Additional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
VP Shunt
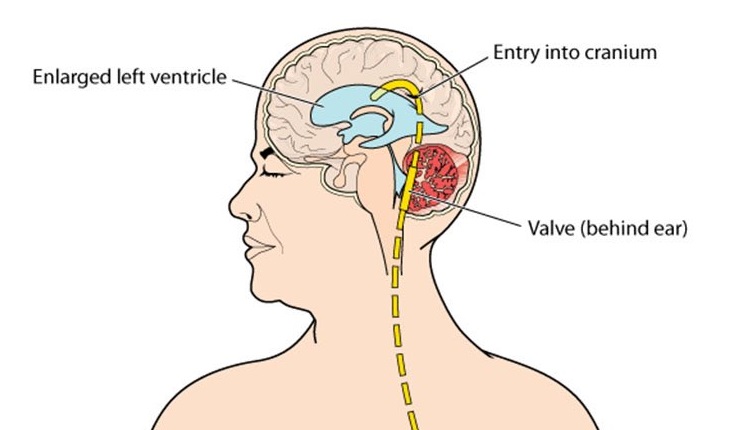
Ventriculoperitoneal shunting is a procedure that removes excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain's cavities (ventricles) (hydrocephalus). This operation is performed under general anaesthesia in the operating room. To drain excess cerebrospinal fluid, a tube (catheter) is delivered from the cavities of the head to the abdomen (CSF).
Disease Overview:
Hydrocephalus
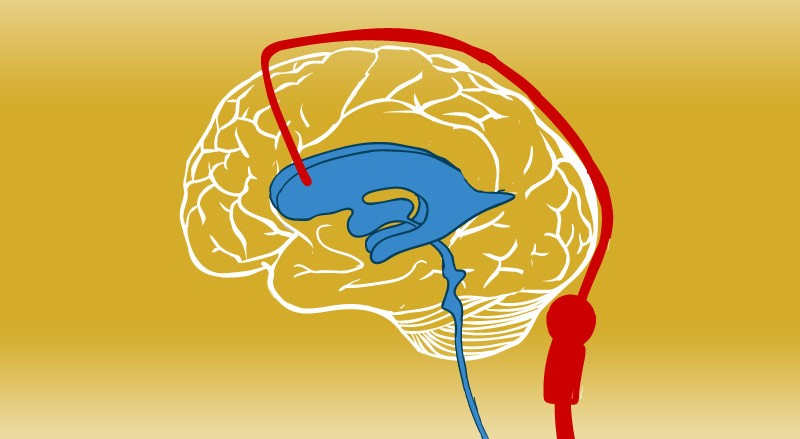
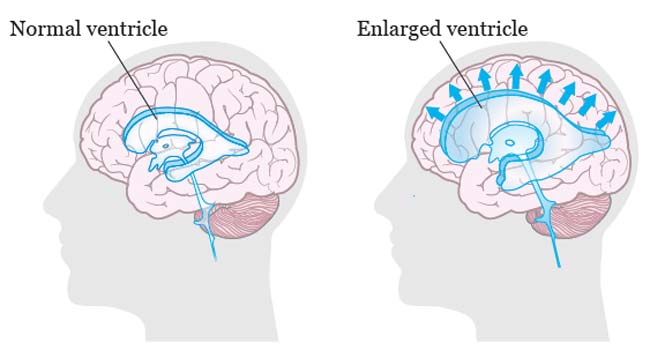
The collection of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain is known as hydrocephalus. The extra fluid expands the ventricles, which exerts pressure on the brain.
The brain and spinal column are generally bathed in cerebrospinal fluid, which circulates via the ventricles. However, excessive cerebrospinal fluid pressure, which is linked with hydrocephalus, can damage brain tissues and cause a variety of brain function disorders.
