Knee Arthroscopy cost in India
The cost of Knee Arthroscopy in India ranges
from USD 1700 to USD 5000
Procedure Description:
Knee Arthroscopy
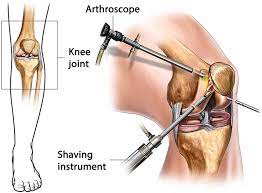
With a knee arthroscopy, a surgeon can see inside the knee joint without having to make a big incision through the skin or other soft tissues. Many different types of knee issues can be diagnosed and treated using arthroscopy.
Disease Overview:
Meniscus tears and cartilage wear
One of the most frequent knee ailments is a torn meniscus. A torn meniscus can be caused by any action that causes you to twist or spin your knee violently, especially when you put your entire weight on it.
Between your shinbone and your thighbone, your knees have two C-shaped pieces of cartilage that function as a cushion. Pain, edoema, and stiffness are all symptoms of a torn meniscus. You may also notice a restriction in knee mobility and difficulty completely extending your knee.
Cartilage is a strong, pliable tissue that may be found all throughout the body. It acts as a shock absorber by covering the surface of joints and allowing bones to move over one another. It can be injured by a sudden accident, such as a sports injury, or over time due to normal wear and strain (osteoarthritis).
Articular (joint lining) cartilage can also be damaged by injury. The cartilage wears away over time, leaving the rough edges of the bone to scrape against one another. The word "osteoarthritis (OA)" refers to the generalised wearing out of cartilage, however all cartilage injury is a component of the osteoarthritis process.
Conservative therapy, such as rest, ice, and medication, can ease the discomfort of a torn meniscus and allow the injury to heal on its own in some cases. A torn meniscus, on the other hand, may necessitate surgery in some circumstances.
Disease Signs and Symptoms:
If your meniscus is torn, it may take up to 24 hours for pain and swelling to appear, especially if the tear is slight. The following indications and symptoms may appear in your knee:
- A feeling of popping
- Stiffness or swelling
- Pain in your knee, especially while twisting or turning it.
- Having trouble completely straightening your knee
- When you try to move your knee, it seems like it's stuck in place.
- You have the sensation that your knee is giving way.
Symptoms of cartilage damage
- joint pain – this may continue even when resting and worsen when you put weight on the joint.
- swelling – this may not develop for a few hours or days.
- stiffness.
- a clicking or grinding sensation.
- the joint locking, catching, or giving way.
Disease Causes:
Any activity that leads you to aggressively twist or rotate your knee, such as vigorous pivoting or quick stops and turns, can cause a torn meniscus. Kneeling, squatting deeply, or lifting anything heavy can all cause a torn meniscus.
Degenerative changes in the knee can cause a torn meniscus in elderly persons with little or no trauma.
Factors that are at risk
A torn meniscus can occur when you engage in activities that require vigorous twisting and turning of the knee. Athletes, particularly those who participate in contact sports such as football or activities that require pivoting, such as tennis or basketball, are at a higher risk.
The chance of a torn meniscus grows as you get older due to wear and tear on your knees.
Wear and tear (simply stated, getting older), repetitive activities (especially twisting, leaping, and deep knee bends), or a severe accident are the most common causes of cartilage deterioration (such as forceful wrenching or a direct impact).
Inflammation, disintegration, and the progressive and final loss of cartilage in the joints are the causes of osteoarthritis. The cartilage wears down with time, causing the bones to grind together. In order to compensate, the bones thicken, but this causes extra friction and discomfort.
Disease Diagnosis:
A torn meniscus is frequently detected during a physical examination. To assist establish the origin of your signs and symptoms, your doctor may move your knee and leg into different positions, watch you walk, and ask you to squat.
X-rays are used in imaging examinations. A torn meniscus is not visible on X-rays since it is comprised of cartilage. X-rays, on the other hand, can help rule out other knee disorders that cause similar symptoms.
