PDA Closure cost in India
The cost of PDA Closure in India ranges
from USD 4000 to USD 9000
PDA Closure
A transcatheter PDA closure is a minimally-invasive (non-surgical) procedure to close the ductus arteriosus. Specialized heart doctors called pediatric cardiac interventionists use a procedure called cardiac catheterization to place a small device in the vessel, which closes the PDA.
Procedure Description:
PDA Closure
A transcatheter PDA closure is a minimally-invasive (non-surgical) procedure to close the ductus arteriosus. Specialized heart doctors called pediatric cardiac interventionists use a procedure called cardiac catheterization to place a small device in the vessel, which closes the PDA.
Disease Overview:
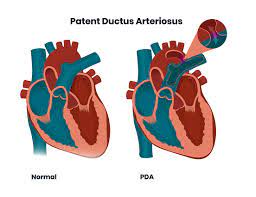
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
The two main blood arteries that emerge from the heart have a persistent opening known as the patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). The cardiac condition exists from birth. It is therefore a congenital cardiac defect. An embryo's blood flow system in the womb includes an aperture known as the ductus arteriosus. It normally shuts down soon after delivery. It is referred to as a patent ductus arteriosus if it stays open.
Small patent ductus arteriosus frequently doesn't cause issues and may never require medical attention. But a big untreated patent ductus arteriosus might cause blood with low oxygen content to flow in the incorrect direction. This may result in cardiac failure and other problems by weakening the heart muscle.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
The age of the patient and the size of the opening determine the symptoms of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). It's possible that a little PDA has no symptoms. Some persons experience symptoms only as adults. Heart failure symptoms may appear shortly after delivery in a big PDA.
A sizable PDA discovered in a baby or young child could result in:
1- Poor nutrition causes poor development.
2- Sweating when you eat or cry.
3- continuous rapid breathing or dyspnea.
4- simple to exhaust.
5- accelerated heart rate.
Disease Causes:
It's unknown what specifically causes congenital cardiac abnormalities. The first six weeks of pregnancy are when a baby's heart forms and begins to beat. The main blood arteries that supply and drain the heart expand. This is the period when various cardiac conditions may start to manifest.
The ductus arteriosus, a temporary aperture, is between the two main blood arteries that leave the baby's heart before delivery. The aorta and the pulmonary artery are those vessels. Before delivery, the opening is essential for a baby's blood flow. It diverts blood from a developing baby's lungs. The mother's blood provides oxygen to the infant.
The following are risk factors for patent ductus arteriosus (PDA):
1. An early birth. Compared to kids born full term, premature births are more likely to result in patent ductus arteriosus.
2. Genetic disorders and other family histories. An increased risk factor for a PDA could include a family history of birth defects related to heart issues. Additionally, there is a higher likelihood of Down syndrome among babies born with an extra 21st chromosome.
3. German measles in the womb. Pregnancy-related German measles, commonly known as rubella, can affect a developing baby's heart. To find out if you're immune to rubella, get a blood test done before getting pregnant. For people who are not immune, there is a vaccine available.
being high altitude birth. Compared to newborns born at lower altitudes, babies born above 8,200 feet (2,499 meters) are more likely to experience a PDA.
4. Being a woman. In females, patent ductus arteriosus is twice as common.
Disease Diagnosis:
In addition to performing a physical examination, the healthcare provider inquires about your medical background. With a stethoscope, the caregiver may listen for a heart murmur, which is a sound that the heart makes.
The following tests could be performed to identify patent ductus arteriosus:
1- Echocardiogram. This test creates images of the beating heart using sound waves. An echocardiography can also identify elevated lung artery pressures.
2. A chest X-ray. This examination reveals the state of the lungs and heart.
3. An ECG is obtained. The electrical impulses that comprise a heartbeat are captured by this short and easy test. It displays the heart's beating rate in both rapid and slow waves.
4. Catheterization of the heart. In most cases, a PDA can be diagnosed without this test. However, if a PDA coexists with other cardiac issues, it might be done. A catheter is a long, thin, flexible tube that is led to the heart by being put into a blood artery, generally in the wrist or groin. The medical professional may be able to treat the patent ductus arteriosus during this examination.
Disease Treatment:
The age of the patient determines the course of treatment for a patent ductus arteriosus. Some individuals with minor PDAs who aren't having any issues just need to have routine checks to monitor for any concerns. The medical professional monitors the PDA of a premature baby on a regular basis to ensure that it closes.
The following are advanced therapies for closing a patent ductus arteriosus:
1. Closing the aperture with a coil or plug and a narrow tube known as a catheter. We refer to this type of care as a catheter procedure. It makes a repair possible without requiring open cardiac surgery. A tiny tube is inserted by the medical professional into a blood vessel in the groin and guided to the heart during a catheter procedure. The catheter has a plug or coil passing through it. The ductus arteriosus is sealed off by the coil or stopper. Usually, there is no need for an overnight hospital stay for the procedure.
2. Open cardiac surgery with PDA closure. Surgical closure is the term for this procedure. If medication is ineffective if the PDA is big or causing problems, heart surgery may be required.
In order to access the child's heart, the surgeon creates a tiny incision between the ribs. Stitches or clips are used to seal the opening. A youngster often needs a few weeks to recuperate completely from this type of operation. Certain individuals who are born with a PDA require ongoing medical examinations, even following closure of the incision. The doctor may do tests as part of these examinations to look for any issues.
Country wise cost comparison for PDA Closure:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $4860 |
| Iran | $2652 |
| Iran | $2519 |
Treatment and Cost
14
Total Days
In Country
- 2 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 12 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from