the DJ stent. The patient is made to lay down on a table, and a local anaesthetic Jelly is injected into the urinary canal, following which a scope is introduced, and the DJ stent is visualised and retrieved using endoscopic forceps.
Double-J (DJ) stents are one of the most basic and often used urological instruments. To minimise issues such as encrustations, stone formation, fractures, and stent blockades, the DJ stent should be changed or removed between 6 weeks to 6 months.
Disease Overview:
Urinary obstruction
A ureteral obstruction occurs when one or both of the tubes that convey urine from the kidneys to the bladder become blocked. Ureteral blockage is treatable. If not addressed, however, symptoms can swiftly progress from moderate — pain, fever, and infection — to severe — renal failure, sepsis, and death.
Obstruction of the urethra is rather frequent. Severe consequences are uncommon since it is curable.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
There may be no indications or symptoms of ureteral blockage. The location of the blockage, whether partial or total, the speed with which it develops, and whether it affects one or both kidneys all influence the signs and symptoms.
The following are possible signs and symptoms:
- Pain
- Changes in the amount of urine you excrete (urine output)
- Urination problems
- Urine with blood
- Infections of the urinary tract
- Blood pressure that is too high (hypertension)
Disease Causes:
There are a variety of reasons for ureteral blockage, some of which are present at birth (congenital). They are as follows:
A second ureter (duplicated). This congenital abnormality results in the formation of two ureters on the same kidney. The development of the second ureter might be complete or incomplete. Urine can back up into the kidney and cause harm if either ureter isn't working properly.
Where the ureter attaches to the kidney or bladder, there is a blockage (obstruction). Urine flow is stifled as a result of this. The ureter-kidney connection (ureteropelvic junction) can become blocked, causing the kidney to enlarge and finally stop operating. This disorder can be congenital or develop as a result of normal childhood growth, an accident or scarring, or, in rare circumstances, a malignancy.
Urine may back up into the kidneys if the ureter and bladder meet in a blockage (ureterovesical junction).
Ureterocele. A little bulge in the ureter (ureterocele) can form if a ureter is too thin and doesn't enable urine to pass fully. The part of the ureter closest to the bladder is generally where a ureterocele develops. This can obstruct urine flow and cause urine to back up into the kidney, potentially causing damage to the kidneys.
Fibrosis of the retroperitoneum. Fibrous tissue develops in the region below the abdomen, causing this unusual illness. The fibres may proliferate as a result of cancer tumours or the use of certain migraine medications. Because the fibres wrap and clog the ureters, urine backs up into the bladder.
Other factors to consider
Ureteral blockage can result from a variety of internal (intrinsic) or external (extrinsic) reasons, including:
- Stones in the kidneys
- Tumors, both malignant and non-cancerous
- Clots in the blood
- Lymph nodes that have grown in size
- Endometriosis in women is an example of internal tissue proliferation.
- Long-term enlargement of the ureter wall, commonly caused by TB or schistosomiasis, a parasitic illness.
Disease Diagnosis:
During standard prenatal ultrasounds, which may show aspects of the growing foetus, including the kidneys, ureters, and bladder, doctors frequently detect ureteral obstruction issues before birth. After birth, providers frequently do another ultrasound to review the kidneys.
If your doctor believes you have a blocked ureter, he or she may order any of the following tests and scans to confirm the diagnosis:
Tests of the blood and urine. Your doctor looks for symptoms of infection and the presence of creatinine in your blood and urine, which indicates that your kidneys aren't performing correctly.
Ultrasound. Your physician can see your kidneys and ureters with a retroperitoneal ultrasound, which is an ultrasound of the area behind your abdominal organs.
Catheterization of the bladder. Your provider inserts a tiny tube (catheter) into the urethra, injects dye into your bladder, and takes X-rays of your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra before and during urination to check for incomplete or obstructed urine flow.
Nuclear scan of the kidneys. A tracer containing a small amount of radioactive material is injected into your arm by your physician or a technician. The radioactivity is detected by a particular camera, which creates photos that your doctor may use to assess your urinary system.
Cystoscopy. In your urethra or through a minor incision, a little tube containing a camera and light is placed. The provider can look within the urethra and bladder thanks to the optical device.
A CT scan creates cross-sectional pictures of your kidneys, ureter, and bladder by combining a series of X-ray scans taken from various angles with computer processing.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of imaging that (MRI). An abdomen MRI creates comprehensive pictures of the organs and tissues that make up your urinary system using a magnetic field and radio waves.
Disease Treatment:
The purpose of ureteral obstruction therapy is to either remove or bypass obstructions, which may aid in the healing of kidney damage. Antibiotics may be used to treat any related infections.
Procedures for Drainage
If you have a ureteral obstruction that is causing you extreme discomfort, you may need an emergency operation to remove urine from your body and temporarily ease the symptoms of the blockage. Your urologist may advise you to:
- A ureteral stent is a hollow tube that is put into the ureter in order to keep it open.
