Aortic coarctation cost in India
The cost of Aortic coarctation in India ranges
from USD 4200 to USD 10000
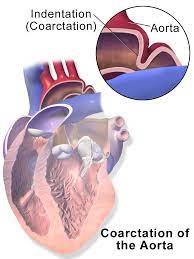
Aortic coarctation
Congenital (existing from birth) coarctation of the aorta can happen in conjunction with other cardiac conditions. A lot of people don't show any symptoms, and the illness is frequently not discovered until adulthood. The most typical adult symptom is hypertension. Rarely, severe cases might result in a baby's heart failing. To treat the narrowing, surgery or a catheter-based technique are required.
Procedure Description:
Aortic coarctation
Congenital (existing from birth) coarctation of the aorta can happen in conjunction with other cardiac conditions. A lot of people don't show any symptoms, and the illness is frequently not discovered until adulthood. The most typical adult symptom is hypertension. Rarely, severe cases might result in a baby's heart failing. To treat the narrowing, surgery or a catheter-based technique are required.
Disease Description:
The largest artery in the body is the aorta. It transfers blood enriched with oxygen from the heart to the body's other organs. The narrowing of the aorta is known as aortic coarctation. In order to pump blood through the aorta, the heart must work harder. A congenital heart abnormality, coarctation of the aorta is typically present from birth. Mild to severe symptoms are possible. It's possible that the illness won't be noticed until maturity.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Symptoms of aortic coarctation vary depending on the degree of aortic narrowing. Not many people experience symptoms. It could take till maturity to diagnose mild coarctation.
Symptoms of severe aortic coarctation may appear in newborns soon after birth. Infancy-related coarctation of the aorta symptoms include:
1. Having trouble breathing
2. Having trouble eating
3. Excessive perspiration
4. Sensitivity
5. Pale skin
When the aorta coarcts beyond infancy, the following symptoms are frequently present:
1. Pain in the chest
2. Headache
3. Elevated blood pressure
4. Chilled feet or cramping legs
5. Weakness in the muscles
6. Bleeding noses
Blood pressure in the arms and legs and ankles may differ depending on the location of the coarctation.
Aortic coarctation frequently coexists with other cardiac conditions. Depending on the kind of congenital cardiac abnormality, other symptoms may exist.
Disease Causes:
It's uncertain what causes aortic coarctation. Usually, the illness is a congenital heart defect, which is a cardiac issue that exists from birth.
Aortic coarctation rarely occurs later in life. Aortic narrowing can result in this condition and the following conditions or events:
1. Traumatic injury
2. Severe atherosclerotic (artery hardening)
3. Takayasu arteritis, or inflamed arteries
Males experience aortic coarctation more frequently than females. An further factor that increases the likelihood of aortic coarctation is the presence of specific hereditary disorders like Turner syndrome. Aortic coarctation frequently coexists with other congenital cardiac conditions.
Disease Diagnosis:
The severity of the problem determines the age at which coarctation of the aorta is identified. Usually, severe aortic coarctation is identified quite early in infancy. An ultrasound can be used to see the problem while pregnant.
A physician diagnoses coarctation of the aorta by looking for the following symptoms:
- Elevated arm blood pressure
- A disparity in blood pressure between the arms and legs, with the legs' blood pressure being lower than the arms'
- Weak or erratic pulse in the lower limbs
- A whooshing sound (heart murmur) brought on by increased blood flow via the constricted artery.
The following tests could be performed to confirm an aortic coarctation diagnosis:
1. Echocardiogram: This examination projects images of the beating heart onto a screen using sound waves. The location and degree of an aortic coarctation can frequently be seen on an echocardiography.
2. Electrocardiogram, often known as an EKG or ECG: This quick and painless test gauges the heart's electrical activity. Electrodes, or sensors, are sometimes affixed to the arms or legs during an ECG.
3. X-ray of the chest. An X-ray of the chest produces images of the lungs and heart. An inflated portion of the aorta, a constriction at the location of the coarctation, or both may be visible on a chest X-ray.
4. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the heart. This test produces fine-grained pictures of the heart and blood arteries using radio waves and magnetic fields. It can display further blood artery damage, other cardiac problems, and the location and severity of the aortic coarctation.
5. A CT scan using computerized tomography. A CT scan produces fine-grained cross-sectional images of the body by using a sequence of X-rays.
6. Catheterization of the heart.
Disease Treatment:
The severity of the condition and the patient's age at the time of diagnosis determine how to treat aortic coarctation. The correction of any additional congenital cardiac abnormalities can take place concurrently.
Medication to manage symptoms and procedures, or surgery to repair the aorta, may be part of the treatment.
Procedures such as surgery:
1. Stenting and balloon angioplasty. This can be the aortic coarctation's initial course of treatment. It is sometimes performed if, following coarctation surgery, narrowing reoccurs.
2. Resection with an end-to-end graft. With this procedure, the constricted piece of the aorta is removed (resection), and the two healthy sections of the aorta are then connected (anastomosis).
3. Aortic subclavian flap replacement. The left subclavian artery, a portion of the blood vessel that supplies blood to the left arm, may be utilized to enlarge the aorta's constricted region.
4-Eschew graft restoration. During this procedure, blood is redirected around the restricted section of the aorta using a tube known as a graft.
5. Aortic patching. To enlarge the blood vessel, the surgeon makes a cut across the restricted section of the aorta and then inserts a synthetic material patch.
Country wise cost comparison for Aortic coarctation:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $5040 |
| Iran | $4481 |
Treatment and Cost
30
Total Days
In Country
- 10 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 20 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from