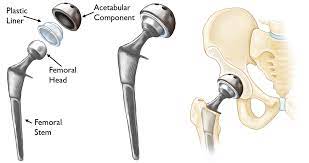
Revision Hip Replacement cost in India
The cost of Revision Hip Replacement in India
ranges from USD 12000 to USD 20000
Procedure Description:
Revision Hip Replacement
A joint revision procedure can be used to replace or resurface a replacement joint that has worn out, become loose, or developed a problem. Regular X-ray exams allow the orthopedic surgeon to watch for changes and schedule revision surgery before a serious issue arises.
Before a new prosthesis may be implanted during revision hip surgery, the old prosthesis, cement, surrounding tissue, and dead bone must all be removed. New methods for hip and knee revision surgery have been patented by Cedars-Sinai Orthopedics surgeons, who often achieve superior results with fewer complications. The postoperative management of revision hip surgery is identical to that of total hip replacement. In addition to other forms of rehabilitation, patients receive home health care, physical and occupational therapy, and home health care.
The dangers involved with any major surgery, along with the complications from this technique, are comparable to those of the initial joint replacement surgery. Because the bone is weaker, revision surgery typically has a lower success rate than the initial procedure.
Disease Overview:
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term inflammatory condition that affects more than your joints. The illness can harm a range of body systems in certain people, including the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels. It is an autoimmune disease in which your immune system assaults your own body's tissues.
Rheumatoid arthritis, unlike osteoarthritis, affects the lining of your joints, creating a painful swelling that can eventually lead to bone degradation and joint deformity.
Rheumatoid arthritis causes inflammation, which can cause harm to other regions of the body. Despite the fact that new types of drugs have greatly improved treatment choices, severe rheumatoid arthritis can still cause physical limitations.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
The following are some of the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis:
- Joints that are painful, heated, and swollen
- Morning stiffness and inactivity are the most common causes of joint stiffness.
- Fever, fatigue, and a lack of appetite
- Smaller joints, such as the joints that connect your fingers to your hands and your toes to your feet, are often the first to be affected by early rheumatoid arthritis.
Wrists, knees, ankles, elbows, hips, and shoulders are frequently affected as the condition advances. Symptoms appear in the same joints on both sides of your body in the majority of instances.
About 40% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis also have indications and symptoms that aren't related to their joints. The following are some of the areas that might be affected:
- Skin\sEyes\sLungs
- Heart\sKidneys
- glands of the salivary
- Tissue of the nerves
- Marrow from the bones
- arteries and veins
The intensity of rheumatoid arthritis symptoms might vary, and they can come and go. Flares, or times of heightened disease activity, alternate with remissions, or periods when the swelling and discomfort lessen or cease. Rheumatoid arthritis causes joints to distort and move out of place over time.
Disease Causes:
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune illness that affects the joints. In a normal state, your immune system aids in the protection of your body against infection and disease. Your immune system assaults healthy tissue in your joints when you have rheumatoid arthritis. It can also affect your heart, lungs, nerves, eyes, and skin, among other things.
Doctors aren't sure what triggers this process, although it appears to have a hereditary component. While your genes do not cause rheumatoid arthritis, they might make you more susceptible to environmental conditions that can start the illness, such as infection with certain viruses and bacteria.
Factors that are at risk
Rheumatoid arthritis can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- It's all about you. Rheumatoid arthritis is more common in women than in men.
- Age. Rheumatoid arthritis can strike at any age, although it most typically strikes people in their forties and fifties.
- History of the family. If someone in your family has rheumatoid arthritis, you may be at a higher risk of developing it.
- Smoking. If you smoke cigarettes, you're more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis, especially if you have a genetic predisposition to the disease. Smoking also appears to be linked to a worsening of illness severity.
- A lot of weight. Obese people tend to have a slightly greater chance of acquiring rheumatoid arthritis.
Disease Diagnosis:
Because the early signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are similar to those of many other diseases, it can be difficult to identify in its early stages. The diagnosis cannot be confirmed by a single blood test or physical finding.
Your doctor will examine your joints for swelling, redness, and warmth during the physical exam. He or she may also assess your muscle strength and reflexes.
Tests on the blood
An high erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR, also known as sed rate) or C-reactive protein (CRP) level in people with rheumatoid arthritis may suggest the existence of an inflammatory process in the body. Rheumatoid factor and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies are two other popular blood tests.
Tests of imaging
X-rays may be recommended by your doctor to monitor the course of rheumatoid arthritis in your joints over time. Your doctor can use MRI and ultrasound tests to assess the degree of the disease in your body.
Disease Treatment:
Rheumatoid arthritis has no known cure. However, clinical trials show that early therapy with disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines (DMARDs) increases the likelihood of symptom remission (DMARDs).
Medications
Your doctor's drug recommendations will be based on the severity of your symptoms and the length of time you've had rheumatoid arthritis.
NSAIDs. NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines) can help to ease pain and inflammation.
Steroids. Corticosteroid medicines relieve inflammation and discomfort while also slowing the deterioration of joints. Bone weakening, weight gain, and diabetes are all possible side effects. Doctors frequently prescribe a corticosteroid to alleviate symptoms rapidly, with the intention of gradually weaning patients off the drug.
DMARDs that are often used. These medications can help to reduce the course of rheumatoid arthritis and prevent irreparable damage to the joints and other tissues. Methotrexate (Trexall, Otrexup, and others), leflunomide (Arava), hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil), and sulfasalazine are all common DMARDs (Azulfidine). Liver damage and serious lung infections are possible side effects.
Therapy
Your doctor may recommend you to a physical or occupational therapist who may teach you exercises to maintain joint flexibility. The therapist may also recommend new ways to complete everyday duties that are less taxing on your joints. You could wish to take up an object with your forearms, for example.
Assistive gadgets can help you avoid putting unnecessary strain on your sore joints. A kitchen knife with a hand grip, for example, can assist safeguard your finger and wrist joints. Buttonhooks, for example, may make getting dressed a lot simpler. Catalogs and medical supply stores are excellent sources of inspiration.
Surgery
If drugs do not prevent or reduce joint deterioration, you and your doctor may decide to have surgery to restore the damaged joints. Surgery may be able to help you regain your capacity to move your joint. It can also help with pain and function.
One or more of the following techniques may be used in rheumatoid arthritis surgery:
- Synovectomy. The inflammatory lining of the joint (synovium) can be removed during surgery to help relieve pain and enhance joint flexibility.
- Tendon resurfacing. Tendons around your joint may loosen or rupture as a result of inflammation and joint injury. The tendons around your joint may be repaired by your surgeon.
- Fusion of the joints. When a joint replacement isn't an option, surgically fusing a joint may be indicated to stabilise or straighten a joint and provide pain relief.
- Replacement of the whole joint. Your surgeon will remove the damaged portions of your joint and replace them with a metal and plastic prosthesis during joint replacement surgery.
- Bleeding, infection, and discomfort are all risks associated with surgery. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages.
Country wise cost comparison for Revision Hip Replacement:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $12420 |
| Thailand | $12588 |
Treatment and Cost
28
Total Days
In Country
- 7 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 21 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$13800
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Turkey
- Kolan International Hospital, Sisli
- Istinye University Bahcesehir Liv Hospital
- Istinye University Medical Park Gaziosmanpasa Hospital
- I.A.U VM Medical Park Florya Hospital
- Altinbas University Medical Park Bahcelievler Hospital
- Medical Park Antalya Hospital
- Medical Park Tarsus Hospital, Mersin
- Thailand