TAVI cost in India
The cost of Transcatheter aortic valve
replacement (TAVR) in India ranges from USD 35000 to USD 50000
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
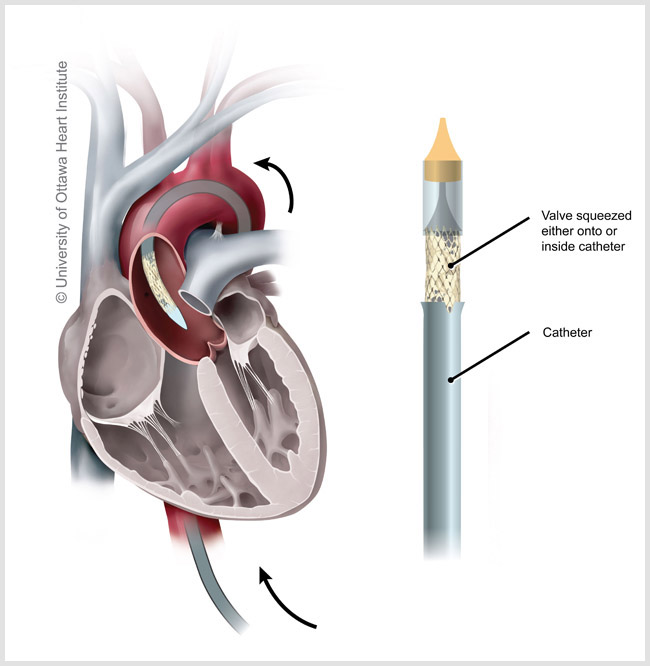
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is a treatment for replacing an aortic valve that has constricted and is unable to open fully. The aortic valve connects the left lower heart chamber to the body's main artery. The narrowing of the aortic valve is known as aortic valve stenosis. The valve dysfunction prevents or delays blood flow from the heart to the body. TAVR is a minimally invasive procedure that employs smaller incisions than open-heart valve surgery. It may be a possibility for those who are unable to undergo cardiac surgery to replace their aortic valves. TAVR helps alleviate chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms of aortic valve stenosis.
Procedure Description:
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is a treatment for replacing an aortic valve that has constricted and is unable to open fully. The aortic valve connects the left lower heart chamber to the body's main artery. The narrowing of the aortic valve is known as aortic valve stenosis. The valve dysfunction prevents or delays blood flow from the heart to the body. TAVR is a minimally invasive procedure that employs smaller incisions than open-heart valve surgery. It may be a possibility for those who are unable to undergo cardiac surgery to replace their aortic valves. TAVR helps alleviate chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms of aortic valve stenosis.
Disease Description:
Severe Aortic Stenosis
Aortic valve stenosis, also known as aortic stenosis, is a narrowing of the aortic valve in the heart. The valve does not fully open, reducing or blocking blood flow from your heart to your body's major artery (aorta) and the rest of your body.
Your therapy will be determined by the severity of your illness. The valve may need to be repaired or replaced, which would necessitate surgery. Severe aortic valve stenosis can be fatal if left untreated.
The following are some of the risk factors for aortic valve stenosis:
- Older age
- Certain heart problems, such as a bicuspid aortic valve, are present at birth (congenital heart disease).
- Infections that have harmed the heart in the past
- Diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure
- Chronic kidney disease
- Radiation treatment to the chest in the past
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
The severity of aortic valve stenosis varies. When the valve is severely narrowed, signs and symptoms appear. Aortic valve stenosis might go unnoticed for many years in some persons.
Aortic valve stenosis can cause the following signs and symptoms:
- A stethoscope recording of an abnormal heart sound (heart murmur).
- With exercise, you may get chest discomfort (angina) or tightness.
- With exertion, you may feel faint, dizzy, or faint.
- Shortness of breath, especially after a vigorous workout
- Fatigue, especially when there is a lot of activity.
- A fluttering, rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
- Not getting enough food (mainly in children with aortic valve stenosis)
- Inadequate weight gain (mainly in children with aortic valve stenosis)
Heart failure can be caused by stenosis of the aortic valve. Fatigue, shortness of breath, swollen ankles and feet are indications and symptoms of heart failure.
Disease Causes:
In aortic valve stenosis, the aortic valve between the lower left heart chamber (left ventricle) and the aorta does not open completely. The area through which blood moves out of the heart to the aorta is narrowed (stenosis). When the aortic valve opening is narrowed, your heart must work harder to pump enough blood into the aorta and to the rest of your body. The extra work of the heart can cause the left ventricle to thicken and enlarge. Eventually the strain can cause a weakened heart muscle and can ultimately lead to heart failure and other serious problems.
