Double Valve Replacement and CABG
India
-
Our Price USD 9360
-
Hospital Price USD 10400
-
You Save : USD 1040
Booking Amount: USD 936. Pay Remaining 90% at the hospital.
Book NowAdditional Credit
Among the important extras we offer as part of the Additional Credit are the following:
-
Site Tourism For The Patient & Attendant
-
Airport Pick & Drop Service
-
Ambulance service at airport
-
Priority appointments with The Doctor
-
Cancel Easily Anytime with Full Refund
-
Room Upgradation
-
Free Online Doctor Consultation Valued at USD 20
-
Free hotel Stay for 5 to 7 days Accordingly
-
Welcome Kit at Arrival
-
Interpreter
-
Medical Visa Assistance
What is Included?
- Doctor consultation charges
- Lab tests and diagnostic charges
- Room charges inside hospital during the procedure
- Surgeon Fee
- Cost of implant
- Nursing charges
- Hospital surgery suite charges
- Anesthesia charges
- Routine medicines and routine consumables (bandages, dressings etc.)
- Food and Beverages inside hospital stay for patient and one attendant.
What is not Included?
- Extra Radiology Investigations
- Healthcare Professionals Charges of other consultations.
- Other Requested Services such as Laundry etc.
- Additional Pharmaceutical Products and Medicines After Discharge from Hospital.
- Management of Conditions Unrelated to Procedures or Pre-Existing.
- The cost of any additional implants will be in addition to the package cost.
Package Description
Double Valve Replacement / Repair
The mitral and aortic valves, as well as the whole left side of the heart, are replaced in a double valve replacement.
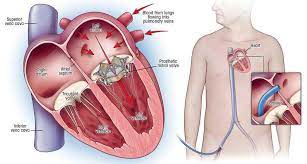
Mitral Valve Replacement: The mitral valve is found on the heart's left side. It's a type of inflow valve. Its function is to enable blood to flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle. If the valve does not fully open or close, surgery may be necessary. It might be difficult for blood to flow through a valve that is too thin. This can cause it to back up, resulting in pulmonary hypertension. Blood might seep back into the lungs if the valve does not shut properly. A congenital flaw, illness, or degenerative disease can all cause this.
A biological valve or a metal artificial valve will be used to replace the damaged valve. Although the metal valve will last a lifetime, it will necessitate the use of blood thinners. The biological valve will last 15 to 20 years, and you will not need to take any blood-thinning medication. Trusted Source reports that the five-year survival rate is around 91 percent. Your age, overall health, any medical disorders you have, and heart function all have a factor in your survival rate.
Aortic valve replacement: The aortic valve is an outflow valve on the left side of the heart. Its function is to enable blood to depart the heart's primary pumping chamber, the left ventricle. Its function also includes closing to prevent blood from leaking back into the left ventricle. If you have a congenital problem or a condition that causes stenosis or regurgitation, you may need surgery on your aortic valve.
A bicuspid valve is the most prevalent form of congenital defect. The aortic valve normally has three leaflets, which are tissue portions. This is called a tricuspid valve. A defective valve has only two leaflets, so it?s called a bicuspid valve.
A recent study found that aortic valve replacement surgery has a 94 percent five-year survival rate. Survival rates depend on: your age, your overall health, Other medical conditions you have, your heart function.
Open Heart Surgery / CABG:
A coronary artery bypass graft involves taking a blood vessel from another part of the body (usually the chest, leg or arm) and attaching it to the coronary artery above and below the narrowed area or blockage.
This new blood vessel is known as a graft. The number of grafts needed will depend on how severe your coronary heart disease is and how many of the coronary blood vessels are narrowed.
A coronary artery bypass graft is carried out under general anaesthetic, which means you'll be unconscious during the operation. It usually takes between 3 and 6 hours. Most people will need to stay in hospital for about 6 to 8 days after having a coronary artery bypass graft.
You should have a follow-up appointment, typically about 6 to 8 weeks after your operation. Recovering takes time and everyone recovers at slightly different speeds. Generally, you should be able to sit in a chair after 1 day, walk after 3 days, and walk up and down stairs after 5 or 6 days. When you go home, you'll need to take things easy for a few weeks. You should be able to return to most of your normal activities after about 6 weeks, including working, driving and having sex. If you have a heavy manual job, you may need to stay off work longer. Most people make a full recovery within 12 weeks.
