Liver Cirrhosis Treatment cost in India
The cost of Liver Cirrhosis treatment in India
ranges from USD 2000 to USD 5000
Procedure Description:
Liver cirrhosis Treatment
The origin and degree of your liver damage will determine how you are treated for cirrhosis. Treatment aims to prevent or treat cirrhosis symptoms and complications, as well as reduce the growth of scar tissue in the liver.
Treating the underlying cause of early cirrhosis may enable liver damage to be minimized. Among the choices are:
1. Treatment for alcohol dependency: Reducing alcohol intake is recommended for those whose cirrhosis was brought on by heavy drinking. Alcohol poisoning affects the liver in any proportion, so it's critical to give up alcohol if you have cirrhosis.
2. Losing weight and controlling blood sugar levels can help people with cirrhosis brought on by nonalcoholic fatty liver disease live healthier lives.
3. Hepatitis control medications. Medications that target hepatitis B or C viruses specifically may prevent additional harm to liver cells.
4. Surgery for liver transplantation: When liver function is lost due to advanced cirrhosis, liver transplantation might be the only available treatment. The process of replacing your liver with a healthy liver from a deceased donor or with a portion of a liver from a living donor is known as a liver transplant.
Disease Overview:
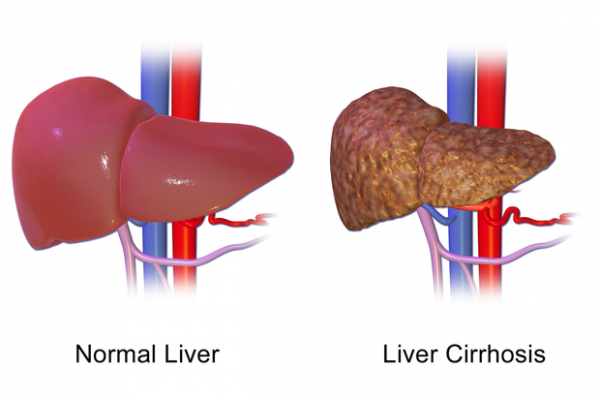
Liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a late stage of liver scarring (fibrosis) induced by a variety of illnesses and disorders, including hepatitis and persistent drinking.
When your liver is wounded, whether from illness, too much alcohol, or something else, it tries to heal itself. Scar tissue arises as a result of this process. Cirrhosis causes scar tissue to grow, which makes it harder for the liver to function (decompensated cirrhosis). Cirrhosis in its advanced stages can be fatal.
Cirrhosis causes liver damage that cannot be reversed. Further damage can be reduced and, in rare cases, reversed if liver cirrhosis is discovered early and the cause is addressed.
Disease Sign and Symptoms:
Cirrhosis frequently has no symptoms until the liver has been severely damaged. When signs and symptoms do appear, they might include the following:
1- Fatigue
2- Bruising or bleeding easily
3- Appetite loss.
4- Nausea
5- Legs, feet, or ankles that swell (edema)
6- Loss of weight
7- Skin that is itchy
8- Skin and eye discoloration are yellow (jaundice)
9- Your abdomen is bloated with fluid (ascites)
10- Your skin has spider-like blood vessels.
11- The palms of the hands are red.
Absent or missed periods that aren't connected to menopause in women; sex drive decrease, breast growth (gynecomastia), or testicular atrophy in males.
Drowsiness, confusion, and slurred speech (hepatic encephalopathy)
Disease Causes:
Cirrhosis can be caused by a variety of diseases and conditions that damage the liver.
The following are some of the reasons:
1- Abuse of alcohol for a long time
2- Hepatitis caused by a virus that has been present for a long time (hepatitis B, C and D)
3- The accumulation of fat in the liver (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease)
4- The accumulation of iron in the body (hemochromatosis)
5- Cystic fibrosis is a disease that affects the lungs.
6- Wilson's illness is a condition in which copper accumulates in the liver.
7- Bile ducts that aren't properly developed (biliary atresia)
8- Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency is a condition in which the body lacks the enzyme alpha-1 antitryp
9- Sugar metabolism diseases that are passed down via the generations (galactosemia or glycogen storage disease)
10- A digestive problem caused by a genetic mutation (Alagille syndrome)
11- The immune system of your body causes liver disease (autoimmune hepatitis)
12- The bile ducts are destroyed (primary biliary cirrhosis)
13- Bile duct scarring and hardening (primary sclerosing cholangitis)
Factors that are at risk
- Overindulging in alcoholic beverages. Cirrhosis is linked to excessive alcohol intake.
- Being overweight is a problem. Obesity raises the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, both of which can develop to cirrhosis.
- Hepatitis caused by a virus. Cirrhosis does not develop in everyone with chronic hepatitis, although it is one of the most common causes of liver disease worldwide.
