Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) cost in India
The cost of Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) in
India ranges from USD 2500 to USD 6000
Procedure Description:
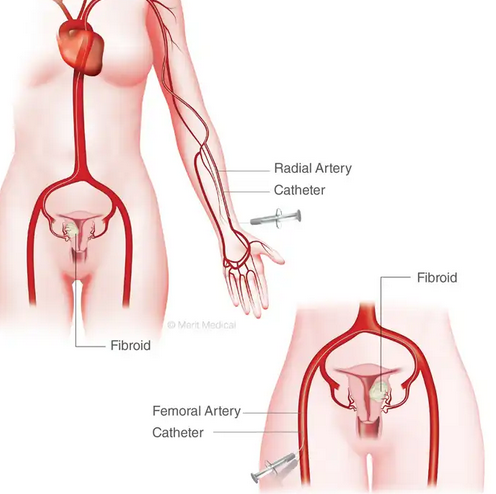
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
By stopping the blood flow to fibroids, uterine fibroid embolization causes them to shrink. The medical professional inserts little particles, resembling tiny grains of sand, into the arteries that supply the fibroids. The particles adhere to the wall of the vessel. This results in the formation of a clot that cuts off the blood supply.
Disease Overview:
Fibroids
Muscular tumors called fibroids develop in the uterine wall. "Myoma" or leiomyoma is another medical word for fibroids. Almost always, fibroids are benign—that is, not malignant. In the uterus, fibroids can develop as many tumors or as a single mass.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
The following are the most typical signs of uterine fibroids:
1- Heavy menstrual blood or unpleasant periods.
2. Extended or more regular intervals.
3. Pain or pressure in the pelvis.
4. Trouble peeing or frequent urination.
5. Expanding the stomach region.
6. Constipation.
7. Pain in the lower back or stomach, or pain during intercourse.
Disease Causes:
It's unclear what specifically causes uterine fibroids. However these elements might be relevant:
1. Genes alter. Gene alterations found in many fibroids are distinct from those found in normal uterine muscle cells.
hormones. The lining of the uterus thickens with each menstrual cycle due to the actions of two hormones, progesterone and estrogen, which help the body get ready for pregnancy. Fibroid growth appears to be aided by these hormones too.
1. Compared to normal uterine muscle cells, fibroids contain a greater number of cells that bind to estrogen and progesterone. Hormone levels decline following menopause, which causes fibroids to shrink.
2. Additional elements for growth. Fibroid growth may be influenced by substances like insulin-like growth factor that support tissue maintenance in the body.
3. Matrix extracellular (ECM). This substance causes cells to adhere to one another like mortar does to bricks. Fibroids are made fibrous by an increase in ECM. Moreover, ECM stores growth substances and modifies the biology of the cells.
According to medical professionals, uterine fibroids could arise from a stem cell found in the uterus's smooth muscle tissue. A single cell repeatedly divides. It eventually becomes a hard, rubbery mass that separates from the surrounding tissue.
Disease Diagnosis:
To assist in the diagnosis of fibroids, two types of ultrasound scans are available:
1. An ultrasound scan of the abdomen, in which the ultrasonography probe is passed across the exterior of the abdomen
2. A transvaginal ultrasound scan, in which your vagina is probed with a tiny ultrasound device.
experiments in the lab. Blood testing may be necessary if you experience irregular menstrual flow in order to determine the likely cause. A complete blood count to screen for anemia from continued blood loss may be one of them. Thyroid issues and bleeding disorders can be checked for with additional blood testing.
You could require additional imaging tests if an ultrasound is insufficient in providing information, such as:
1. MRIs, or magnetic resonance imaging. The location and size of fibroids can be seen in more detail using this test.
2. Ultrasonography. Saline, or sterile salt water, is used in hysterosonography (his-tur-o-suh-NOG-ruh-fee) to enlarge the uterine cavity, the space inside the uterus. This facilitates the process of obtaining images of the uterine lining and submucosal fibroids.
3. Hysterosalpingography: this technique highlights the fallopian tubes and uterus on X-ray pictures by using a dye. If there is a chance of infertility, your doctor might advise it.
