Microwave Endometrial Ablation cost in India
The cost of Microwave Endometrial Ablation in
India ranges from USD 4200 to USD 8000
Procedure Description:
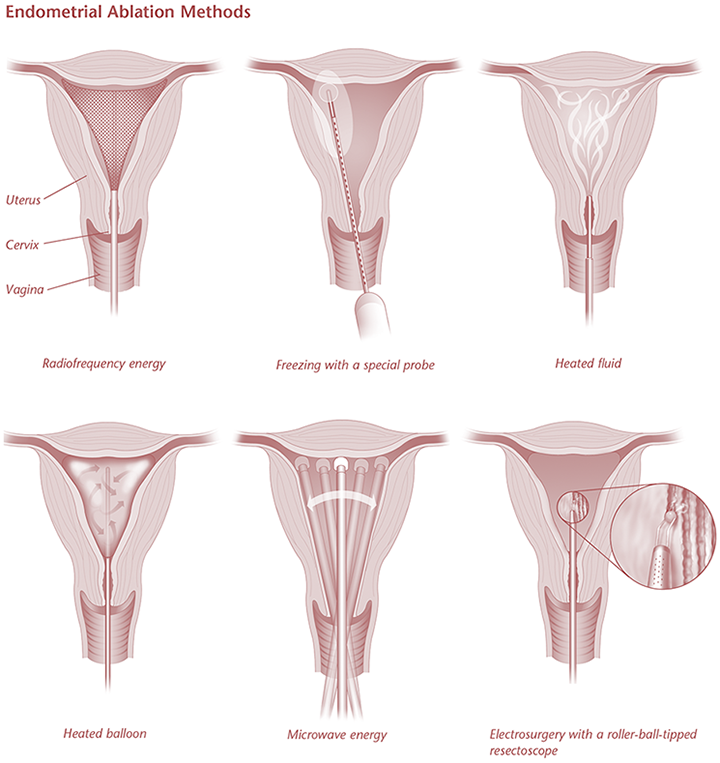
Microwave Endometrial Ablation:
Microwave endometrial ablation (MEA) is a rapid and simple outpatient or day-case surgical procedure. It removes a thin layer of the uterine (womb) lining with the goal of reducing period bleeding to normal or lighter levels. MEA includes placing a specific probe into your womb via your cervix.
Disease Overview:
Some women experience severe or prolonged menstrual bleeding. Previously, this illness was known as menorrhagia. Heavy menstrual bleeding is a typical issue. However, most women do not experience excessive monthly bleeding.
Some women experience menstrual bleeding between periods, or earlier or later in their cycles than usual. Abnormal uterine bleeding is also known as irregular menstrual bleeding. Heavy monthly bleeding, blood flow, and cramping make it difficult to complete your regular tasks.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
The symptoms of excessive menstrual bleeding may include:
- Soak in one or more sanitary pads or tampons every hour for several hours.
- To limit your menstrual flow, you'll need double sanitary protection.
- Getting up at night to change your sanitary pads or tampons.
- Bleeding for over a week.
- Passing blood clots bigger than a quarter.
- Limiting everyday activities due to high menstrual flow.
- Feeling tired, exhausted, or short of breath due to blood loss.
Disease Causes:
In certain circumstances, the cause of significant monthly bleeding remains unknown. However, a number of illnesses can induce severe menstrual bleeding. They include:
1) Hormone imbalance: A typical menstrual cycle involves a balance of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. This regulates the growth of the uterine lining. The uterine lining is also known as endometrium. This lining sheds throughout the menstrual month. When hormones are out of balance, the lining thickens and sheds, resulting in heavy menstrual bleeding or unexpected bleeding between periods.
2) Ovarian problems: Occasionally, the ovaries do not release an egg during a menstrual cycle. This is also called as anovulation. When this occurs, the body does not produce the hormone progesterone as it normally does during the menstrual cycle.
3) Uterine fibroids: These tumors form throughout the reproductive years. They are benign, meaning they are not malignant. Uterine fibroids can cause increased or prolonged menstrual flow.
4) Polyps: These tiny growths on the uterine lining can cause severe or prolonged menstrual flow. They may cause bleeding between periods. Polyps can also induce spotting or bleeding following menopause. These growths are not malignant.
5) Cancer. Cancer of the uterus or cervix can cause abnormal uterine bleeding, as well as irregular or heavy menstrual bleeding.
6) Genetic bleeding diseases. Some bleeding diseases that occur in families result in severe menstrual bleeding. These include von Willebrand's disease, which is characterized by abnormal blood clotting.
7) Medicines. Certain medications might cause heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding. These include hormonal medications, such as birth control tablets containing estrogen and progestin.