Aortic valve stenosis causes include:
Congenital heart defect. Some children are born with just two cusps on their aortic valve (bicuspid aortic valve) rather than three (tricuspid aortic valve). Aortic valves can have one (unicuspid) or four (quadricuspid) cusps on rare occasions.
Calcium buildup on the valve- Calcium is a mineral that may be detected in your bloodstream. Calcium deposits on the heart valves can form as blood runs over the aortic valve repeatedly (aortic valve calcification). Symptoms of aortic valve stenosis caused by growing age and calcium deposit deposition generally don't appear until the age of 70 or 80. Calcium deposits, on the other hand, cause valve cusp stiffening at a younger age in certain persons, particularly those with a congenital aortic valve abnormality. Calcium deposits in heart valves aren't connected to taking calcium supplements or consuming calcium-fortified beverages.
Rheumatic fever: Scar tissue may grow on the aortic valve as a result of this strep throat complication. Scar tissue can limit the aperture of the aortic valve or provide a rough surface on which calcium deposits might accumulate.
Rheumatic fever can harm more than one heart valve in different ways. Rheumatic fever is uncommon in the United States, however some elderly persons had experienced it as children.
Disease Diagnosis:
Your doctor will examine your signs and symptoms, evaluate your medical history, and perform a physical examination to determine if you have aortic valve stenosis. He or she will use a stethoscope to listen to your heart to see whether you have a heart murmur that might indicate an aortic valve problem.
Several tests may be ordered by your doctor to confirm or rule out aortic valve stenosis. Tests can also assist assess the source and severity of an illness.
Tests:
- Echocardiogram: An echocardiography is a type of ultrasonography of the heart. Sound waves are employed to produce moving images of the heart. An echocardiography allows doctors to examine the aortic valve and aorta in greater detail. It can assist in determining the source of aortic valve disease as well as the severity of the condition.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): The electrical activity of the heart is recorded in this noninvasive examination.
- Chest X-ray: It can provide information about the heart and lungs' health.
- Cardiac MRI: It creates precise pictures of the heart using magnetic fields and radio waves.
- Cardiac computerized tomography (CT) scan: In this, Series of X-rays are used to obtain detailed pictures of the heart and heart valves. This imaging approach may be used by doctors to determine the size of the aorta and examine the aortic valve in greater detail.
- Exercise tests or stress tests: These tests often involve walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike while an ECG or echocardiogram is performed.
- Cardiac catheterization: This procedure rarely used to diagnose aortic valve dysfunction. It can, however, be used to assess the degree of aortic valve disease. This can provide further information regarding blood flow and how effectively the heart is functioning.
Disease Treatment:
Aortic valve stenosis treatment is determined by your indications and symptoms as well as the severity of the problem.
If you only have minor symptoms or none at all, you may simply need to see your doctor on a regular basis to have your health monitored. To treat symptoms or lower the risk of problems, your doctor may suggest healthy lifestyle modifications and medicines. Even if you don't have any symptoms, you may require surgery to repair or replace the damaged aortic valve. Aortic valve surgery may be performed concurrently with other cardiac procedures.
Surgery options for aortic valve stenosis include:
Aortic valve repair: Surgeons remove fused valve flaps (cusps) to repair an aortic valve. To treat aortic valve stenosis, surgeons seldom reconstruct the aortic valve. Aortic valve stenosis usually necessitates aortic valve replacement.
Balloon valvuloplasty: Aortic valve stenosis in newborns and children can be treated using this surgery. Adults who have undergone the operation, however, have a tendency for the valve to narrow again, so it's normally reserved for those who are too unwell for surgery or who are waiting for a valve replacement, since they'll require multiple procedures to address the constricted valve over time.
Aortic valve replacement: Your surgeon will remove the diseased aortic valve and replace it with a mechanical valve or a valve manufactured from cow, pig, or human heart tissue during aortic valve replacement (biological tissue valve).
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR): People who are judged to be at moderate or high risk of problems from surgical aortic valve replacement may benefit from this less invasive approach.
Country wise cost comparison for TAVI:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $32580 |
| Iran | $8846 |
Treatment and Cost
18
Total Days
In Country
- 3 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 15 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$36200
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Turkey
- Kolan International Hospital, Sisli
- Istinye University Bahcesehir Liv Hospital
- Istinye University Medical Park Gaziosmanpasa Hospital
- I.A.U VM Medical Park Florya Hospital
- Altinbas University Medical Park Bahcelievler Hospital
- Medical Park Antalya Hospital
- Medical Park Tarsus Hospital, Mersin
- Iran