Hydrocephalus may strike anybody at any age, however it is more common in newborns and individuals aged 60 and up. Hydrocephalus can be treated surgically to restore and maintain normal cerebrospinal fluid levels in the brain. Managing symptoms or issues caused by hydrocephalus frequently necessitates a variety of treatments.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
The signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus differ depending on the age at which it first appears.
Infants
In babies, common indications and symptoms of hydrocephalus include:
- Alterations in the brain
- A bulging or tight soft patch (fontanel) on the top of the skull An exceptionally enormous head A fast growth in the size of the head
Symptoms and physical indicators
- Vomiting and nausea
- Sluggishness or sleepiness (lethargy)
- Irritability
- Unhealthy eating habits
- Seizures
- Downward-looking eyes (sunsetting of the eyes)
- Muscle tone and strength problems
Children of all ages, including toddlers and older children
Signs and symptoms in toddlers and older children may include:
Symptoms and physical indicators
- Headache
- Double eyesight or hazy vision
- Eye motions that are abnormal
- Sleepiness or sluggishness Sleepiness or sluggishness in a toddler
- Vomiting or nausea
- Unstable equilibrium
- Coordination issues
- Appetite problems
- Bladder control problems or frequent urination
- Changes in behaviour and cognition
- Irritability
- Personality shifts
- School performance is deteriorating.
- Delays or difficulties with previously learned tasks like walking or talking
Adults in their twenties and thirties
The following are common indications and symptoms in this age group:
- Headache
- Sluggishness
- Coordination or balance problems
- Urinary incontinence or a frequent need to urinate
- Problems with vision
- Memory, focus, and other cognitive abilities decline, which may have an impact on work performance.
Adults in their latter years
The following are the most prevalent indications and symptoms of hydrocephalus in individuals aged 60 and up:
- Urinary incontinence or a frequent need to urinate
- Loss of memory
- Other thinking or reasoning skills are gradually deteriorating.
- Difficulty walking, which is typically characterised as a shuffling stride or a stuck feeling in the feet.
- Coordination or balance issues
Disease Causes:
An imbalance between the amount of cerebrospinal fluid generated and the amount absorbed into the circulation causes hydrocephalus.
Cerebrospinal fluid is generated by the tissues that line the brain's ventricles. It travels through interconnected channels in the ventricles. The fluid ultimately finds its way into regions around the brain and spine. Blood arteries in tissues on the surface of the brain absorb the majority of it.
Cerebrospinal fluid is vital for brain function because it:
- Allowing the comparatively hefty brain to float within the skull by keeping it buoyant.
- To protect the brain from harm, it is cushioned.
- Getting rid of waste materials produced by the brain's metabolism
- Flowing back and forth between the brain cavity and the spinal column to maintain a constant pressure within the brain — compensating for fluctuations in brain blood pressure.
One of the following causes too much cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles:
Obstruction. A partial obstruction of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, either from one ventricle to another or from the ventricles to other regions around the brain, is the most prevalent condition.
Absorption is poor. A issue in absorbing cerebrospinal fluid is less prevalent. This is frequently linked to inflammation of brain structures as a result of illness or injury.
Overproduction. Cerebrospinal fluid is occasionally produced faster than it can be absorbed.
Disease Diagnosis:
The following factors are commonly used to make a diagnosis of hydrocephalus:
- Your responses to the doctor's signs and symptoms questions
- A complete physical examination
- An examination of the nervous system
- Tests of the brain
- Examination of the nervous system
The sort of neurological exam a person receives is determined on their age. In the office, the neurologist may ask questions and do basic tests to assess muscle condition, mobility, well-being, and the functioning of the senses.
Imaging of the brain
The following imaging studies can aid in the diagnosis of hydrocephalus and the identification of the underlying causes of the symptoms:
Ultrasound. Because it is a reasonably easy and low-risk technique, this test is frequently used for an initial screening of neonates. The ultrasound equipment is positioned over a soft region on the top of a baby's head called the fontanel.
During standard prenatal checkups, ultrasound may diagnose hydrocephalus before delivery.