8) Other medical issues. A variety of other medical disorders might cause excessive menstrual bleeding. They include liver, renal, and thyroid diseases.
Disease Diagnosis:
A member of your healthcare team will most likely inquire about your medical history and menstrual cycle. You may be requested to keep a journal of days with and without bleeding. Keep track of how heavy your flow was and how many sanitary pads or tampons you needed to keep it under control. Following a physical examination, your doctor or another member of your care team may recommend certain tests or procedures. They may include:
1- Blood testing. Your blood may be examined for iron deficiency anemia. Other illnesses, such as thyroid abnormalities or blood clotting issues, may also be evaluated in the sample.
2- Pap test. This test collects cells from your cervix. They are examined for inflammation or alterations that may be precancerous, which indicates they could progress to cancer.
4. Endometrial biopsy. Your doctor may collect a tissue sample from the interior of your uterus. A pathologist will examine for uterine cancer or precancerous lesions.
5. Ultrasound. This imaging technique employs sound waves to produce images of your uterus, ovaries, and pelvis.
A member of your healthcare team will most likely inquire about your medical history and menstrual cycle. You may be requested to keep a journal of days with and without bleeding.
Keep track of how heavy your flow was and how many sanitary pads or tampons you needed to keep it under control.
The results of these initial tests may lead to further testing, including:
1. Sono hysterography: During this test, a tube is used to inject fluid into your uterus via your vagina and cervix. Your doctor will then use ultrasound to look for issues in the lining of your uterus.
2. Hysteroscopy: A small, illuminated tool is passed through your vagina and cervix into your uterus. This allows your doctor to examine the interior of your uterus.
Disease Treatment:
The treatment for heavy menstrual bleeding is determined by several factors. These include your overall health and medical history.
- The cause and severity of the ailment.
- How well you tolerate specific medications or procedures.
- The possibility that your periods could soon become less heavy.
- You intend to have children.
- How the disease alters your lifestyle.
- Your viewpoint or personal preferences.
If medications do not relieve your severe menstrual bleeding, surgery may be necessary. Treatment alternatives include:
1. Dilation and curettage, generally known as D&C. In this treatment, your doctor will open your cervix. This is also known as dilating the cervix. The doctor will then scrape or vacuum tissue from the uterine lining. This procedure is also known as curettage.
2. Uterine artery embolization. The purpose of this surgery is to prevent blood supply to uterine fibroids. Blocking blood flow to fibroids promotes their shrinkage. During the surgery, the surgeon inserts a catheter into the major artery in the thigh.
3. Focused ultrasound. This technique decreases fibroids by targeting and killing them using ultrasound waves and radiofrequency radiation. It requires no incisions.
4. Myomectomy. This refers to the surgical excision of uterine fibroids. Depending on the size, quantity, and location of the fibroids, your surgeon may conduct the myomectomy using numerous small incisions in the abdomen.
5. Endometrial ablation. This surgery destroys the uterine lining. The process of killing tissue is often referred to as ablation. To destroy the tissue, the surgeon applies heat, radio waves, or a laser to the uterine lining.
6. Endometrial resection. The surgeon uses an electrosurgical wire loop to remove the uterine lining. Pregnancy is not suggested following this operation.
7. Hysterectomy. During this treatment, the uterus and cervix are removed. It terminates menstrual periods and the capacity to become pregnant. Hysterectomy is performed under anesthetic and may necessitate a brief hospital stay.
Country wise cost comparison for Microwave Endometrial Ablation:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $4680 |
| United Arab Emirates | $5898 |
Treatment and Cost
10
Total Days
In Country
- 1 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 9 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$5200
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- United Arab Emirates
- Burjeel Hospital, Abu Dhabi
- New Hope IVF Gynaecology & Fertility Hospital, Sharjah
- Iranian Hospital, Dubai
- Kings College Hospital Dubai
- Zulekha Hospital Sharjah
- Burjeel Hospital for Advanced Surgery Dubai
- Burjeel Medical City, Abu Dhabi
- NMC Royal Hospital, Khalifa City, Abu Dhabi
- NMC Royal Hospital Sharjah
- AL NOOR HOSPITAL, Abu Dhabi
- Al Zahra hospital, Dubai
- NMC Specialty Hospital, Al Nahda, Dubai
- Singapore
- Mount Elizabeth Hospital, Singapore
- National University Hospital, Singapore
- Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
- Changi General Hospital, Singapore
- Gleneagles Hospital, Singapore
- Johns Hopkins Singapore International Medical Centre, Singapore
- Thomson Medical Centre, Singapore
- Mount Alvernia Hospital, Singapore
- Novena Medical Centre, Singapore
- Alexandra Hospital, Singapore
- Saudi Arabia