Device Closure- ASD VSD cost in India
The cost of Device Closure- ASD VSD in India
ranges from USD 5000 to USD 9000
Procedure Description:
Device Closure- ASD VSD
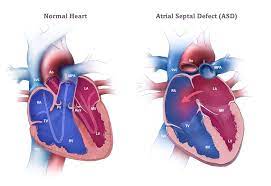
An ASD closure device (atrial septal defect) is an opening in the heart's membrane that connects two chambers. The right atrium contains deoxygenated blood, which is transferred to the lungs for purification after passing through the right ventricle. In Atrial Septal Disorder, there is a small hole in the wall dividing the atria known as the atrial septum. As a result, oxygen-rich blood escapes from the left atrium to the right, causing blood to flow in the opposite direction. when a result, the right atrium is put under additional strain when oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mix, putting increased pressure on the right atrium to send more blood to the lungs.
VSD device closure is an opening in the wall (septum) that separates the two lower chambers of the heart (ventricles). Typically, this wall shuts before delivery. The lower two chambers of the heart are known as ventricles. These are divided by a membrane known as the Ventricular Septum, which prevents oxygenated blood from leaving the left ventricle and entering the right ventricle, which contains deoxygenated blood. The deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle is subsequently sent to the lungs for purification.
When a VSD device is closed, a hole forms in the ventricular septum. As a result of the left-to-right reversal of blood flow, oxygenated blood mixes with deoxygenated blood. As a result, there is an excess of blood rushing to the lungs, causing the heart to overwork in order to give oxygenated blood to the body.
Disease Overview:
An atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital cardiac defect that results in a hole in the atrial septum. This is the muscular wall that separates the heart's two upper chambers (atria). Small ASDs normally do not require treatment. Larger ones may necessitate percutaneous (nonsurgical) correction or surgery to reduce the likelihood of significant consequences.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
Most children show no indications or symptoms. A heart murmur is the most prevalent (and, in many cases, the sole indication). Their healthcare provider will notice it while listening to their heart using a stethoscope.
Other symptoms in children may include
1- being underweight.
2- Growth delays.
3. Recurrent respiratory infections.
Children with greater ASDs may experience symptoms including 1- cardiac arrhythmias, albeit this is extremely unusual.
2- Easily exhausted during exercising.
3- Difficulties breathing.
Adults with ASD may experience symptoms by the age of 40. The severity of the ASD's effects on the heart and lungs determines the symptoms that appear. They include:
1- Fatigue.
2- Shortness of breath during exertion.
3. Heart palpitations.
4- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia).
5. Arm and leg swelling.
6- Blue skin tone (cyanosis).
Disease Causes:
It is unclear what causes atrial septal defects. Congenital cardiac abnormalities, on the other hand, are frequently the result of prenatal genetic alterations. Some ASD-related genetic abnormalities impact the genes NKX2.5/CSX and TBX5.
Some variables increase a birthing parent's chances of having a baby with congenital heart disease. These factors include:
1. Alcohol consumption.
2. Smoking and tobacco use.
3. Taking some prescription drugs.
Disease Diagnosis:
Your doctor will perform one or more tests to diagnose you with an ASD and determine how it affects your heart. This includes:
1- Electrocardiography (ECG or EKG). An ECG displays your heart's electrical activity. It can detect arrhythmias or other issues with your heart's electrical circuitry.
2- Chest X-ray. This test will determine whether your right atrium and right ventricle are enlarged. It will also indicate whether your lungs' blood vessels are compromised.
3. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE). This test illustrates how left-to-right blood shunting (induced by ASD) affects the heart. It can also display information relating to pulmonary hypertension.
4. Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE). A transesophageal echocardiogram is an ultrasound that is performed through the esophagus. It depicts the size, shape, and location of an ASD. It can also monitor your heart valves. TEE is commonly utilized for ASD surgery and percutaneous correction.
5- intracardiac echocardiography (ICE). This is an ultrasound of your heart. A tiny camera (echo probe) is inserted into your heart via a peripheral vein. This test reveals the size, shape, and direction of blood flow across the ASD. It is commonly utilized in the percutaneous (nonsurgical) correction of ASD.
In some circumstances, a cardiac CT scan or MRI may be employed. They are more beneficial to persons with related defects or less frequent kinds of ASD.
Disease Treatment:
Atrial septal defects can be repaired surgically or percutaneously (without surgery).
Treatment for ASD is determined by several factors, including the kind and severity of the condition.
- How the ASD affects your heart.
- You have other medical issues, such as pulmonary hypertension, valve disease, or coronary artery disease.
Small ASDs normally do not require correction. Even if no symptoms are present, bigger ASDs should be corrected. This avoids significant difficulties down the future.
When you notice evidence of heart or lung damage, you must get it repaired. Your provider will suggest treatment if:
- The right side of your heart is larger than normal.
- There is substantial shunting (blood flow via the ASD).
Certain ASD symptoms may be treated with drugs prescribed by your clinician. But there are none.
Percutaneous (nonsurgical) repair of ASDs: This method of repair involves closing the opening in your atrial septum with a device known as a septal occluder. A catheter, or long, thin tube, is used to insert the device.
Surgery is required for primary ASDs, coronary sinus abnormalities, and the majority of sinus venosus ASDs. These are uncommon anomalies that must be treated by a cardiac surgeon with experience in congenital heart disease. Some persons may be able to have robotic-assisted or minimally invasive surgery.
A tissue patch is typically used to seal the ASD after surgical treatment. The tissue is commonly derived from your own pericardium (the membrane that surrounds your heart). Some secundum ASDs can be surgically closed with stitches and no patch.
Country wise cost comparison for Device Closure- ASD VSD:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $4680 |
| Turkey | $13348 |
| Thailand | $17794 |
Treatment and Cost
20
Total Days
In Country
- 5 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 15 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$5200
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Turkey
- Kolan International Hospital, Sisli
- Istinye University Bahcesehir Liv Hospital
- Istinye University Medical Park Gaziosmanpasa Hospital
- I.A.U VM Medical Park Florya Hospital
- Altinbas University Medical Park Bahcelievler Hospital
- Medical Park Antalya Hospital
- Medical Park Tarsus Hospital, Mersin
- Thailand