The cost of Cerebral angioplasty in India ranges
from USD 4000 to USD 10000
Procedure Description:
Cerebral angioplasty
In order to restore blood flow to the brain, a surgery called cerebral angioplasty—also referred to as carotid angioplasty or vertebral angioplasty—opens clogged arteries. Carotid artery disease is the result of the artery becoming blocked by plaque, which is made up of fat or calcium deposits. This reduces the amount of oxygen-rich blood that reaches the brain.
In order to expand the constricted area, the surgeon inserts and inflates a small balloon into the obstructed artery during the procedure. Stenting, which entails inserting a tiny metal coil called a stent inside the obstructed artery, is frequently done in conjunction with cerebral angioplasty.
Disease Overview:
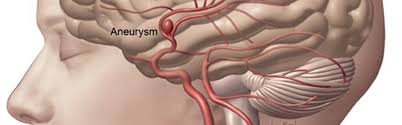
Cerebral aneurysm: An abnormal localized dilatation of an artery in the brain caused by a weakening of the inner muscle layer (the intima) of a blood vessel wall is known as a cerebral or intracranial aneurysm. A "blister-like" dilatation of the vessel forms, which has the potential to thin out and burst at any time. A subarachnoid hemorrhage is the term used to describe the resulting bleeding into the area around the brain (SAH). This type of bleeding may result in a coma, a stroke, or even death.
Aneurysms are typically located in the subarachnoid space, which is a region inside the skull around the base of the brain. Indeed, ruptured cerebral aneurysms are the cause of 90% of SAHs, and the phrases are frequently used interchangeably.
Aneurysms vary in size, ranging from approximately 1/8 inch to almost one inch. Giant aneurysms are aneurysms greater than one inch; they are very risky and challenging to treat. It is unknown precisely how cerebral aneurysms form, expand, and burst.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
Aneurysm rupture symptoms include:
1. Thunderclap headache, also referred to as "the worst headache of my life," is a severe headache with an abrupt onset.
2. Throwing up and nausea.
3. Tight neck.
4. Double or blurry vision.
5. Light sensitivity (photophobia).
6. Convulsions.
7. A dilated pupil and drooping eyelid.
8. Pain behind and above the eyes.
9. Perplexity.
10. numbness or weakness.
11- unconsciousness.
Disease Causes:
When the walls of an artery in your brain weaken and thin, brain aneurysms can occur. They typically develop where arteries split. It is possible to have a brain aneurysm from birth. Usually, this results from an anomaly (birth defect) in the wall of an artery. The weakening of an artery might be caused by a number of additional reasons.
The genetic variables listed below can worsen arterial health and raise your chance of brain aneurysm development:
1. The syndrome of vascular Ehlers-Danlos.
2. Polycystic kidney disease that is autosomal dominant.
3. Syndrome Marfan.
4- Dysplasia fibromuscular.
5. Maturation of the arteriovenous vein.
6. Having a parent or biological sibling who is a first-degree relative who has a history of brain aneurysms.
Over time, the following circumstances and conditions may cause your artery walls to weaken:
1- Smoking.
2- High blood pressure.
3- Use of drugs, especially cocaine.
4- Drinking too much alcohol.
Disease Diagnosis:
Most patients with brain aneurysms that haven't ruptured are unaware that they have one. One could be discovered by a medical professional during a brain imaging exam you had for a different condition, like as MRI or CT scan.
Make an appointment at the ER or dial 911 if you experience symptoms indicative of a brain aneurysm, such as a strong headache. A medical professional will prescribe tests to check for ruptured brain aneurysms. These examinations could consist of:
1. A CT scan, or computed tomography: To check if blood has seeped into your brain, this is frequently the first imaging test that a doctor would do.
2. MRI scan: Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) provides fine-grained images of the arteries supplying your brain and can reveal the exact location, size, and form of an aneurysm.
3. A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in your wrist or groin by a neurosurgeon or interventional neuroradiologist during a cerebral angiography procedure. This CT scan can identify blockages in the arteries that supply your brain or neck. It can also detect weak points, such as an aneurysm, in an artery.
The fourth test is called a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) study, and it evaluates the chemicals in the fluid that surrounds and shields your brain and spinal cord.
Disease Treatment:
Surgery or endovascular therapy are necessary for the repair of a ruptured aneurysm. When an aneurysm is treated endovascularly, the artery is opened up from within. In addition, you might receive symptom-relieving medications. Discuss potential therapies for an unruptured aneurysm with your healthcare physician. Examine whether treating the aneurysm carries a higher risk than keeping it untreated.
Surgery:
When a brain aneurysm ruptures, there are two typical treatment choices. These treatments might be thought of in some situations to treat an unruptured aneurysm. However, for certain individuals with unruptured aneurysms, the known hazards might be greater than the possible benefits.
Surgical clipping: An aneurysm is closed off with this operation. To access the aneurysm, the neurosurgeon must remove a portion of your skull. Next, the blood vessel feeding the aneurysm is located by the neurosurgeon. To block blood flow into the aneurysm, the surgeon puts a tiny metal clip on its neck.
Endovascular therapy: This method may be safer and less intrusive than surgical clipping. In endovascular treatment, the aneurysm is accessed by passing a catheter, a tiny plastic tube, through the artery. The cerebral arteries are reached by the catheter. Stents or coils may then be inserted.
Flow diversion: A more recent endovascular therapy option for brain aneurysms is flow diversion. In order to redirect blood flow away from the aneurysm, a stent is inserted into the blood vessel during the treatment. We refer to the stent that is implanted as a flow diverter. Cerebral aneurysm angioplasty
Country wise cost comparison for Cerebral angioplasty:
| Country |
Cost |
| India |
$4320 |
| Iran |
$7898 |