Osteotomy cost in India
The cost of Osteotomy in India ranges from USD 12500 to USD 20000
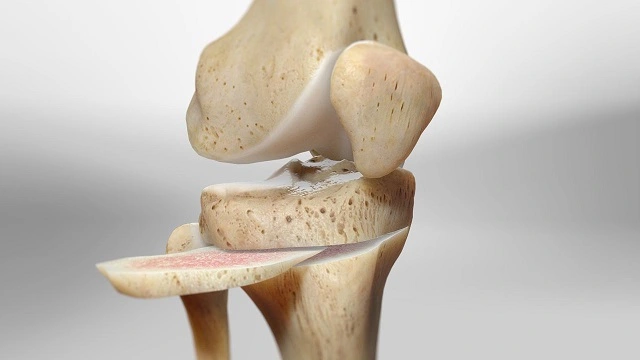
Osteotomy:
An osteotomy is a surgical technique used to straighten or reshape your bones. It involves cutting bone and occasionally inserting bone tissue. Any bone in your body, including the jaw, elbow, spine, shoulder, hips, knees, legs, toes, and feet, can have an osteotomy performed by your surgeon. It is a treatment for issues at the joints, which are the points where two bones unite.
Osteotomy procedures come in a variety of forms and modifications. They are frequently called after the surgeon who invented the technique or after the way the bone is sliced, reshaped, or altered.
Procedure Description:
Osteotomy:
An osteotomy is a surgical technique used to straighten or reshape your bones. It involves cutting bone and occasionally inserting bone tissue. Any bone in your body, including the jaw, elbow, spine, shoulder, hips, knees, legs, toes, and feet, can have an osteotomy performed by your surgeon. It is a treatment for issues at the joints, which are the points where two bones unite.
Osteotomy procedures come in a variety of forms and modifications. They are frequently called after the surgeon who invented the technique or after the way the bone is sliced, reshaped, or altered.
Disease Overview:
Osteoarthritis
The most prevalent kind of arthritis, osteoarthritis, affects millions of individuals throughout the world. When the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones breaks away over time, it causes this condition.
Although osteoarthritis may affect any joint, it is most typically seen in the hands, knees, hips, and spine.
Although the damage to joints cannot be undone, the symptoms of osteoarthritis may typically be treated. Staying active, eating a nutritious diet, and receiving some treatments may help reduce disease development and improve pain and joint function.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
Osteoarthritis symptoms often appear gradually and worsen with time. The following are some of the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis:
1- Pain. It is possible that the affected joints will pain during or after movement.
2- Stiffness. Joint stiffness may be more obvious when you first wake up or after a period of inactivity.
3- Tenderness. When you apply light pressure to or near your joint, it may become sensitive.
4- Flexibility is being lost. It's possible that you won't be able to move your joint completely across its range of motion.
5- The sense of grating. When you utilise the joint, you may notice a grating sensation and hear popping or cracking.
Disease Causes:
Osteoarthritis develops when the cartilage that cushions the ends of your bones in your joints deteriorates over time. Cartilage is a tough, slick tissue that allows for practically frictionless joint movement.
If the cartilage is fully worn down, bone will rub against bone.
Osteoarthritis is sometimes referred to as a wear-and-tear condition. However, osteoarthritis affects the entire joint, not only the cartilage. It causes bone alterations and the connective tissues that keep the joint together and connect muscle to bone to deteriorate. Inflammation of the joint lining is also a side effect.
Factors that are at risk
The following are some of the factors that might raise your risk of osteoarthritis:
Getting older. Osteoarthritis becomes more common as people get older.
Sex. Women are more prone than males to get osteoarthritis, while the reason for this is unknown.
Obesity. Osteoarthritis is exacerbated by excess body weight in various ways, and the more you weigh, the higher your risk. Weight gain puts strain on weight-bearing joints like your hips and knees. Fat tissue also creates proteins that can cause severe inflammation in and around joints.
Injuries to the joints Osteoarthritis can be exacerbated by injuries sustained while participating in sports or as a result of an accident. Even injuries that appear to have healed many years ago might put you at risk for osteoarthritis.
Stress on the joint on a regular basis. If your profession or an activity you participate in puts repetitive stress on a joint, that joint may develop osteoarthritis over time.
Genetics. Osteoarthritis is a condition that some people inherit.