MRI. This technique creates comprehensive pictures of the brain using radio waves and a magnetic field. Although this test is harmless, it is loud and demands that you lie motionless.
Excess cerebrospinal fluid can create enlarged ventricles, which can be seen on MRI images. They can also be utilised to figure out what's causing the hydrocephalus or what's causing the symptoms.
Some MRI scans may need minor anaesthesia in children. Some facilities, on the other hand, employ a quick variant of MRI that doesn't require sedation.
CT scan is a type of x-ray. Cross-sectional pictures of the brain are obtained using this specialist X-ray technique. Scanning is rapid and painless. However, because this test necessitates laying motionless, a youngster is frequently given a light sedative.
CT scanning gives less detailed pictures than MRI and involves a tiny level of radiation exposure. CT scans for hydrocephalus are typically reserved for urgent situations.
Disease Treatment:
Hydrocephalus can be treated with one of two surgical procedures.
Shunt
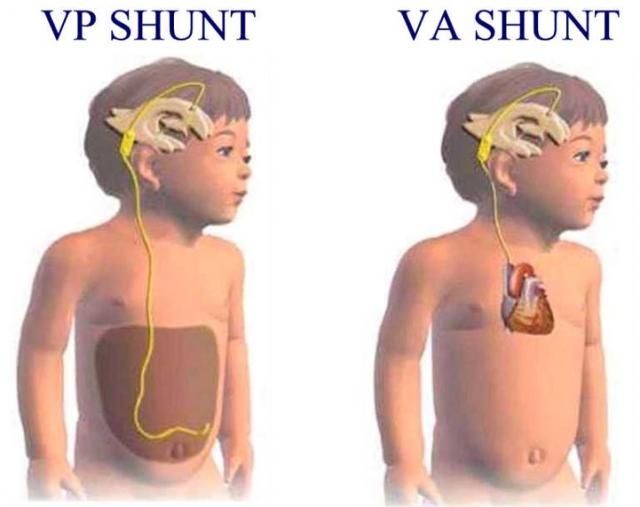
The surgical implantation of a drainage system, known as a shunt, is the most frequent therapy for hydrocephalus. It's made up of a long, flexible tube with a valve that maintains brain fluid flowing in the appropriate direction and at the right pace.
The tube is normally inserted into one of the brain's ventricles on one end. The tube is then tunnelled through the skin to a different portion of the body, such as the belly or a heart chamber, where the extra fluid may be absorbed more easily.
Hydrocephalus patients typically require a shunt system for the remainder of their lives. They must be monitored on a regular basis.
Third ventriculostomy (endoscopic)
For certain patients, endoscopic third ventriculostomy is a surgical technique that can be used. The surgeon examines the interior of the brain using a tiny video camera. To let cerebrospinal fluid to drain out of the brain, your surgeon cuts a hole in the bottom of one of the ventricles or between the ventricles.
Surgical complications
Both surgical treatments have the potential to cause problems. Because of mechanical issues, blockages, or infections, shunt systems can stop draining cerebrospinal fluid or regulate drainage poorly. Ventriculostomy complications include bleeding and infections.