Risks of surgery
As with all types of surgery, a coronary artery bypass graft carries a risk of complications. These are usually relatively minor and treatable, such as an irregular heartbeat or a wound infection, but there's also a risk of serious complications, such as a stroke or heart attack.
After surgery
After having a coronary artery bypass graft, most people will experience a significant improvement in symptoms such as breathlessness and chest pain, and their heart attack risk will be lowered. But a coronary artery bypass graft isn't a cure for coronary heart disease. If you don't make lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly, your grafted arteries will also eventually become hardened and narrowed.
Sometimes, a coronary artery bypass graft may need to be repeated or you may need a procedure to widen your arteries using a small balloon and a tube called a stent (coronary angioplasty).
Disease Overview
Heart valve disease
In heart valve disease, one or more of the valves in your heart doesn't work properly. Your heart has four valves that keep blood flowing in the correct direction. In some cases, one or more of the valves don't open or close properly. This can cause the blood flow through your heart to your body to be disrupted.
Signs and Symptoms
Some people with heart valve disease might not have symptoms for many years. When signs and symptoms occur, they might include:
- Whooshing sound (heart murmur) when a doctor is listening to the heart with a stethoscope
- Chest pain
- Abdominal swelling (more common with advanced tricuspid regurgitation)
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath, particularly when active or lying down
- Swelling of your ankles and feet
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Irregular heartbeat
Disease Causes
The four heart valves, which keep blood flowing in the right direction, are the mitral, tricuspid, pulmonary and aortic valves. Each valve has flaps (leaflets) that open and close once per heartbeat. If one or more of the valves fail to open or close properly, the blood flow through your heart to your body is disrupted.
Heart valve disease may be present at birth (congenital). It can also occur in adults due to many causes and conditions, such as infections and other heart conditions.
Heart valve problems include:
Regurgitation. The valve flaps don't close properly, causing blood to leak backward in your heart. This commonly occurs due to valve flaps bulging back, a condition called prolapse.
Stenosis. The valve flaps become thick or stiff and possibly fuse together. This results in a narrowed valve opening and reduced blood flow through the valve.
Atresia. The valve isn't formed, and a solid sheet of tissue blocks the blood flow between the heart chambers.
Diagnosis:
Your doctor will conduct a physical examination and listen for a heart murmur, a possible sign of a heart valve condition. You might have several tests to diagnose your condition.
Tests might include:
- Echocardiography: Sound waves directed at your heart from a wandlike device (transducer) produce video images of your heart in motion. This test assesses the structure of your heart, the heart valves and the blood flow through your heart.
- Transesophageal echocardiogram: a small transducer attached to the end of a tube is inserted down the tube leading from your mouth to your stomach (esophagus). This test helps your doctor get a closer look at the heart valves than is possible with a regular echocardiogram.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Wires (electrodes) attached to pads on your skin measure electrical impulses from your heart. An ECG can detect enlarged chambers of your heart, heart disease and abnormal heart rhythms.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can help your doctor determine whether the heart is enlarged, which can indicate certain types of heart valve disease. A chest X-ray can also help doctors determine the condition of your lungs.
- Cardiac MRI: A cardiac MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of your heart. It can determine the severity of your condition and assess the size and function of your lower heart chambers.
- Exercise tests or stress tests: Different exercise tests help measure your activity tolerance and monitor your heart's response to physical exertion. If you can't exercise, you might be given medications that mimic the effect of exercise on your heart.
Disease Treatment
Heart valve disease treatment depends on your symptoms, the severity of the condition, and whether your condition is worsening.
A doctor trained in heart disease (cardiologist) will provide your care. Treatment might include monitoring your condition with regular follow-up visits. You might be asked to:
- Make healthy lifestyle changes
- Take medications to treat symptoms
- Take blood thinners to reduce the risk of blood clots if you have a certain irregular heart rhythm called atrial fibrillation
Surgery or other procedures:
You might eventually need heart valve surgery to repair or replace the diseased heart valve even if you don't have symptoms. If you need surgery for another heart condition, your doctor might repair or replace the diseased valve at the same time.
