Duodenal Switch cost in India
The cost of Duodenal Switch in India ranges from USD 6500 to USD 12000
Procedure Description:
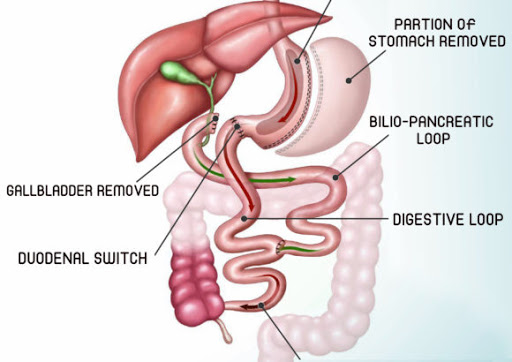
Duodenal Switch
Your stomach and small intestine are altered during a weight-loss procedure called the duodenal switch. It combines an intestinal bypass, which shortens the distance food travels through your intestines, with a gastrectomy, which involves removing a portion of your stomach.
Disease Overview:
Severe Obesity
Obesity is a complicated condition characterised by an excess of body fat. Obesity is more than an aesthetic issue. It's a medical condition that raises your chance of developing other diseases and health issues including heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, and some malignancies.
There are a variety of reasons why some people struggle to lose weight. Obesity is usually caused by a combination of genetic, physiological, and environmental variables, as well as dietary, physical activity, and exercise decisions.
The good news is that even small weight loss can help or avoid obesity-related health concerns. Weight loss can be aided by a better diet, more physical activity, and behavioural changes. Obesity can also be treated with prescription drugs and weight-loss treatments.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
- Excess body fat, particularly around the waist, is a common indication of obesity in adults.
- Asthma
- Excessive perspiration
- Snoring.
- Sleeping problems
- Moisture buildup in the creases of the skin causes skin issues.
- Inability to carry out simple bodily actions that were previously uncomplicated.
Disease Causes:
Obesity develops when you consume more calories than you burn via typical everyday activity and exercise, despite genetic, behavioural, metabolic, and hormonal factors on body weight. These extra calories are stored as fat in your body.
Most people's diets are excessively calorie-dense, owing to fast food and high-calorie drinks. Obese people may consume more calories before feeling satisfied, feel hungry sooner, or eat more as a result of stress or worry.
Many individuals work in positions that aren't as physically demanding, therefore they don't burn as many calories at work. Because to conveniences like remote controls, escalators, internet shopping, and drive-through banking, even ordinary tasks require less calories.
Disease Diagnosis:
A physical exam and other tests are usually performed by your doctor to identify obesity.
The following are examples of examinations and tests:
Taking a look at your medical history. Your doctor may inquire about your weight history, weight-loss efforts, physical activity and exercise routines, eating patterns and hunger management, previous medical conditions, medicines, stress levels, and other health concerns. Your doctor may also look at your family's medical history to discover whether you're at risk for certain diseases.
A complete physical examination. Measuring your height, monitoring vital signs including heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature, listening to your heart and lungs, and inspecting your abdomen are all part of this process.
BMI (Body Mass Index) is a measurement of how healthy you are. Your BMI will be measured by your doctor (BMI). Obesity is defined as a BMI of 30 or greater. The higher the number, the greater the risk to one's health. Your BMI should be examined at least once a year since it may assist identify your overall health risks and possible treatments.
Taking a measurement of your waist circumference. Fat around the waist, also known as visceral fat or abdominal fat, has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and diabetes. Women with waist circumferences of more than 35 inches (89 centimetres) and males with circumferences of more than 40 inches (102 centimetres) may face more health risks than those with smaller waist circumferences.
Waist circumference should be tested at least once a year, much as BMI.
Other health issues are being investigated. Your doctor will assess any existing health issues you may have. Other probable health issues that your doctor will examine for include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, an underactive thyroid, liver problems, and diabetes.
Disease Treatment:
Obesity therapy aims to help people achieve and maintain a healthy weight. This improves general health and reduces the incidence of obesity-related problems.
To understand and alter your food and exercise patterns, you may need to engage with a team of health specialists, including a nutritionist, a behavioural counsellor, or an obesity specialist.
A moderate weight loss — 5 percent to 10% of your overall weight — is generally the first treatment target. That indicates that if you weigh 200 pounds (91 kilogrammes), you just need to shed 10 to 20 pounds (4.5 to 9 kilogrammes) to see a significant improvement in your health. The higher the advantages, though, the more weight you lose.