Any failure needs immediate treatment, surgical modifications, or other measures. A fever or return of the previous hydrocephalus symptoms should necessitate a visit to your doctor.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
5 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. P. N. Renjen
Neurologist- Stroke (Thrombolytic Therapy), Botox Therapy for Post Stroke Spasticity, Surgical Epilepsy, DBS (Deep Brain Stimulation) and Headache, Celebrovasculkar Surgey
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
36 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Rahul Gupta
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Endovascular Neurosurgeon, microscopic surgery, Meningiomas, Craniopharyngioma, Brain Tumor Surgery, Cranio Vertebral anomalies, Intraventricular Tumour Surgery, Skull Base Anterior Surgery, Pituitary Adenoma including endonasal, Endoscopic Acoustic Schwanomas, CSF rhinorrhia, Cerebrovascular Neurosurgery
Fortis Hospital Noida Noida, India
27 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Prof. (Col.) Dr. Bipin Walia
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Brain Tumour Surgery, Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery, Kyphoplasty, Brain suite, Laminectomy, Traumatic brain injury (tbi) treatment, Cervical Disc Replacement
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
26 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Tarun Sharma
Neuro surgeon,Spine Surgeon- Peripheral nerve, Pediatric neurosurgery, Epileptic Surgery, Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy, Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) of the brain and spinal cord, Foot Drop, Foot Drop Spinal Surgery, Petrosal Sinus Sampling
Metro Hospital (Heart Institute with Multispeciality) Faridabad, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Praveen Gupta
Neurologist- Stroke Intervention, Stroke Rehabilitation, Celebral Palsy, Advanced Second line management for multiple scleoris, Epileptic Surgery, DBS Surgery
Fortis Memorial Research Institute Gurgaon, India
18 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Ravi Bhatia
Neuro surgeon- Neuro Oncology, Craniovertebral Junction (CVJ) Anomalies, Brain and Spine Tumors, Celebrovasculkar Surgey
Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi New Delhi, India
60 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Shamsher Dwivedee
Neurologist- Alzheimer Specialist, Epilepsy Disorder, Stroke Specialist, Headache Specialist, Sleep Disorder, Parkinson's Disease, Dementias, Neuromuscular Disorders
Vimhans Nayati Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
33 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Asha Kishore
Neurologist- Ankle surgery, Knee Replacement, Hip resurfacing with computer navigation, Anthroscopic Meniscus Surgery, ACL Reconstruction Procedure
Aster Medcity, Kochi Cochin, India
31 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. L. N. Tripathy
Neuro surgeon- Traumatic Brain Injury, Spinal Cord Injury, Microsurgery, Aneurysm Specialist, Functional Neurosurgery, Spinal Fusion, Degenerative Spine Disorder
Medica Superspeciality Hospitals, Kolkata Kolkata, India
35 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Harshil Shah
Neuro surgeon- Spine Surgery, Traumatic Brain Injury, Traumatic Brain Injury, Skull Base Surgery, Spine Surgery, Managing trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia, Spine Surgery, Brain Surgery and Brain Aneursym Surgery, Spinal instrumentation, Endoscopic Neurosurgery, Pituitary Surgery, Spine Surgery, Spine Surgery, Spine Surgery
Shalby Multi-Specialty Hospitals, Ahmedabad Ahmedabad, India
16 Years of Experience
Similar Packages
Frequently Asked Questions
India's VP Shunt package costs vary depending on what's included and what isn't. The best hospitals for VP Shunt provide a complete package that includes all costs associated with the patient's care and investigations from beginning to end. In India, the VP Shunt package covers hospitalization, anesthesia, and surgery expenses. Exiting the package early, post-operative problems, and the discovery of a new ailment could all drive up the cost of a VP Shunt in India.
The cost of VP Shunt in India starts from USD$ 3550. VP Shunt in India is available across many hospitals in different states.
In India, there are numerous top hospitals for VP Shunt procedures. The following are a few of the most well-known hospitals in India for VP Shunt: Fortis Hospital Manipal Hospital, Gurugram BLK-Max Super Speciality Hospital Indraprastha Apollo Hospital Fortis Hospital, Shalimar Bagh Dharamshila Narayana Super specialty Hospital
In addition to the expense of the VP Shunt, the patient must also cover the cost of daily meals and lodging at a guest home. These fees can change, with a starting point of $25 USD per person.
Following are a few well-known Indian cities that provide VP Shunt: Bengaluru's New Delhi Gurugram
The usual length of stay in the hospital following the VP Shunt procedure is four days. During this time, the patient's recuperation is evaluated by the medical team by imaging scans and blood tests. The patient is released as soon as they believe everything is proceeding as planned.