Heart valve surgery is usually performed through a cut (incision) in the chest. Doctors sometimes do minimally invasive heart surgery, which involves smaller incisions than those made for open-heart surgery. In some medical centers, doctors perform robot-assisted heart surgery, a type of minimally invasive heart surgery in which surgeons use robotic instruments to conduct the procedure.
Heart Valve replacement: If the valve can't be repaired, surgeons might remove the damaged valve and replace it with a mechanical valve or a valve made from cow, pig or human heart tissue (biological or tissue valve).
CABG: A coronary artery bypass graft involves taking a blood vessel from another part of the body (usually the chest, leg or arm) and attaching it to the coronary artery above and below the narrowed area or blockage.
This new blood vessel is known as a graft. The number of grafts needed will depend on how severe your coronary heart disease is and how many of the coronary blood vessels are narrowed.
Information related to Treatment
Package Details
Days in Hospital
7 Days
Days in Hotel
*
14 Days
Room Type
Private

Treating Doctor
Dr. Naresh Trehan
Cardiac Surgeon- Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, MIDCAB Sugery
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
43 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Praveer Aggarwal
Cardiologist- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting, Coronary Angiogram, Peripheral Angiography, Coronary Angioplasty / Bypass Surgery, Cardiac Ablation, Cardiac Catheterisation
Fortis Escorts Heart Institute New Delhi, India
31 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Umesh Kohli
Interventional Cardiologist- Echocardiography, Pacemaker Implantation, Coronary Angiography, Coronary Angiogram, Cardiac Ablation, Cardiac Catheterisation, ASD VSD repair, Cardioversion, Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDS), Peripheral Angioplasty, Non Invasive Cardiology, Chest Pain Treatment, Bypass Surgery, CT angiogram, Cardiology, Balloon Mitral Valbuloplasty
Accord Super specialty Hospital Faridabad, India
24 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr Roopa Salwan
Cardiologist- Echocardiography, Left ventricular assist device (LVAD), Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, Pacemaker Implantation, Coronary Angiography, Bypass Heart Surgeon, Epilepsy Disorder, Cerebral Palsy Surgeon, Balloon Angioplasty, Mitral valve replacement, Cardiac Ablation, Congenital Heart Disorder CHD, Carotid Angioplasty And Stenting, Pacemaker Implantation, Hypertension Treatment, ICD implantation, Mycardial Infarction, Prevention of Blockage, Atherosclerosis & Heart At, Holistic Heart Wellness & Health Care - Ayurveda, Preventing Post Bypass Surgery Blockages, Preventing Restenosis, Stent Surgery, PTCA or Coronary Angioplasty, Myocarditis Treatment, Atrial fibrillation treatment, Mitral insufficiency treatment, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy treatment, Ventricular tachycardia treatment, Cardiac catheterizations, Hip Disorders, Pacemaker Implantation, Echocardiography, Hypertension Treatment, Echocardiography, Carotid Angioplasty And Stenting, Pacemaker Implantation, Cardiac Ablation, Pacemaker Implantation
Max Super Speciality Hospital New Delhi, India
32 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. S.K. Jain
Cardiac Surgeon- Aortic surgery, Heart valve replacement, Mitral valve replacement, Aortic Valve Replacement & Repairs
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
40 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Ramesh Kumar Bapna
Cardiac Surgeon- Cardiac Thoracic and Vascular Surgery
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
41 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Surinder Bazaz
Cardiac Surgeon- Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Cardiovascular Surgery
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
42 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Indivar Upadhyay
Cardiac Surgeon- Aortic surgery, Heart transplant, Heart transplant, Paediatric Cardiac Surgeon, Abdominal Aortic Aneursym
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
32 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Bhuvnesh K Aggarwal
Cardiac Surgeon- Cardiovascular and Cardiothoracic Surgery
Medanta-The Medicity, Gurgaon Gurgaon, India
32 Years of Experience

Treating Doctor
Dr. Tarlochan Singh Kler
Cardiologist- Coronary Artery Disease, Cardiac Arrhythmias, Bradycardia, Blocked Arteries, Tachycardia, Angina, Atherosclerosis
Fortis Flt. Lt. Rajan Dhall Hospital, Vasant Kunj, Delhi New Delhi, India
35 Years of Experience
Similar Packages
Frequently Asked Questions
India's healthcare sector has grown significantly over the last several decades, and the country is proud of the number of well-maintained healthcare providers who are internationally recognized for their skill in performing heart valve replacement operations. The following is a list of Indian hospitals that are suggested for Double Valve Replacement and CABG Surgery 1-Apollo Hospitals Indraprastha, New Delhi 2-Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, Okhla, Delhi 3-BLK Super Specialty Hospitals, New Delhi 4-Sarvodaya Hospitals And Research Center, Faridabad 5-BGS Global Hospitals, Bangalore 6-Fortis Hospitals Mulund, Mumbai 7-Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai 8-Sevenhills Hospitals, Mumbai
In India, the starting price for a heart double valve replacement procedure is $9,500. When compared to other western nations, India surely provides the most cost-effective and efficient heart valve surgery care. It is important to note that costs might differ depending on a number of factors, including the surgeon's experience, the hospital of your choice, the style of room and facilities selected, and the patients' conditions.