- Percutaneous nephrostomy is a procedure in which a catheter is inserted into your back and used to drain the kidney directly (percutaneous nephrostomy).
- A catheter is a tube that connects the bladder to an external drainage bag through the urethra. This is especially critical if you have bladder issues that are causing your kidneys to drain poorly.
Your doctor will be able to advise you on the best procedure or combination of treatments for you. Depending on your situation, drainage methods may give temporary or permanent relief.
Surgical operations
Ureteral blockages can be treated using a variety of surgical methods. The sort of surgery you need is determined by your circumstances.
One of the following surgical procedures can be used to treat ureteral obstruction:
Endoscopic surgery is a type of surgery that involves the use of A lighted scope is sent through the urethra into the bladder and other areas of the urinary system in this minimally invasive treatment.
A incision is made into the damaged or obstructed region of the ureter to enlarge it, and then a hollow tube (stent) is placed in the ureter to keep it open. This method can be used to diagnose as well as treat a problem.
Open surgery is a type of surgery in which the patient is To remove the obstruction and repair your ureter, the surgeon makes an incision in your belly.
Laparoscopic surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery. In this surgery, the surgeon makes one or more small incisions in your skin to introduce a small tube containing a light, a camera, and other devices. Laparoscopic surgery with the help of a robot. A robotic system is used by the surgeon to execute a laparoscopic surgery.
The number and amount of incisions utilised for the treatment, as well as your recuperation period following surgery, are the key distinctions between various surgical techniques. The type of operation and the best surgical technique to treat your disease are determined by your doctor (urologist).
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
1 Days
Days in Hotel
*
2 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. Sanjay Gogoi
Urologist- Renal Transplant, Congenital Disorders Evaluation / Treatment, Fitsula treatment, Urogynaecology, Transurethral resection prostate surgery (TURP), Robotic urological surgery
Max Super Speciality Hospital, Dwarka New Delhi, India
24 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Aditya Pradhan
Urologist- Renal Transplant, Kidney Stone Treatment, Prostate Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Renal Transplant, Laparoscopic Urologicsl Surgery, Prostate Cancer
BLK-Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
29 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Sureshkumar Bhagat
Urologist- Circumcision, Ureteroscopy, Minimally invasive surgery, Blood in Urine, Reconstructive Urology
Fortis Healthcare Ltd., Mulund Mumbai, India
20 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Pankaj Maheshwari
Urologist- Lithotripsy, Kidney Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Lithotripsy, Kidney Cancer, Urinary tract infections, Prostate Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Kidney Cancer, Endourology Andrology, Bladder Cancer, Prostate Cancer, LASER surgery
Fortis Healthcare Ltd., Mulund Mumbai, India
33 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. P P Singh
Urologist- Urologic oncologist, Kidney Transplant, Kidney Transplant, Kidney Transplant, UTI Treatment, Uro Oncology, Uro Oncology, Redo Surgery in Urology, Laparoscopic Urologicsl Surgery, Uro Oncology, Redo Surgery in Urology
PSRI Hospital New Delhi, India
32 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Shilpi Tiwari
Urologist- Microsurgery, Infertility Specialist, Infertility Specialist, Andrology, Urologic Oncology, Endourology, Andrology, Endourology
Vimhans Nayati Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
16 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Amit K Devra
Urologist- Kidney Transplant, Pediatric Urology Surgeon, Pediatric Urology Surgeon, Kidney Transplant, Kidney Transplant, Endourology, Endourology, Female Urology, Minimal access urological surgery, Endoscopic/laser prostate surgeries
Jaypee Hospital Noida, India
24 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Shalabh Agrawal
Urologist- Gallbladder Stone, Kidney Stone Specialist, Prostate Cancer, Urinary tract infections, Urinary Incontinence (Ui), Urogynaecology, Prostate Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Urological Cancers, Prostate disease, Prostate Cancer, Minimally invasive and laser treatment of kidney stones, Endoscopic/laser prostate surgeries, Microsurgical urological procedures, Urogynaecology, Fistulas, Reconstructive paediatric, Penile implants
CK Birla Hospital, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
20 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Suresh Rawat
Urologist- Uro Oncology, Uro Oncology, Uro Oncology, Pediatric Urology, Female Urology, Endourology Andrology, Reconstructive Urology
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
40 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Narasimhan Subramanian
Urologist- Urologic oncologist, Robotic Surgeon, Robotic Surgeon, Kidney Transplant, Robotic Surgeon, Varicocele Surgery, Kidney Transplant, Kidney Transplant, Male Infertility, Endourology, Endourology, Prostate disease, Urogynae, Laparoscopic nephrectomy, Laparoscopic prostatectomy, Cryosurgery, Radiofrequency ablation of Kidney, Robotic assisted radical laparoscopic prostatectomy, Hydrocele Testis treatment, Laser Prostate Surgery, Transurethral Resection of the Prostate
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
38 Years of Experience