Deformities of the bones. Some people are born with faulty cartilage or deformed joints.
Some metabolic disorders. Diabetes and an overabundance of iron in the body are two examples (hemochromatosis).
Bone spurs are a kind of bone spur. These additional fragments of bone might grow around the afflicted joint and feel like hard lumps.
Swelling. This might be due to inflammation of the soft tissues around the joint.
Disease Diagnosis:
During the physical exam, your doctor will look for soreness, edoema, redness, and flexibility in the afflicted joint.
Tests of imaging
Your doctor may suggest that you acquire photographs of the afflicted joint by:
X-rays. Cartilage loss is shown by a narrowing of the area between the bones in your joint, which is not visible on X-ray pictures. Bone spurs surrounding a joint can also be seen on an X-ray.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of imaging that (MRI). An MRI produces comprehensive pictures of bone and soft tissues, including cartilage, using radio waves and a strong magnetic field. An MRI isn't always required to diagnose osteoarthritis, although it can give additional information in some circumstances.
Tests in the lab
The diagnosis can be confirmed by testing your blood or joint fluid.
Tests on the blood. Although no blood test exists to diagnose osteoarthritis, some tests can help rule out other causes of joint pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
Fluid analysis of the joints. A needle may be used by your doctor to collect fluid from an inflamed joint. The fluid is then examined for inflammation and to see if your discomfort is due to gout or an infection instead of osteoarthritis.
Disease Treatment:
Osteoarthritis can't be cured, but therapies can help you feel better and move more freely.
Medications
The following medications can help reduce osteoarthritis symptoms, particularly pain:
Acetaminophen. Acetaminophen has been demonstrated to benefit some patients with mild to severe osteoarthritis pain. Acetaminophen used in excess of the authorised amount might harm the liver.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) are medications that are used to treat inflammation (NSAIDs). Osteoarthritis pain is usually relieved by using over-the-counter NSAIDs in the appropriate amounts. Prescriptions are available for stronger NSAIDs.
Stomach distress, cardiovascular difficulties, blood problems, and liver and kidney damage are all possible side effects of NSAIDs. NSAIDs administered as gels to the skin over the afflicted joint have less adverse effects and may provide similar pain relief.
Duloxetine is an antidepressant that is also licenced for the treatment of chronic pain, particularly osteoarthritis pain.
Therapy
Physical therapy is a type of treatment that involves the use of A physical therapist can demonstrate exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding your joint, promote flexibility, and lessen discomfort. Regular mild exercise, such as swimming or walking, that you perform on your own might be just as helpful.
Occupational therapy is a term used to describe a type of treatment An occupational therapist can assist you in figuring out how to do regular chores without aggravating your already painful joint. If you have osteoarthritis in your hands, for example, a toothbrush with a big handle may make cleaning your teeth simpler. If you have knee osteoarthritis, a seat in the shower might assist ease the strain of standing.
Electrical nerve stimulation applied to the skin (TENS). To treat pain, a low-voltage electrical current is used. Some patients with knee and hip osteoarthritis find it helpful in the short term.
Surgical and other interventions
If conservative therapy are ineffective, you may wish to explore surgeries like:
Injections with cortisone. Corticosteroid injections into your joint may reduce discomfort for a few weeks. Your doctor numbs the region around your joint before injecting medicine through a needle into the joint space. Because cortisone injections can increase joint deterioration over time, the number of shots you can have each year is usually restricted to three or four.
Injections of lubricant. Hyaluronic acid injections may help reduce discomfort by providing cushioning in the knee, however other evidence shows that these injections are no better than a placebo. Hyaluronic acid is a substance that is naturally present in joint fluid.
Bones are realigned. An osteotomy may be beneficial if osteoarthritis has injured one side of your knee more than the other. A surgeon performs a knee osteotomy by cutting through the bone above or below the knee and then removing or adding a wedge of bone. Your body weight is shifted away from the worn-out area of your knee as a result of this.
Joint replacement is a procedure that involves replacing a joint. Your surgeon will remove your damaged joint surfaces and replace them with plastic and metal pieces during joint replacement surgery. Infections and blood clots are two surgical hazards. Artificial joints can wear out or become loose over time, necessitating replacement.
Country wise cost comparison for Osteotomy:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $12078 |
Treatment and Cost
18
Total Days
In Country
- 2 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 16 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$13420
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Saudi Arabia