Surgery to replace the heart's double valve is advised for patients who exhibit severe symptoms and valve malfunction. In India, valve issues are mostly caused by rheumatic heart disease. Heart valve surgery is a routine treatment carried out in large multispecialty hospitals. India is well known throughout the world for its superior cardiac care philosophy and for having highly skilled and accomplished cardiac surgeons. In comparison to Western nations, India has a high success rate for heart valve replacement surgery, which guarantees patients a healthy life after the procedure. Top hospitals in India are renowned for providing sincere care, being open 24/7, having personnel who understand English, and having cutting-edge rehabilitation facilities. As a result, thousands of patients with aortic valve stenosis can swiftly return to their homes in this nation, which is the most sought-after travel destination globally.
While small issues do not require surgery and do not require much attention, mild issues can be treated with the assistance of heart valve replacement surgery. The majority of patients in India who underwent heart valve replacement surgery are now leading normal lives. The high success rate of procedures carried out in India demonstrates how well a patient recovers from surgery. The patient is typically instructed to take a few drugs for a few weeks following the procedure. Note that the length of the drug may be shortened or eliminated entirely based on the patient's condition and level of recovery. Patients should visit the physician in accordance with the follow-up programme. The doctor might run a few tests during the follow-up appointment to see if the tissue has healed, and he would then watch to see how the new valve is operating. The suggested hospitals in India assist patients in getting back to their regular schedules, which guarantees a quick healing process.
There is a pool of skilled cardiac surgeons in India who practise at some of the country's most reputable hospitals. Indian cardiologists are highly knowledgeable in cardiology and cardiac science, having received their training at prestigious medical schools both domestically and overseas. For surgery to replace your heart's double valve, consult the best cardiologist in India. 1-Dr. Balbir Singh - Max Hospital. 2-Dr. Naresh Trehan - Medanta Hospital Gurgaon. 3-Dr. Anil Bhan - Medanta Hospital Gurgaon. 4-Dr. Vivek Jawali - Fortis Hospital , Bangalore 5-Dr. Ashok Seth - Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, Okhla , Delhi 6-Dr. Sandeep Attawar - Manipal Hospitals Goa, Dona Paula , Panjim 7-Dr. Bhaba Nanda Das - Apollo Hospital Delhi. 8-Dr. Z S Meharwal – Fortis Escort Heart Institute Delhi
The cost of a heart double valve replacement procedure in India varies depending on a few criteria. Among these are a few of the following: - Hospital type: primary, secondary, or tertiary care - Hospitalization location - First, second, or third tier city selection - The surgeon's training, credentials, and experience - Artificial or tissue valves are the types of valves employed. - No. of valves in use: mitral, aortic, or both - The price of examination, including 2D echo, CAG, and other blood tests.
When doing heart valve replacement surgery in India, the following two types of valves are used: Another name for a prosthetic valve is an artificial or mechanical valve. Pyrolytic carbon is most frequently used to make mechanical valves. Because they do not wear out as quickly as biological valves, they are predicted to last longer and reduce the need for another procedure after a few years. Blood thinners are more necessary when dealing with mechanical valves. Tissue valves are sometimes referred to as biological, bioprosthetic, or bovine valves. This kind of valve is modelled after the heart of a pig and the sac surrounding the heart of a cow. The cost is higher than that of a mechanical valve. Patients who receive a biological valve can recuperate more quickly in terms of the valve's functionality and require less blood-thinning medications.