4. The hysteroscopy. In order to perform this examination, your doctor will pass a tiny, illuminated telescope into your uterus through your cervix called a hysteroscope.
Disease Treatment:
The optimal course of action for uterine fibroids is not clear-cut. There are numerous options for treatment. Consult your care provider about strategies to relieve any symptoms you may be experiencing.
Numerous individuals with uterine fibroids are asymptomatic. Alternatively, their symptoms are tolerable and only somewhat bothersome. In that scenario, your best course of action might be to wait with caution.
Cancer isn't what fibroids are. Seldom do they cause problems for expectant mothers. They frequently grow slowly, if at all, and then they usually get smaller after menopause, when the quantities of reproductive hormones decrease.
An noninvasive treatment does not require incisions, which are surgical cuts. Furthermore, there is no insertion of tools into the body. The process known as MRI-guided focused ultrasound surgery (FUS) for uterine fibroids is:
- A non-invasive method of treatment that keeps the uterus intact. Because it's done as an outpatient procedure, you won't need to stay overnight at the hospital.
These operations include either tiny or no cuts. Compared to open surgery, they are associated with shorter recovery times and fewer problems. Treatments for uterine fibroids that are minimally invasive include:
1. Embolism of the uterine artery. The arteries that feed blood to the uterus are injected with tiny particles known as embolic agents. Fibroids are starved of blood by the particles, which makes them shrink and eventually die.
2. Ablation using radiofrequency. During this process, the blood vessels that supply the uterine fibroids shrivel and are destroyed by the heat generated by radiofrequency energy. This can be accomplished by making tiny incisions in the stomach region, a form of surgery.
3. Myomectomy, either robotic or laparoscopic. Your surgeon removes the fibroids and leaves the uterus in place during a myomectomy.
A laparoscopic operation may be the choice between you and your physician if there are few fibroids. This involves removing the fibroids from the uterus using tiny devices inserted through tiny abdominal incisions.
4. Hysteroscopic removal of myoma. If the fibroids—also known as submucosal fibroids—are inside the uterus, this treatment can be an option. Tools that are inserted into the uterus through the cervix and vagina are used to remove the fibroids.
5. Ablation of the uterus. The heavy menstrual flow may be lessened using this technique. An electric current, heat, microwave energy, hot water, or cold temperature can all be produced by a device that is placed inside the uterus.
Traditional open operations involving a larger incision can be performed as follows:
1. Myomectomy of the abdomen. By making a bigger incision in the abdomen, which is the region of the stomach, fibroids are removed during this sort of surgery. If you have several fibroids, really large fibroids, or very deep fibroids, your doctor might advise it.
2. Hysterectomy. By this surgery, the uterus is removed. It's still the only long-term, clinically supported treatment for uterine fibroids. A hysterectomy prevents you from becoming a parent. In addition, menopause is triggered by the removal of your ovaries during the surgical procedure.
3. Myomectomy, laparoscopic or robotic. During a myomectomy, your surgeon eliminates the fibroids while leaving the uterus in situ.
If there are few fibroids, your doctor and you may decide on a laparoscopic procedure. This entails making tiny abdominal incisions to introduce tiny devices that remove the fibroids from the uterus.
4. Myoma excision by hysteroscopic means. This treatment may be an option if the fibroids, often referred to as submucosal fibroids, are located inside the uterus. The fibroids are removed using instruments that are introduced into the uterus through the vagina and cervix.
5. The uterus is abated. By adopting this strategy, the heavy menstrual flow may be decreased. A device inserted into the uterus has the ability to produce electric current, heat, microwave energy, hot water, or cold temperature.
Country wise cost comparison for Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE):
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $2970 |
| Turkey | $6186 |
Treatment and Cost
8
Total Days
In Country
- 1 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 7 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$3300
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Turkey
- Kolan International Hospital, Sisli
- Istinye University Bahcesehir Liv Hospital
- Istinye University Medical Park Gaziosmanpasa Hospital
- I.A.U VM Medical Park Florya Hospital
- Altinbas University Medical Park Bahcelievler Hospital
- Medical Park Antalya Hospital
- Medical Park Tarsus Hospital, Mersin
- Saudi Arabia