Disease Diagnosis:
Cirrhosis of the liver in its early stages is frequently asymptomatic. Cirrhosis is frequently discovered during a regular blood test or checkup. A combination of laboratory and imaging tests is frequently performed to assist confirm a diagnosis.
Tests Your doctor may request one or more tests to see if you have a liver disease, such as:
Tests in the lab Blood tests may be ordered by your doctor to look for indicators of liver disease, such as high bilirubin levels, as well as specific enzymes that signal liver damage. Creatinine levels in your blood are measured to determine renal function. Hepatitis viruses will be tested on you. Your blood's capacity to clot is also tested using an international normalised ratio (INR).
Your doctor may be able to determine the underlying cause of cirrhosis based on the findings of the blood tests. He or she may also conduct blood tests to determine the severity of your cirrhosis.
Imaging tests are performed. MRE (magnetic resonance elastography) may be suggested. The liver hardening or stiffening is detected with this noninvasive advanced imaging technique. Other imaging tests, such as an MRI, CT scan, or ultrasound, may be performed as well. Biopsy. For diagnosis, a tissue sample (biopsy) is not always required. Your doctor, on the other hand, may utilise it to determine the severity, extent, and source of liver damage. If you have cirrhosis, your doctor will most likely recommend routine diagnostic tests to check for signs of disease progression or complications, particularly esophageal varices and liver cancer.
Disease Treatment:
Cirrhosis treatment is determined by the cause and severity of your liver damage. The treatment's aims are to decrease the growth of scar tissue in the liver, as well as to prevent or treat cirrhosis symptoms and consequences. If you have serious liver damage, you may need to be admitted to the hospital.
Cirrhosis treatment for the underlying cause
It may be feasible to reduce liver damage in early cirrhosis by addressing the underlying cause. Among the possibilities are:
An alcohol addiction treatment programme. Cirrhosis induced by excessive alcohol use should be avoided at all costs. If quitting drinking is tough, your doctor may suggest an alcohol addiction treatment programme. It is vital to stop drinking if you have cirrhosis since any amount of alcohol is hazardous to the liver.
Loss of weight. Cirrhosis caused by nonalcoholic fatty liver disease can be improved if the patient loses weight and keeps their blood sugar under control.
Hepatitis treatment medications. Through particular therapy of these viruses, medications may reduce additional damage to liver cells caused by hepatitis B or C.
Medications to treat cirrhosis's additional causes and symptoms. Certain kinds of liver cirrhosis can be slowed down with medication. Medication, for example, may greatly slow the course of primary biliary cirrhosis in those who are detected early.
Other drugs can help with itching, exhaustion, and discomfort, among other things. To combat malnutrition caused by cirrhosis and to avoid weak bones, nutritional supplements may be provided (osteoporosis).
Transplantation of the liver
When the liver fails to function in severe forms of cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be the sole choice for therapy. A liver transplant is a process in which your liver is replaced with a healthy liver from a deceased donor or a portion of a living donor's liver.
One of the most prevalent causes for a liver transplant is cirrhosis. Candidates for a liver transplant go through a series of tests to see if they are healthy enough to undergo a successful surgery.
Those with alcoholic cirrhosis have traditionally been barred from receiving a liver transplant due to the danger of relapsing into hazardous drinking following the procedure. Recent research, on the other hand, suggests that people with severe alcoholic cirrhosis have post-transplant survival rates comparable to those of liver transplant recipients with other types of liver disease.
Country wise cost comparison for Liver Cirrhosis Treatment:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $2160 |
| Turkey | $43871 |
| Canada | $93782 |
Treatment and Cost
9
Total Days
In Country
- 2 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 7 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$2400
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated doctors are:
- Italy
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Turkey
- Kolan International Hospital, Sisli
- Istinye University Bahcesehir Liv Hospital
- Istinye University Medical Park Gaziosmanpasa Hospital
- I.A.U VM Medical Park Florya Hospital
- Altinbas University Medical Park Bahcelievler Hospital
- Medical Park Antalya Hospital
- Medical Park Tarsus Hospital, Mersin
- Thailand
- Bangpakok 9 International Hospital
- Bumrungrad International Hospital
- Bangkok Hospital
- Bangkok International Hospital
- Samitivej Hospital
- BNH Hospital
- Aek Udon International Hospital
- Phuket International Hospital
- Bangkok Christian Hospital
- Thonburi Hospital
- Kasemrad Hospital Sriburin
- Canada
- Toronto General Hospital
- Jewish General Hospital
- Montreal General Hospital (McGill University Health Centre)
- Royal Jubilee Hospital (RJH)
- The Royal Victoria Hospital (McGill University Health Centre)
- Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CHUM)
- Victoria General Hospital
- St Michaels Hospital Toronto
- Hamilton General Hospital
- MCMASTER UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE
- University of Ottawa Heart Institute
- Italy