All weight-loss plans need dietary adjustments as well as increased physical activity. The treatment options that are best for you are determined by the degree of your obesity, your general health, and your commitment to follow through with your weight-loss strategy.
dietary modifications
Obesity may be overcome by reducing calories and adopting healthy eating habits. Although you may lose weight rapidly at initially, long-term weight reduction is regarded the safest and most effective strategy to reduce weight and keep it off permanently.
There is no such thing as the best weight-loss diet. Choose one that incorporates nutritious meals that you believe will be beneficial to you. Obesity can be treated with dietary adjustments such as:
Calorie restriction. The key to losing weight is to cut down on your calorie intake. The first step is to assess your current eating and drinking habits to determine how many calories you consume on a regular basis and where you may make changes. You and your doctor can decide how many calories you need to consume each day to lose weight, but 1,200 to 1,500 calories for women and 1,500 to 1,800 calories for men is a common number.
Desserts, sweets, fats, and processed meals, for example, have a lot of calories in a small amount of food. Fruits and vegetables, on the other hand, give a greater serving size with less calories.
You may lessen hunger pains, consume fewer calories, and feel better about your meal by eating bigger amounts of lower-calorie meals, all of which contribute to how pleased you feel overall.
Making better decisions. Eat more plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, to improve your overall nutrition. Lean protein sources, such as beans, lentils, and soy, as well as lean meats, should be prioritised. If you enjoy fish, make it a point to eat it twice a week. Salt and added sugar should be kept to a minimum. Consume minimal amounts of fats and ensure that they come from heart-healthy sources like olive, canola, and nut oils.
Restricting the consumption of particular foods. Certain diets restrict certain dietary groups, such as high-carbohydrate or high-fat meals.
Inquire with your doctor about which diet regimens are efficient and which may be beneficial to you. Sugar-sweetened drinks are a certain way to eat more calories than you meant. Limiting or eliminating these drinks is a smart place to start when it comes to calorie reduction.
Meal substitutes. These programmes include substituting their goods for one or two meals, such as low-calorie shakes or meal bars, and eating nutritious snacks and a healthy, balanced third meal that is low in fat and calories. This sort of diet can help you lose weight in the short term. These diets, on the other hand, are unlikely to educate you how to improve your whole lifestyle. So, if you want to keep your weight off, you may need to stick to your diet.
Quick remedies should be avoided. Fad diets that promise quick and effortless weight reduction may attract you. However, the truth is that there are no miracle meals or fast solutions. Fad diets may benefit in the short term, but they don't appear to be much better in the long run than regular diets.
Similarly, you could lose weight on a crash diet, but you'll most likely gain it back after you stop. You must acquire healthy eating habits that you can sustain over time if you want to lose weight – and keep it off.
Physical activity and exercise
Obesity therapy must include increased physical activity or exercise:
Exercise. Obese people must engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical exercise each week to avoid additional weight gain or sustain a small weight decrease. As your endurance and fitness develop, you'll probably need to progressively increase the quantity of exercise you do.
Continue to go forward. Even though regular aerobic exercise is the most effective technique to burn calories and lose weight, any additional movement aids in the process. Instead of taking the elevator, park further away from store doors and use the stairs. A pedometer can keep track of how many steps you take in a day. Every day, many individuals aim to walk 10,000 steps. To attain that target, gradually increase the amount of steps you walk each day.
Changes in behaviour
A behaviour modification programme can assist you in making lifestyle adjustments and losing and maintaining weight loss. Examining your existing routines to see what circumstances, stressors, or events may have led to your obesity are among the steps to follow.
Counseling. Talking to a mental health professional about eating-related emotional and behavioural disorders might be beneficial. Therapy can help you understand why you overeat and how to cope with worry in a healthy way. You can also learn how to keep track of your nutrition and physical exercise, recognise eating triggers, and deal with food compulsions. Counseling can be done alone or in a group setting.
Medication for weight loss
Weight-loss drugs should be used in conjunction with, not lieu of, diet, exercise, and behavioural modifications. Your doctor will evaluate your medical history as well as any potential side effects before prescribing a medicine for you.
The following are the most regularly prescribed drugs for the treatment of obesity that have been authorised by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA):
- Bupropion-naltrexone is a combination of the drugs bupropion and naltrex (Contrave)
- Liraglutide is a drug that is used to treat diabetes (Saxenda)
- Orlistat is a diet pill that helps you lose weight (Alli, Xenical)
- Topiramate-phentermine (Qsymia)
- Weight-loss drugs aren't always effective, and their benefits might fade over time. You may regain much or all of the weight you lost after you stop using a weight-loss prescription.