MRI. A powerful magnetic field is used to create detailed photographs of both the hard and soft tissues of your knee. It's the most accurate imaging test for detecting a torn meniscus.
Arthroscopy
To inspect the interior of your knee, your doctor may use an arthroscope. A small incision near your knee is used to introduce the arthroscope.
The gadget includes a light and a tiny camera that displays an enlarged image of the inside of your knee on a monitor. To trim or repair the rip, surgical equipment might be placed through the arthroscope or additional tiny incisions in your knee.
Imaging tests such as a weight-bearing X-ray and/or a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan may be required. A clinician can use these tests to detect and assess any damage to the articular cartilage, underlying bone, and surrounding tissues and ligaments.
Country wise cost comparison for Knee Arthroscopy:
| Country | Cost |
|---|---|
| India | $2340 |
| Turkey | $2457 |
| Thailand | $5022 |
| United Arab Emirates | $6411 |
| Singapore | $13308 |
| Canada | $4357 |
Treatment and Cost
10
Total Days
In Country
- 1 Day in Hospital
- 2 No. Travelers
- 9 Days Outside Hospital
Treatment cost starts from
$2600
Popular Hospital & Clinic
Featured Hospital
0 Hospitals
Related Packages
More Related Information
Some of the top rated hospitals are:
- Thailand
- Bangpakok 9 International Hospital
- Bumrungrad International Hospital
- Bangkok Hospital
- Bangkok International Hospital
- Samitivej Hospital
- BNH Hospital
- Aek Udon International Hospital
- Phuket International Hospital
- Bangkok Christian Hospital
- Thonburi Hospital
- Kasemrad Hospital Sriburin
- United Arab Emirates
- Burjeel Hospital, Abu Dhabi
- New Hope IVF Gynaecology & Fertility Hospital, Sharjah
- Iranian Hospital, Dubai
- Kings College Hospital Dubai
- Zulekha Hospital Sharjah
- Burjeel Hospital for Advanced Surgery Dubai
- Burjeel Medical City, Abu Dhabi
- NMC Royal Hospital, Khalifa City, Abu Dhabi
- NMC Royal Hospital Sharjah
- AL NOOR HOSPITAL, Abu Dhabi
- Al Zahra hospital, Dubai
- NMC Specialty Hospital, Al Nahda, Dubai
- Singapore
- Mount Elizabeth Hospital, Singapore
- National University Hospital, Singapore
- Singapore General Hospital, Singapore
- Changi General Hospital, Singapore
- Gleneagles Hospital, Singapore
- Johns Hopkins Singapore International Medical Centre, Singapore
- Thomson Medical Centre, Singapore
- Mount Alvernia Hospital, Singapore
- Novena Medical Centre, Singapore
- Alexandra Hospital, Singapore
- Canada
- Toronto General Hospital
- Jewish General Hospital
- Montreal General Hospital (McGill University Health Centre)
- Royal Jubilee Hospital (RJH)
- The Royal Victoria Hospital (McGill University Health Centre)
- Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CHUM)
- Victoria General Hospital
- St Michaels Hospital Toronto
- Hamilton General Hospital
- MCMASTER UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTRE
- University of Ottawa Heart Institute
- Jordan
- King Abdullah University Hospital
- Istishari Hospital
- Al Khalidi Hospital & Medical Center
- Al Essra Hospital
- The Specialty Hospital
- Islamic Hospital
- Jordan Hospital
- Abdulhadi Hospital
- Queen Alia Heart Institute
- King Hussein Hospital
- Istiklal Hospital
- United Kingdom
- Cancer Centre London
- The Highgate Hospital
- The Holly Hospital
- The Parkside Hospital
- Circle Reading Hospital
- Shirley Oaks Hospital
- St Edmunds Hospital
- The London Clinic
- Woodlands Hospital
- The Christie NHS Foundation Trust
- Royal Marsden Hospital
- Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
- London Bridge Hospital, HCA Healthcare
- Saudi Arabia
- Italy