Weight-loss endoscopic treatments
There are no incisions in the skin required for these operations. Flexible tubes and instruments are placed via the mouth and down the neck into the stomach after you have been sedated. The following are examples of common procedures:
The procedure is known as endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty. Stitches are placed in the stomach to limit the quantity of food and drink that the stomach can hold at one time. Eating and drinking less over time helps the average person lose weight.
Weight loss with an intragastric balloon. A tiny balloon is inserted into the stomach during this surgery. The balloon is then filled with water to minimise the amount of space in your stomach, making you feel fuller while eating less.
Endoscopic weight-loss procedures
There are no skin incisions necessary for these procedures. After you've been anaesthetized, flexible tubes and equipment are inserted through your mouth and down your neck into your stomach. Here are some instances of typical procedures:
Endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty is the name of the operation. The stomach is stitched to limit the amount of food and liquid that can be held in the stomach at one time. The ordinary individual may lose weight by eating and drinking less over time.
An intragastric balloon can help you lose weight. During this procedure, a small balloon is placed into the stomach. After that, the balloon is filled with water to reduce the amount of space in your stomach, making you feel full while eating less.
Surgical Weight Loss
Weight-loss surgery, often known as bariatric surgery, restricts the quantity of food you can consume comfortably or reduces the absorption of food and calories. This, however, might lead to dietary and vitamin shortages.
The following are some of the most common weight-loss surgeries:
Gastric banding that can be adjusted. An inflatable band divides the stomach into two pockets during this surgery. To create a narrow passage between the two pouches, the surgeon tightens the band like a belt. The ring prevents the aperture from widening and is meant to remain in place indefinitely.
Gastric bypass surgery is a procedure in which the stomach is bypassed. The surgeon forms a tiny pouch at the top of the stomach during gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y). The small intestine is then sliced and linked to the new stomach a short distance below the primary stomach.
Food and liquids skip the stomach and move directly from the pouch into this section of the intestine.
Gastric sleeve is a kind of gastric sleeve that is used to A portion of the stomach is removed in this treatment, resulting in a decreased food reservoir. It's a less difficult procedure than gastric bypass.
Your ability to lose weight following surgery is contingent on your willingness to make long-term adjustments in your diet and activity habits.
Other options for therapy
Hydrogels are another therapy option for obesity. These edible pills, which are only available by prescription, contain small particles that absorb water and expand in the stomach, making you feel full. Before meals, the capsules are consumed and passed through the intestines as faeces.
Blockage of the vagal nerve. The procedure entails implanting a device beneath the skin of the abdomen that transmits periodic electrical pulses to the abdominal vagus nerve, which notifies the brain when the stomach is empty or full.
Aspirate from the stomach. A tube is inserted into the stomach via the abdomen in this surgery. After each meal, a percentage of the stomach contents is drained out.
Country wise cost comparison for Duodenal Switch:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $7020 |
| Thailand | $6786 |
| Canada | $24123 |
Treatment and Cost
18
Total Days
In Country
- 4 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 14 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$7800
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Turkey
- Kolan International Hospital, Sisli
- Istinye University Bahcesehir Liv Hospital
- Istinye University Medical Park Gaziosmanpasa Hospital
- I.A.U VM Medical Park Florya Hospital
- Altinbas University Medical Park Bahcelievler Hospital
- Medical Park Antalya Hospital
- Medical Park Tarsus Hospital, Mersin
- Thailand
- Bangpakok 9 International Hospital
- Bumrungrad International Hospital
- Bangkok Hospital
- Bangkok International Hospital
- Samitivej Hospital
- BNH Hospital
- Aek Udon International Hospital
- Phuket International Hospital
- Bangkok Christian Hospital
- Thonburi Hospital
- Kasemrad Hospital Sriburin
- Canada
- Toronto General Hospital
- Jewish General Hospital
- Montreal General Hospital (McGill University Health Centre)
- Royal Jubilee Hospital (RJH)
- The Royal Victoria Hospital (McGill University Health Centre)
- Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CHUM)
- Victoria General Hospital
- St Michaels Hospital Toronto
- Hamilton General Hospital
- MCMASTER UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE
- University of Ottawa Heart Institute
- Saudi Arabia